Summary
Conclusion
Stimulation of pancreatic sensory nerves by capsaicin produced secretory effects probably caused, at least in part, by the release of CGRP.
Background
In the pancreas calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) has been localized in the sensory nerves, but its physiological role is unknown. This study was undertaken to compare the changes of pancreatic enzyme secretion produced by CGRP and by stimulation or destruction of sensory nerves.
Methods
To stimulate sensory nerves, low doses of capsaicin (0.25–0.5 mg/kg) were given intraduodenally to the conscious rats with chronic pancreatic fistula. To inactivate sensory nerves high doses of capsaicin (100 mg/kg) were given subcutaneously 10 d before tests. For the in vitro experiments pancreatic slices and isolated pancreatic acini were prepared from intact and capsaicin-denervated rats.
Results
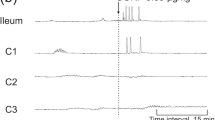
In conscious rats, CGRP given subcutaneously (5–10 μg/kg) and low doses of capsaicin given intraduodenally reduced basal pancreatic secretion. In isolated pancreatic acini, CGRP (10−10–10−6 M), but not capsaicin, increased basal or secretagog-stimulated amylase release. In pancreatic slices (containing nerve fibers) capsaicin (10−10–10−6 M) increased enzyme secretion, and this secretion was abolished by previous inactivation of sensory nerves by this neurotoxin. Capsaicin deactivation did not affect the secretory response of pancreatic acini to CGRP, cerulein, or urecholine. Sensory denervation by capsaicin did not change basal protein secretion, but reduced that produced by feeding or diversion of pancreatic juice to the exterior during first 2 h of the tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rosenfeld MG, Mermod JJ, Amara SG, Swanson LW, Sawchenko PE, Rivier J, Vale WW, Evans RM; Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue specific RNA processing.Nature 1983; 304: 129–135.
Sternini C, De Giorgio R, Anderson K, Watt JH, Brunicardi FC, Widdson AL, Wong H, Reber HA, Walsh JH, Go VL. Species differences in the immunoreactive patterns calcitonin gene-related peptide in the pancreas.Cell Tissue Res 1992; 269 (3): 447–458.
Sternini C, Card JP. Ultrastructural characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing fibers and islet cells in the rat pancreas.Pancreas 1991; 6(4): 375–384.
Maton PN, Pradhan T, Zhou ZC, Gardner JD, Jensen RT. Activities of calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and related peptides at the CGRP receptor.Pancreas 1990; 11(3): 485–489.
Bunnet NW, Mulvihill SJ, Debas HT. Calcitonin generelated peptide inhibits exocrine secretion from the rat pancreas by a neurally mediated mechanism.Exp Physiol 1991; 76(1): 115–123.
Debas HT, Nelson MT, Bunnet NW, Mulvihill SJ. Selective release of somatostatin by calcitonin gene-related peptide and influence on pancreatic secretion.Ann NY Acad Sci 1992; 657: 289–298.
Messmer B, Zimmerman FG, Lenz HJ. Regulation of exocrine pancreatic secretion by cerebral TRH and CGRP-role of VIP, muscarinic and adrenergic pathways.Am J Physiol 1993; 264: G237-G242.
Zhou ZC, Villanueva MI, Noguchi M, Jones SW, Gardner JD, Jensen RT. Mechanism of action of calcitonin-gene related peptide in stimulating pancreatic enzyme secretion.Am J Physiol 1986; 257: G391-G397.
Maton PN, Pradhan T, Moore S. C-terminal peptides of calcitonin gene-related peptide act as agonist at the cholecystokinin receptor.Peptides 1990; 11(6): 1163–1167.
Grider JR. CGRP as a transmitter in the sensory pathway mediating peristaltic reflex.Am J Physiol 1994; 266(29): G1139-G1145.
Sternini C, Reeve JR, Brecha N. Distribution and characterization of calcitonin gene-related peptide immunoreactivity in the digestive system of normal and capsaicin-treated rats.Gastroenterology 1987; 93(4): 852–862.
Holtzer P. Capsaicin: cellular targets, mechanism of action, and selectivity for thin sensory neurons.Pharmacol Rev 1991; 43: 143–201.
Konturek SJ, Szlachcic A, Dembiński A, Warzecha Z, Jaworek J, Stachura J. Nitric oxidein pancreatic secretion and hormone-induced pancreatitis in rats.Int J Pancreatol 1994; 15(1): 19–28.
Amsterdam D, Solomon TE, Jamieson JD. Sequential dissociation of exocrine pancreas into lobules, acini and individual cells.Meth Cell Biol 1978; 20: 262–278.
Bernfeld P. Amylases alfa and beta.Meth Enzymol 1955; 5: 139–148.
Li Y, Kolligs F, Owyang Ch. Mechanism of action of calcitonin gene-related peptide in inhibiting pancreatic enzyme secretion.Gastroenterology 1993; 105: 194–201.
Edwards AV, Bloom SR. Pancreatic endocrine responses to substance P and calcitonin gene-related peptide in conscious calves.Am J Physiol 1994; 267 (6 Pt 1): E847-E852.
Kirchgessner A, Gershon MD. Innervation of the pancreas by neurons in the gut.J Neurosci 1990; 10: 1625–1642.
Kirchgessner A, Gershon MD. Presynaptic inhibition by serotonin of nerve-mediated secretion of pancreatic amylase.Am J Physiol 1995; 268: G339-G345.
Karlsson S, Sundler F, Ahren B. Neonatal capsaicin-treatment in mice: effects on pancreatic peptidergic nerves and 2-deoxy-D-glucose induced insulin and glucagon secretion.J Auton Nerv Syst 1992; 39(1): 51–59.
Tharakan T, Kirchgessner AL, Baxi LV, Gershon MD. Appearance of neuropeptides and NADPH-diaphorase during development of the enteropancreatic innervation.Brain Res Dev Brain Res 1995; 84(1): 26–38.
Masuda M, Tomita H, Okubo K, Miyasaka K. Vagal efferent nerve-dependent inhibitory action of pancreatic polypeptide and peptide YY in conscious rats.J Auton Nerv Syst 1994; 50(2): 131–138.
Gicquel N, Nagain C, Chariot J, Tsocas A, Levenez F, Corring T, Roze C. Modulation of pancreatic secretion by capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons in the rat.Pancreas 1994; 9(2): 203–211.
Li Y, Owyang C. Endogenous cholecystokinin stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion via vagal afferent pathway in rats.Gastroenterology 1994; 107(2): 525–531.
Chey WY. Hormonal control of pancreatic secretion. InThe Pancreas: Biology, Pathology and Disease, Go VLW, DiMagno EP, Gardner JD, Lebenthal E, Reber HA, Scheele GA, eds. Raven, New York, 1993.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jaworek, J., Konturek, S.J. & Szlachcic, A. The role of CGRP and afferent nerves in the modulation of pancreatic enzyme secretion in the rat. Int J Pancreatol 22, 137–146 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02787472
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02787472