Abstract
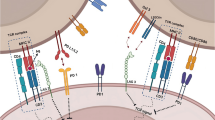
Members of the pancreatic ribonuclease (RNase) family have diverse activities toward RNA that could cause them to function during host defense and physiological cell death pathways. This activity could be harnessed by coupling RNases to cell binding ligands for the purpose of engineering them into cell-type specific cytotoxins. Therefore, the cytotoxic potential of RNase was explored by linking bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A via a disulfide bond to human transferrin or antibodies to the transferrin receptor. The RNase hybrid proteins were cytotoxic to K562 human erythroleukemia cells in vitro with an IC50 around 10−7 M, whereas>10−4 M of native RNase was required to inhibit protein synthesis. Cytotoxicity required both components of the conjugate since excess transferrin or ribonuclease inhibitors added to the medium protected the cells from the transferrin-RNase toxicity. Importantly, the RNase conjugates were found to have potent antitumor effects in vivo. Chimeric RNase fusion proteins were also developed. F(ab′)2-like antibody-enzyme fusions were prepared by linking the gene for human RNase to a chimeric antitransferrin receptor heavy chain gene. The antibody enzyme fusion gene was introduced into a transfectoma that secreted the chimeric light chain of the same antibody, and cell lines were cloned that synthesized and secreted the antibody-enzyme fusion protein of the expected size at a concentration of 1–5 ng/mL. Culture supernatants from clones secreting the fusion protein caused inhibition of growth and protein synthesis toward K562 cells that express the human transferrin receptor but not toward a nonhuman derived cell line. Since human ribonucleases coupled to antibodies also exhibited receptor mediated toxicities, a new approach to selective cell killing is provided. This may allow the development of new therapeutics for cancer treatment that exhibit less systemic toxicity and, importantly, less immunogenicity than the currently employed ligand-toxin conjugates.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gilliland, D. G., Steplewski, Z., Collier, R. J., Mitchell, K, Chang, T., and Koprowski, H. (1980) Antibody directed cytotoxic agents: use of monoclonal antibody to direct the action of toxin A chains to colorectal carcinoma cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 4539–4543.
Krolick, K. A., Villemez, C., Isakson, P., Urh, J., and Vitetta, E. (1980) Selective killing of neoplastic B cells by antibodies coupled to the A chain of ricin.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 5419–5423.
Youle, R. J. and Neville, D. M. (1980) Anti-Thy 1.2 monoclonal antibody linked to ricin is a potent cell-type-specific toxin.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 5483–5486.
Sawler, D. L., Bartholomew, R. M., Smith, L. M., and Dillman, R. (1985) Human immune response to multiple injections of murine monoclonal IgG.J. Immunol. 135, 1530–1535.
Schroff, R. W., Foon, K. A., Beatty, S. M., Oldham, R., and Morgan, A. (1985) Human anti-murine immunoglobulin response in patients receiving monoclonal antibody therapy.Cancer Res. 45, 879–885.
Rybak, S. M. and Youle, R. J. (1991) Clinical use of immunotoxins: monoclonal antibodies conjugated to protein toxins,Immunol. Allergy Clin. North Am. 11:2, 359–380.
Harkonen, S., Stoudemire, J., Mischak R., Spetler, L., Lopez, H., and Scannon, P. (1987) Toxicity and immunogenicity of monoclonal antimelanoma antibody-ricin A chain immunotoxins in rats.Cancer Res. 47, 1377–1385.
Hertler, A. (1988) Human immune response to immunotoxins, inImmunotoxins (Frankel, A. E., ed.), Kluwer Academic, Boston/Dordrecht/ Lancaster, pp. 475–480.
Boulianne, G. L., Houzumi, N., and Schulman, M. J. (1985) Production of functional chimeric mouse/human antibodies.Nature (Lond.) 643–646.
Morrison, S. L., Johnson, M. J., Herzenberg, L. A., and Oi, V. T. (1984) Chimeric human antibody molecules: mouse antigen-binding domains with human constant regions.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 6851–6855.
Jones, P. T., Dear, P. H., Foote, J., Neuberger, M. S., and Winter, G. (1986). Replacing the complementary-determining regions in a human antibody with those from a mouse.Nature (London) 321, 522–525.
Riechmann, L., Clark, M., Waldmann, H., and Winter, G. (1988) Reshaping human antibodies for therapy.Nature (Lond.) 332, 323–327.
