Abstract
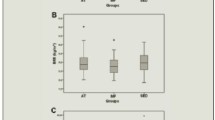
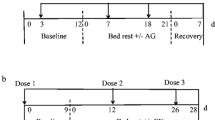
The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effect of acute (abrupt restriction of muscular activity) and rigorous bed-rest conditions on urinary and plasma calcium changes in endurance trained volunteers. The studies were performed on 30 long distance runners ages 23–25 who had a peak oxygen uptake of 66.0 mL/min/kg and had run 14.0 km/d on the average prior to their participation in the study. The volunteers were divided into three groups: The volunteers in the first group were under normal ambulatory conditions (control subjects), the second group was subjected to an acute bed-rest regime (acute bedrested subjects), and the third group was submitted to a rigorous bed-rest regime (rigorous bedrested subjects). The second and third groups of volunteers were kept under a rigorous bed rest regime for 7 d. During the pre-bed-rest period and during the actual bed-rest periods (acute and rigorous bed-rest periods), urinary excretion of calcium and plasma calcium and parathyroid hormone (PTH) concentrations were determined. During the 1st d of acute and rigorous bed-rest periods, urinary excretion and plasma concentration of calcium increased significantly (P≤0.05), while plasma parathyroid hormone content decreased significantly (P≤0.05). On the 3rd d of the experimental period, urinary excretion and plasma calcium concentration decreased somewhat, during the 7th d, calcium in urine and plasma increased further, while parathyroid hormone content in plasma increased somewhat on the 3rd d and decreased again on the 7th d of the experimental period. The changes were more pronounced in the volunteers who were subjected to acute bed-rest conditions than in the volunteers who were submitted to rigorous bed-rest conditions. It was concluded that exposure to acute bed-rest conditions induces significantly greater urinary and serum calcium changes than rigorous bed-rest conditions in endurance trained volunteers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye. A. Kovalenko and N. N. Gurovskiy, Hypokinesia, Meditsina, Moscow (1980).
I. V. Fedorov, Metabolism Under Hypodynamic Conditions, Izdatel’stvo Nauka, Moscow (1983).
J. E. Greenleaf, E. M. Bernauer, H. L. Young, J. T. Morse, R. W. Staley, L. T. Juhos, and W. Van Beaumont, Fluid and electrolytes shifts during bed rest with isometric and isotonic exercise,J. Appl. Physiol. 42, 59–66 (1977).
J. Durnin and M. Rahaman, The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness,Brit. J. Nutr. 21, 681–689 (1967).
Y. G. Zorbas, K. M. Nashimoto, and M. N. Yamamoto, Diuresis, plasma and itercompartmental changes in endurance trained volunteers during acute and ordinary bed rest conditions,Model. Simul. Control. 23, 49–69 (1993).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and M. N. Togawa, Renal excretion of water in men under hypokinesia and physical exercise with fluid and salt supplementation,Acta Astronautica. 21, 599–605 (1990).
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, and A. N. Marketi, Body mass changes in endurance trained volunteers during prolonged restriction of muscular activity and chronic hyperhydration,Sports Med. Trains. Rhab. 4, 21–29 (1993).
Y. G. Zorbas, V. R. Bobylev, and A. N. Marketi, Physical exercise in preserving men’s body mass under hypokinesia,Inter. J. Rehab. Research. 12, 326–330 (1989).
Y. G. Zorbas, A. B. Merkov, and A. N. Nobahar, Nutritional status of men under hypokinesia,J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 9, 333–342 (1987).
Y. G. Zorbas, A. B. Merkov, and A. N. Nobahar, Metabolic changes in man under hypokinesia and physical exercise,J. Environ. Pathol. Toxicol. Oncol. 9, 361–370 (1987).
Y. G. Zorbas, G. I. Nizamov, and M. N. Tanaka, Circulatory reactions of men under hypokinesia and physical exercise with chronic hyperhydration,Model. Simul. Control. 19, 49–64 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorbas, Y.G., Federenko, Y.F. & Yaroshenko, Y.N. Urinary and plasma calcium changes in endurance trained volunteers during exposure to acute and rigorous bed rest conditions. Biol Trace Elem Res 54, 75–86 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785321
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785321