Abstract
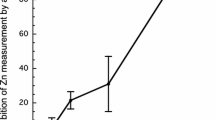
A new analytical affinity chromatography method was developed for measuring the free [Zn2+] concentration in bovine milk. The column was generated by immobilizing avidin and attaching biotinylated metallothionein (MT) on controlled-pore glass beads. Zinc bound to the MT column at physiological free [Zn2+] concentration and was dissociated again in an elution buffer of pH 2. The distributions of extrinsically added65Zn and native zinc in different fractions of milk were virtually identical, validating the use of extrinsic labeling in studies of the free [Zn2+] concentration in milk. Extrinsically labeled whey fractions were mixed with standard solutions whose free [Zn2+] concentrations were calculated by computer model.65Zn retained by the column provided an indication of free [Zn2+] concentration in the mixture, and by interpolation, in the original milk. The free [Zn2+] concentration measured by the affinity chromatography method in the milk of a group of six cows was 90.4±29.7 pM. This value is similar to estimates of free [Zn2+] concentrations in other biological fluids by entirely different methods. Measurement of free [Zn2+] may be helpful in understanding the physiology and biochemistry of zinc metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. C. Neville, R. P. Keller, C. E. Casey, and J. C. Allen,J. Dairy Sci. 77, 1964–1975 (1994).
C. E. Casey, M. C. Neville, and K. M. Hambidge,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 49, 773–785 (1989).
S. J. Vaillancourt and J. C. Allen,Biol. Trace Element Res. 30, 185–196 (1991).
N. W. Solomons,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32, 856–871 (1979).
R. M. Forbes and J. W. Erdman, Jr.Ann. Rev. Nutr. 3, 213–231 (1983).
N. W. Solomons, inModern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 7th ed., M. E. Shils and V. R. Young, eds., Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, pp. 238–262 (1988).
J. Scholmerich, A. Freudemann, E. Kottgen, H. Wietholtz, B. Steiert, E. Lohle, D. Haussinger, and W. Gerok.Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 45, 1480–1486 (1987).
B. Sandstrom, L. Davidson, A. Cederblad, and B. Lonnerdal,J. Nutr. 115, 411–414 (1985).
R. Ellis, J. L. Kelsay, R. D. Raynolds, E. R. Morris, P. B. Moser, and C. W. Frazier,J. Am. Diet Assoc. 87, 1043–1047 (1987).
T. C. A. McGann, W. Buchheim, R. D. Kearney, and T. Richardson,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 760, 415–420 (1983).
B. Sandstrom, C. L. Keen, and B. Lonnerdal,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 38, 420–428 (1983).
K. M. Hambidge, P. A. Walravens, C. E. Casey, R. M. Brown, and C. Bender,J. Pediatr. 94, 607 (1979).
R. A. DiSilvestro and R. J. Cousins.Ann. Rev. Nutr. 3, 261–288 (1983).
D. S. Norton and F. W. Heaton,J. Inorg. Biochem. 13, 1–9 (1980).
B. C. Starcher, J. G. Glauber, and J. G. Madaras,J. Nutr. 110, 1391–1397 (1980).
M. P. Menard, C. C. McCormick, and R. J. Cousins,J. Nutr. 11, 1353–1361 (1981).
R. J. Cousins, inClinical, Biochemical, and Nutritional Aspects of Trace Elements, A. S. Prasad, ed., Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 117–128 (1982).
R. F. Bonewitz, E. C. Foulkes, E. J. O’Flaherty, and V. S. Hertzberg.Am. J. Physiol. 244, G314-G320 (1983).
Association of Official Analytical Chemistry,Official Methods of Analysis. 13th ed., Assoc. Offic. Anal. Chem., Washington, DC (1980).
TK Solver Plus. Universal Technical Systems, Inc. Rockford, IL, p. 130 (1987).
A. E. Martell and R. M. Smith, inCritical Stability Constants, vol. 3:Other Organic Ligands, Plenum, New York, p. 161 (1977).
A. E. Martell and R. M. Smith,Critical Stability Constants, vol. 5:First Supplement, Plenum, New York p. 329 (1982).
S. Kotrly and L. Sucha,Handbook of Chemical Equilibria in Analytical Chemistry, Ellis Horwood Limited, Chichester, West Sussex, England, 414 pp. (1985).
P. Zhang, New Methods for Measuring Free Zinc(II) Concentration in Biological Fluids and their Application in Bovine Blood and Milk. Ph.D. Dissertation, North Carolina State University, Raleigh 129 pp. (1994).
V. G. Janolino and H. E. Swaisgood,Biotechnol. Bioeng. 24, 1069–1080 (1982).
G. DuVal, H. E. Swaisgood, and H. R. Horton,J. Appl. Biochem. 6, 240–250 (1984).
N. M. Green and E. J. Toms,Biochem. J. 133, 687–698 (1973).
Instructions of NHS-LC-Biotinylation Kit. 21430. Pierce Chemical Co. Rockford, IL (1990).
O. N. Mathur and N. K. Roy,Indian J. Dairy Sci. 35, 374 (1982).
S. Parkash and R. Jenness,J. Dairy Sci. 50, 127–134 (1967).
P. Blakeborough, D. N. Salter, and W. I. Gurr,Biochem. J. 209, 505–512 (1983).
H. Singh, A. Flynn, and P. F. Fox,J. Dairy Res. 56, 249–263 (1989).
B. Lonnerdal, A. G. Stanislowski, L. S. Hurley,J. Inorg. Biochem. 12, 71–78 (1980).
M. T. Martin, K. F. Licklider, J. G. Brushmiller, F. A. Jacobs,J. Inorg. Biochem. 15, 55–65 (1981).
G. R. Magneson, J. M. Puvathingal, and W. J. Ray, Jr.J. Biol. Chem. 262, 11,140–11,148 (1987).
R. J. Cousins,Physiol. Rev. 65, 238–309 (1985).
R. D. Comeau, K. W. McDonald, G. L. Tolman, M. Vasak, and F. A. Liberatore,Prep. Biochem. 22, 151–164 (1992).
P. Zhang and J. C. Allen,J. Dairy Sci. 75(Suppl. 1), 106 (1992).
P. Zhang and J. C. Allen,J. Nutr., in press (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, P., Allen, J.C. Free zinc concentration in bovine milk measured by analytical affinity chromatography with immobilized metallothionein. Biol Trace Elem Res 50, 135–148 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789416
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02789416