Rybak, S. M., Saxena, S. K., Ackerman, E. J., and Youle, R. J. (1991) Cytotoxic potential of RNase and RNase hybrid proteins.J. Biol. Chem. 266, 21,202–21,207.
Newton, D. L., Ilercil, O., Laske, D. W., Oldfield, E., Ryback, S. M., and Youle, R. J. (1992) Cytotoxic ribonuclease chimeras: targeted tumoricidal activity in vitro and in vivo.J. Biol. Chem., submitted.
Rybak, S. M., Hoogenboom, H. R., Meade, H., Ravs, J. C., Schwartz, D., and Youle, R. J. (1992) Humanization of immunotoxins,Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3165–3169.
McClure, B. A., Haring, V., Ebert, P. R., Anderson, M. A., Simpson, R. J., Sakiyama, F., and Clarke, A. E. (1989) Style self-incompatibility products of Nicotiana alata are ribonucleases.Nature (Lond.) 342, 955–957.
Darzynkiewicz, Z., Carter, S. P., Mikulski, S. M., Ardelt, W., and Shogen, K. (1988) Cytostatic and cytotoxic effects of Pannon (P-30 protein) a novel anti-cancer agent.Cell Tissue Kinetics 21, 169–182.
Mikulski, S. M., Viera, A., Ardelt, W., Menduke, H., and Shogen, K. (1990) Tamoxifen and trifluoroperazine (stelazine) potentiate cytostatic/cytotoxic effects of P-30 protein, a novel protein possessing anti-tumor activity.Cell Tissue Kinetics 23, 237–246.
Ardelt, A., Mikulski, S. M., and Shogen, K. (1991) Amino acid sequence of an anti-tumor protein fromRana pipiens oocytes and early embryos.J. Biol. Chem. 256, 245–251.
Mikulski, S. M., Ardelt, W., Shogen, K., Vernstein, E. H., and Menduke, H. (1990) Striking increase of survival of mice bearing M109 Madison Carcinoma treated with a novel protein from amphibian embryos.J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 82, 151–153.
Beintema, J., Schuller, C., Irie, M., and Carsana, A. (1988) Molecular evolution of the ribonuclease superfamily.Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 51, 165–192.
Roth, J. S. (1963) Ribonuclease activity and cancer: a review.Cancer Res. 23, 657–666.
Matousek, J. (1973) The effect of bovine seminal ribonuclease (AS RNase) on cells of Crocker tumour in mice.Experientia 29, 858,859.
Vescia, S., Tramontano, D., Augusti-Tocco, G., and D'Allessio, G. (1980) In vitro studies on selective inhibition of tumor cell growth by seminal ribonuclease.Cancer Res. 40, 3740–3744.
Slifman, N. R., Loegering, D. A., McKean, D. J., and Gleich, G. J. (1986). Ribonuclease activity associated with human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin and eosinophil cationic protein.J. Immunol. 137, 2913–2917.
Spry, C. (1988)Eosinophils: A Comprehensive Review and Guide to the Scientific and Medical Literature. Oxford University Press, Oxford, New York.
Tepper, R. I., Pattengale, P. K., and Leder, P. (1989) Murine interleukin-4 displays potent anti-tumor activity in vivo.Cell 57, 503–512.
Ghiabi, M., Gallagher, G. T., and Wong, D. T. (1992) Eosinophils, tissue eosinophilia and eosinophil-derived transforming growth factor A in hamster oral carcinogenesis.Cancer Res. 52, 389–893.
Young, J., Peterson, C., Venge, P., and Cohn, Z. A. (1986) Mechanism of membrane damage mediated by human eosinophil cationic protein.Nature (Lond.) 321 613–616.
Rosenberg, H. F., Tenen, D. G., and Ackerman, S. J. (1989) Molecular cloning of the human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin: a member of the ribonuclease gene family.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86, 4460–4464.
Reddi, E. K. (1975) Nature and possible significance of human serum ribonuclease.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 67, 110–118.
Blank, A., Dekker, C., Shieven, G. Sugiyama, R., and Thelen, M. (1981)Human Body Fluid Ribonucleases: Detection, Interrelationships and Significance. IRL, London, pp. 203–209.
Fett, J. W., Strydom, D. J., Lobb, R. R., Alderman, E. M., Bethune, J. L. Riordan, J. F., and Vallee, B. L. (1985) Isolation and characterization of angiogenin an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells.Biochemistry 24, 5480–5485.
