Abstract
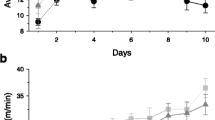
A double-blind study of the effects of supplementing with selenium vs. placebo on the physiological responses to acute and chronic exercise was conducted in 24 healthy, nonsmoking males, mean age 22.9±2.1 yr, randomly divided into two groups of 12 (Pla/Sel). After a controlled period in the absence of training, all subjects were put on an individualized endurance training program with the same rules of progression and overload (3 sessions/wk×10 wk). Supplementation, either real (240 μg of organic selenium/d in Sel group) or imaginary (Pla group) was administered during the same period. In each of the conditions Pre- and Post- (training ± sel supplementation), muscle, plasma, and systemic parameters were determined before (BF) and after (AF) acute exercise, involving the repetition of muscle work cycles separated by 5-min recovery periods, combining 20 min at 65% and a maximal duration of 100% VO2 max of running on a treadmill, leading the subjects to exhaustion between 2 h 40 min and 3 h 30 min. Changes in parameters as a function of three independent variables:
-
1.
Acute exercise (E);
-
2.
Chronic exercise (T); and
-
3.
Selenium supplementing (S)
were tested with ANOVA and the Student\rsst-test on paired series. Among the variables examined, muscle glutathione peroxidase (GPx) presented a remarkable behavior. Enzymatic activity:
-
1.
Decreased significantly (p<0.05,n=24) between the beginning and the end of acute exercise: 29.6±12 vs. 20.8±8.1 IU·g protein−1 in Pre conditions;
-
2.
Remained at the same level in resting conditions between the beginning and end of training (from Pre to Post) regardless of the group: 33.5±10.8 vs. 32.3±19.8 and 25.7±12.4 vs. 23.5±10.2 IU·g protein−1 in Pla and Sel subjects, respectively; and
-
3.
Increased from 23.5±10.2 to 37.3±28.5 (P=0.057) during acute exercise in Post-conditions (after training) in supplemented subjects (Sel group).
The situation was as if acute exercise played the role of allosteric stimulator of the GPx reaction in muscle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. J. A. Davies, L. Packer, and G. A. Brooks,Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 209, 539–554 (1981).
J. O. Holloszy and E. F. CoyleJ. Appl. Physiol. 56, 831–838 (1984).
H. Hoppeler, H. Howald, K. Conley, S. L. Lindstedt, H. Claassen, P. Vock and E. R. WeibelJ. Appl. Physiol. 59, 320–327 (1985).
K. J. A. Davies, A. T. Quintanilha, G. A. Brooks and L. PackerBiochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 107, 1198–1205 (1982).
R. R. JenkinsSports Med. 5, 156–170 (1988).
B. Haliwell and J. M. C. GuteridgeFree Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 1st ed., Clarendon, Oxford, 107–135 (1985).
H. M. AlessioMed. Sci. Sports Exerc. 25, 218–224 (1993).
M. H. Laughlin, T. Simpson, W. L. Sexton, O. R. Brown, J. K. Smith, and R. J. KorthuisJ. Appl. Physiol. 68, 2337–2343 (1990).
J. D. Robertson, R. J. Maughan, G. G. Duthie and P. C. MorriceClin. Sci. 80, 611–618 (1991).
L. L. JiMed. Sci. Sports Exerc. 25, 225–231 (1993).
L. L. Ji, F. W. Stratman, and H. A. LardyArch. Biochem. Biophys. 263, 137–149 (1988a).
L. L. Ji, F. W. Stratman, and H. A. LardyArch. Biochem. Biophys. 263, 150–160 (1988b).
H. Lew and A. QuintanilhaEur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinetics 16, 59–68 (1991).
C. K. Sen, E. Marin, M. Kretzschmar, O. HänninenJ. Appl. Physiol. 73, 1265–1272 (1992).
G. Storz, L. A. Tartaglia, and B. N. AmesScience 248, 189–194 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tessier, F., Hida, H., Favier, A. et al. Muscle GSH-Px activity after prolonged exercise, training, and selenium supplementation. Biol Trace Elem Res 47, 279–285 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790128
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790128