Abstract
It has been suggested that the injury induced by reperfusion of the ischemic myocardium could result, in part, from the cytotoxic effects of oxygen free radicals. Since various trace elements are involved in several of the reactions leading to free radical production, we have measured plasma levels of copper, zinc, selenium, and iron:
-
1.
In 18 patients (mean age 60 yr old) subjected to thrombolytic therapy within 6 h after the onset of a myocardial infarction (G1);
-
2.
In 16 patients with coronary artery disease, but without a history of a previous myocardial infarction (MI) (mean age 50 yr old, G2); and
-
3.
In 50 healthy volunteers divided into two subgroups according to age (mean age 33 yr old, G3 and 55 yr old, G4).
Plasma myosin levels were used to estimate quantitatively the extent of the infarcted mass. Plasma trace element levels were measured in blood samples following centrifugation and storage at −80°C.
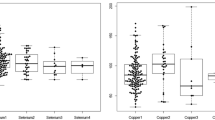
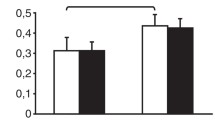
The main results were as followed: In G1 patients who have been subjected to thrombolysis, an important release of myosin was measured in plasma, with a peak at D6 (1678 vs 95 μU/L at H0). In those G1 patients after MI:
-
1.
A significant increase in plasma copper levels was observed from day 4 to day 10 postinfarction (×1.15 in reference to the baseline data at H0);
-
2.
A decrease in plasma zinc levels was observed and was maximum 12 h after the onset of the thrombolytic treatment;
-
3.
A decrease in selenium concentration was observed in G1, as well as in G2 patients, compared to the control groups (80% of G3 and G4 values); and
-
4.
A significant decrease in plasma iron levels was observed in G1 (67.8% of G3 and G4 control values) and was significant from H0 to day 7 (p<0.01).
In conclusion, this study underlined the time-course evolution of plasma trace element levels in the followup of patients who have been subjected to thrombolysis following a MI and the potential prognostic implication of such variations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Jennings, H. Sommers, G. Symth, H. Flack, and H. Linn,Arch. Pathol. 70, 82 (1960).
R. Engelman, R. Chandra, and F. Baumann,Surgery 80, 266 (1972).
M. Hess, N. Manson, and E. Okabe,Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 60, 1382 (1982).
B. Halliwell,Biochem. J. 205, 461 (1982).
B. Halliwell, and J. Gutteridge,Methods in Enzymology, vol. 186, L. Packer and A. Glazer, eds., Academic, San Diego, pp. 1–85 (1990).
F. Boucher, S. Pucheu, C. Coudray, A. Favier, and J. de Leiris,FEBS Lett. 302, 261 (1992).
S. Pucheu, C. Coudray, N. Tresallet, A. Favier, and J. de Leiris,Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 7, 701 (1993).
N. Koukay, (1989) Rôle du zinc et du sélénium dans la génération des radicaux l ibres lors des accidents ischémiques du myocarde. Thesis, Grenoble.
F. Kok, A. Hofman, J. Witteman and A. de Bruijn,JAMA 261, 1161 (1989).
A. Olson and W. Hamlin,Clin. Chem. 15, 438 (1969).
A. Favier, Mise au point de microdosages des oligoéléments Fe, Cu, Zn, Mn par absorption atomique de flamme. Rôle de ces éléments dans la gestation. Thesis, Grenoble, (1981).
J. Machecourt, J. Dumoulin, J. Calop, L. Foroni, M. Terisse, T. Henon, G. Vanzetto, B. Denis, J. Bassaud, and J. Cassagnes,Eur. Heart. J. 14, 75 (1993).
Gissi-Gruppo Italiano per lo Studio della Streptochinasi nell’Infarto Miocardico.Lancet 1, 397 (1986).
J. O. Leger, C. Calzolari, J. Brugada, P. Puech, and J. Leger,Arch. Mal. Coeur 10, 1447 (1987).
J. Arnaud, J. Bellanger, P. Chappuis, A. Favier, and M. Galliot,Ann. Biol. Clin. 43, 77 (1985).
J. Arnaud, J. Bellanger, F. Bienvenu, P. Chappuis, and A. Favier,Ann. Biol. Clin. 44, 77 (1986).
J. Arnaud, A. Prual, P. Preziosi, A. Favier, and S. Hercberg,J. Trace Element Electrolytes Health Dis. 7, 199–204 (1993).
H. A. Katus, T. Yasuda and H. K. GoldAm. J. Cardiol. 54, 964 (1984).
Y. Gauduel and M. Duvelleroy,J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 16, 459 (1984).
C. Guarnieri, F. Flamigni and C. Caldarera,J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 12, 797 (1980).
J. Sullivan, A. Blotcky, and M. Jetton,J. Nutr. 109, 1432 (1979).
M. Singh, R. Singh, and A. Khare,Angiology 36, 504 (1985).
J. Gutteridge and J. Stocks,Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 14, 257 (1981).
J. Salonen, G. Alfthan, and J. Huttunen,Lancet 2, 175–179 (1992).
J. Ringstad, B. Jacoben, and Y. Thomassen,J. Trace Element Electrolytes Health Dis. 1, 27 (1987).
D. Rowley, B. Halliwell, and T. Westmark,Arch. Bioch. Biophys. 225, 279 (1983).
R. Shamberger,Biochemistry of the Essential Ultratrace Elements, Frieden E., ed., Plenum, New York, pp. 201–237 (1984).
V. K. Jain and G. Mohan,Biol. Trace Element Res. 31, 317 (1991).
C. Coudray, M. J. Richard, F. Laporte, P. Faure, A. M. Roussel and A. Favier,J. Nutr. Med. 3, 13 (1992).
P. Faure, A. M. Roussel, T. Foulon, P. Groslambert, A. Hadjian, and A. Favier,Biol. Trace Element Res. 28, 135 (1991).
W. Beisel,Med. Clin. North. Am. 60, 831 (1988).
J. Salonen, K. Nyyssönen, H. Korpela, J. Tuomilehto, R. Seppänen and R. Salonen,Circulation 86, 803 (1992).
R. Bolli, B. S. Patel, W. X. Zhu, P. G. O’Neill, C. J. Hartley, and M. L. Charlat,Am. J. Phys. 253, 1372 (1987).
M. de Sousa,La Recherche 19, 763 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pucheu, S., Coudray, C., Vanzetto, G. et al. Time-course of changes in plasma levels of trace elements after thrombolysis during the acute phase of myocardial infarction in humans. Biol Trace Elem Res 47, 171–182 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790115
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02790115