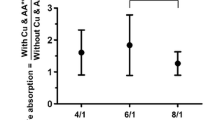
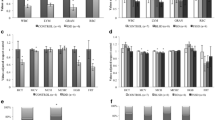
Abstract
Interactions between dietary Cu, Se, and vitamin E in ascorbate-induced hemolysis of erythrocytes obtained from rats fed diets deficient or adequate in these elements were investigated. Hemolysis was affected by all three dietary factors, through closely interrelated but distinct mechanisms. In vitamin E-deficient cells, hemolysis was increased and the amount of hemolysis was directly related to the amount of hemoglobin breakdown. Deficiency of Cu or Se decreased hemolysis, but only in vitamin E-deficient cells. Vitamin E did not affect the breakdown of hemoglobin, but Cu and Se did. Hemolysis and hemoglobin breakdown were decreased by the addition of glucose, through mechanisms independent of that involving reduced glutathione metabolism. These results suggest that vitamin E acts within erythrocyte membranes to prevent products of hemoglobin breakdown from initiating peroxidation and subsequent hemolysis. Effects of Cu and Se are linked with that of vitamin E by the involvement of glutathione peroxidase and Cu superoxide dismutase in the cytoplasmic breakdown of hemoglobin, rather than by a direct effect of these enzymes on lipid peroxidation. It is concluded that the erythrocyte, because of its high heme content, probably represents a special system in terms of peroxidative pathways, and these findings may not be directly applicable to other tissues.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Noguchi, A. H. Cantor, and M. L. Scott,J. Nutr.,103, 1502 (1973).
W. G. Hoekstra, inTrace Element Metabolism in Animals—2, W. G. Hoekstra, J. W. Suttie, H. E. Ganther, and W. Mertz, eds., University Park Press, Baltimore, 1974, pp. 61–77.
E. W. Kellogg and I. Fridovich,J. Biol. Chem. 252, 6721 (1977).
D. D. Tyler,FEBS Lett. 51, 180 (1975).
T. C. Pederson and S. D. Aust,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 52, 1071 (1973).
J. M. McCord and I. Fridovich,J. Biol. Chem. 244, 6049 (1969).
R. A. Weisigner and I. Fridovich,J. Biol. Chem. 248, 3582 (1973).
D. I. Paynter, R. J. Moir, and E. J. Underwood,J. Nutr. 109, 1566 (1979).
D. G. Hafeman, R. A. Sunde, and W. G. Hoekstra,J. Nutr. 104, 580 (1974).
K. Schwarz,Fed. Proc. 24, 58 (1965).
L. S. Jensen,Proc. Soc. Expl. Biol. Med. 149, 113 (1975).
Hill, C. H., inTrace Elements in Human Health and Disease, vol. 2, A. S. Prasad, ed., Academic Press, New York, 1976, pp. 281–300.
M. K. Hill, S. D. Walker, and A. G. Taylor,N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 12, 261 (1969).
G. G. Thomson and B. M. Lawson,N. Z. Vet. J. 18, 79 (1970).
M. L. Quaife and P. L. Harris,Ind. Eng. Chem. Anal. Ed. 18, 707 (1946).
J. T. Rotruck, A. L. Pope, H. E. Ganther, and W. G. Hoekstra,J. Nutr. 102, 689 (1972).
E. Beutler, O. Duron, and B. M. Kelly,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 61, 882 (1963).
D. E. Paglia and W. N. Valentine,J. Lab. Clin. Med. 70, 158 (1967).
D. I. Paynter,Aust. J. Agric. Res. 30, 695 (1979).
G. B. Storer,Biochem. Med. 11, 71 (1974).
E. J. van Kampen and W. G. Zijlstra,Clin. Chim. Acta. 6, 538 (1961).
J. H. Watkinson,Anal. Chem. 38, 92 (1966).
G. W. Snedecor and W. G. Cochran, inStatistical Methods, Iowa State University Press, Ames, Iowa, 1967, pp. 250–253, 359–361.
P. A. Abraham and J. L. Evans, inTrace Substances in Environmental Health, vol. 5, D. D. Hemphill, ed., University of Missouri, Columbia, 1972, pp. 335–347.
H. W. Bennetts, A. B. Beck, and R. Harley,Aust. Vet. J. 24, 237 (1948).
E. J. Underwood, inTrace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th Ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977, pp. 84–86.
J. R. Prohaska and H. E. Ganther,Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 76, 437 (1977).
R. A. Lawrence and R. F. Burk,J. Nutr. 108, 211 (1978).
H. E. Ganther, D. G. Hafeman, R. A. Lawrence, R. E. Serfass, and W. G. Hoekstra, inTrace Elements in Human Health and Disease, vol. 2 A. S. Prasad, ed., Academic Press, New York, 1976, pp. 165–234.
B. Goldberg, and A. Stern,Arch. Biochem. Biophys,178, 218 (1977).
G. Cohen, inErythrocyte Structure and Function, G. L. Brewer, ed., Liss, New York, 1975, pp. 685–698.
A. L. Tappel,Fed. Proc. 32, 1870 (1973).
D. E. Hulquist, R. H. Douglas, and R. T. Dean, inErythrocyte Structure and Function, G. L. Brewer, ed., Liss, New York, 1975, pp. 297–301.
R. E. Lynch, G. R. Lee, and G. E. Cartwright,J. Biol. Chem. 251, 1015 (1976).
A. M. Michelson, inSuperoxide and Superoxide Dismutases, A. M. Michelson, J. M. McCord, and I. Fridovich, eds., Academic Press, New York, 1977, pp. 245–255.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Paynter, D.I., Martin, G.B. Investigations into combined dietary deficiencies of copper, selenium, and vitamin E in the rat. Biol Trace Elem Res 2, 175–191 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785353
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785353
Index Entries
- Copper, interactions with Se and Vitamin E in rats
- selenium, interactions with Cu and vitamin E in rats
- vitamin E, interactions with Cu and Se in rats
- dietary deficiencies, of Cu, Se, and vitamin E in rats
- interactions of Cu, Se, and vitamin E in rats
- hemolysis mechanisms, and Cu−Se-vitamin E interactions in rats