Strydom, D. J., Fett, J. W., Lobb, R. R., Alderman, E. M., Bethune, J. L. Riordan, J. F., and Vallee, B. L. (1985) Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin.Biochemistry 24, 5486–5494.
Kurachi, K., Davie, E. W., Strydom, D. J., Riordan, J. F., and Vallee, B. L. (1985) Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor.Biochemistry 24, 5494–5499.
Shapiro, R., Riordan, J. F., and Vallee, B. L. (1986) Characteristic ribonucleolytic activity of human angiogenin.Biochemistry 25, 3527–3531.
St. Clair, D. K., Rybak, S. M., Riordan, J. F., and Vallee, B. L. (1987) Angiogenin abolishes cell-free protein synthesis by specific ribonucleolytic inactivation of ribosomes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 84, 8330–8334.
O'Keefe, D. O. and Draper, R. K. (1986) Characterization of a, transferrin-diphtheria toxin conjugate.J. Biol. Chem. 260, 932–937.
Raso, V. and Basala, M. (1984) A highly cytotoxic human transferrinricin A chain conjugate used to select receptor-modified cells.J. Biol. Chem. 259, 1143–1149.
Wagner, E., Zenke, M., Cotten, M., et al. (1990) Transferrin-polycation conjugates as carriers for DNA uptake into cells.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 3410–3414.
Prior, T. I., Fitzgerald, D. J., and Pastan, I. (1991) Barnase Toxin: a new chimeric toxin composed of pseudomonas exotoxin A and Barnase.Cell 64, 1017–1023.
Saxena, S. K., Rybak, S. M., Winkler G., Meade, H. M., Mc Gray, P., Youle, R. J., and Ackerman, E. J. (1991) Comparison of RNases and toxins on injection intoXenopus oocytes.J. Biol. Chem. 266, 21,208–21,214.
Hudson, T. H. and Neville, D. M. (1988) Enhancement of immunotoxin action: Manipulation of the cellular routing of proteins, inImmunotoxins (Frankel, A. E., ed.), Kluwar Academic, Boston/Dordrecht/Lancaster, pp. 371–389.
Hoogenboom, H. R., Raus, J. M., and Volckaert, G. (1991) Targeting of tumor necrosis factor to tumor cells: secretion by myeloma cells of a genetically engineered antibody-tumor necrosis factor hybrid molecule.Biochem. Biophys. Acta 1096, 345–354.
Hoogenboom, H. R., Volckaert, G., and Raus, J. M. (1991) Construction and expression of antibody-tumor necrosis factor fusion proteins.Mol. Immunol. 28, 1027–1037.
Hoogenboom, H. R., Raus, J. M., and Volckaert, G. (1990) Cloning and expression of a chimeric antibody directed against the human transferrin receptor.J. Immunol. 144, 3211–3217.
Casadei, J., Powell, M. J., and Kenten, J. H. (1990) Expression and secretion of aequorin as a chimeric antibody by means of a mammalian expression vector.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 2047–2051.
Williams, G. T. and Neuberger, M. S. (1986) Production of antibody taggted enzymes by myeloma cells: application to DNA polymerase I Klenow fragment.Gene 43, 319–324.
Pastan, I., Willingham, M., and FitzGerald, D. (1986) Immunotoxins.Cell 47, 641–648.
Vitetta, E. S., Fulton, R. J., and May, R. D. (1987) Redesigning nature's poisons to create anti-tumor reagents.Science 238, 1098–1104.
Newton, D. L., Walbridge, S., Mikulski, S. M., Ardelt, K. S., Ackerman, S. J., Rybak, S. M., and Youle, R. J. (1983) Toxicity of an antitumor ribonuclease to Purkinje neurons.J. Neuroscience, in press.
Wu, Y. N., Mikulski, S. M., Ardelt, W., Rybak, S. R., and Youle, R. J. (1993) A cytotoxic ribonuclease.J. Biol. Chem. 268, 10,686–10,693.
Rybak, S. M., Newton, D. L., Mikulski, S. M., and Viera, A., and Youle, R. J. (1993) Cytotoxic onconase and ribonuclease A chimeras.Drug Targeting and Delivery, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rybak, S.M., Hoogenboom, H.R., Newton, D.L. et al. Rational immunotherapy with ribonuclease chimeras. Cell Biophysics 21, 121–138 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789483
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789483