Abstract
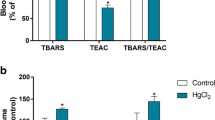
Alveolar macrophages collected by pulmonary lavage from male Fisher-344 rats at intervals (24–72 h) after HgCl2 injection (1–5 mg/kg, sc) were analyzed by several techniques. Within 24–72 h, the macrophages showed morphological signs of activation (hypertrophy and ruffled plasma membrane). Lipid peroxidation (increased malondialdehyde concentration) was not detected until 48 h. Dose- and time-related effects of HgCl2 on malondialdehyde concentration and time-related effects of HgCl2 on malondialdehyde concentration and mercury content of alveolar macrophages were observed 24–72 h postinjection. Diminished cell viability occurred only at 72 h after the highest dosage of HgCl2. This study demonstrates that the alveolar macrophage was a cellular target for mercury toxicity following parenteral exposure to HgCl2.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. D. Koller, Immunosupression produced by lead, cadmium and mercury,Amer. J. Vet. Res. 34, 1457, 1458 (1973).
D. A. Lawrence, Heavy metal modulation of lymphocyte activities,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 57, 439–451 (1981).
C. L. Gaworski, and R. P. Sharma, The effects of heavy metals and [3H]thymidine uptake in lymphocytes,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 46, 305–313 (1978).
J. H. Gainer, Effects of heavy metals and of deficiency of zinc on mortality rates in mice infected with encephalomyocarditis virus,Amer. J. Vet. Res. 38, 869–872 (1977).
J. B. Galvin and S. G. Oberg, Toxicity of hexavalent chromiun to the alveolar macrophage in vivo and in vitro,Environ. Res. 33, 7–16 (1984).
M. Labedzka, H. Gulyas, N. Schmidt, and G. Gercken, Toxicity of metallic ions and oxide to rabbit alveolar macrophages,Environ. Res. 48, 255–274 (1989).
B. M. Babior, The respiratory burst of phagocytes,J. Clin. Invest. 73, 599 (1984).
R. B. Johnston, Enhancement of phagocytosis-associated oxidative metabolism as a manifestation of macrophage activation,Lymphokines 3, 33–56 (1981).
C. F. Nathan, Mechanism of macrophage antimicrobial activity.Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 77, 620–630 (1983).
S. Asvadi and J. A. Hayes, Acute lung injury induced by cadmium aerosol. II. Free airway cell response during injury and repair,Amer. J. Pathol. 90, 89–98 (1978).
R. F. Henderson, A. H. Rebar, J. A. Pickrell, and G. J. Newton, Early damage indicators in the lung. III. Biochemical and cytological response of the lung to inhaled metal salts.Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 50, 123–136 (1979).
F. W. Jr. Sunderman, S. M. Hopfer, S. M. Lin, M. C. Plowman, T. Stojanovic, S. H. Y. Wong, O. Zaharia, and L. Ziebka, Toxicity to alveolar macrophages in rats following parenteral injection of nickel chloride,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 100, 107–118 (1989).
M. D. Cohen, Z. Yang and J. T. Zelikoff, Immunotoxicity of particulate lead: In vitro exposure alters pulmonary macrophage tumor necrosis factor production and activity,J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. 42, 377–392 (1992).
M. Yamada, S. Takahashi, H. Sato, T. Kondo, T. Kikuchi, K. Furuya, and I. Tanaka, Solubility of nickel oxide particles in various solutions and rat alveolar macrophages,Biol. Trace Element Res. 36, 89–98 (1993).
R. C. Lantz, G. Parliman, G. J. Chen, and D. E. Carter, Effect of arsenic exposure on alveolar macrophage function. I. Effect of soluble As(III) and As(V),Environ. Res. 67, 183–195 (1994).
H. Fukino, M. Hirai, Y. M. Hsueh, and Y. Yamane, Effect of zinc pretreatment on mercuric chloride-induced lipid peroxidation in the rat kidney,Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 73, 395–401 (1984).
F. W. Jr. Sunderman, Metals and lipid peroxidation,Acta Pharmacol. Toxicol. 59, 248–255 (1986).
M. Yonaha, E. Itoh, Y. Ohbayashi, and M. Uchiyama, Induction of lipid peroxidation in rats by mercuric chloride,Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharmacol. 28, 105–112 (1980).
M. Lundborg, A. Johansson, and P. Camner, Morphology and release of lysozyme following exposure of rabbit lung macrophages to nickel or cadmium in vitro,Toxicology 46, 191–203 (1987).
S. H. Y. Wong, J. A. Knight, S. M. Hopfer, O. Zaharia, C. N. Leach Jr., and F. W. Sunderman Jr., Lipoperoxides in plasma as measured by liquid chromatographic separation of malondialdehyde-thiobarbituric acid adduct,Clin. Chem. 33, 214–220 (1987).
R. B. Johnston Jr., Monocytes and macrophages,N. Engl. J. Med. 318, 747–752 (1988).
Y. L. Huang, S. L. Cheng, and T. H. Lin, Lipid peroxidation in rats administrated with mercuric chloride,Biol. Trace Element Res. (in press, 1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, YL., Lin, TH. Toxicity to alveolar macrophages in rats following parenteral injection of mercuric chloride. Biol Trace Elem Res 54, 1–8 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785315
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02785315