Abstract
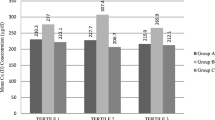
The Zn/Cu ratio was examined in the serum of three groups of persons: healthy volunteers, diabetic patients on diabetic diet (NIDDM), and diabetic patients on diabetic diet and insulin (IDDM). Zinc, copper, the Zn/Cu serum ratio, and the blood glucose level were determined during fasting and 2 h after breakfast. Zn and Cu serum levels in NIDDM and IDDM patients were decreased. The Zn/Cu ratio was higher in both groups of diabetic patients. These changes in the Zn and Cu levels as well as in the Zn/Cu ratio were not related to chronic diabetic complications.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. F. McCarty and E. J. Rubin,Med. Hypotheses 2, 139–151 (1984).
W. Mertz,Fed. Proc. 11, 2807–2812 (1982).
W. B. Kinlow, A. S. Levine, J. E. Morley, S. E. Silvis, and C. J. McClain,Am. J. Med. 2, 273–277 (1983).
W. K. Canfield, K. M. Hambridge, and L. K. Johnson,J. Pediatric Gastroenterology Nutr. 4, 577–584 (1984).
J. Casey, W. R. Elinn, J. S. Vao, V. Fahey, J. Pawlovski, and J. J. Bergan,Surgery 6, 822–827 (1983).
B. Haeggloef, G. Halimans, G. Holmgren, J. Ludvigsson, and S. Falkmer,Acta Endocrinol. 1, 88–95 (1983).
R. Noto, R. Alicata, L. Sfogliano, S. Neri, and M. Bifarella,Acta Diabetol. Latina 1, 81–85 (1983).
A. M. Wahid, S. A. H. Fathi, and M. R. Aboul-Khair,Clin. Lab. 9, 9–16 (1988).
M. S. Agren, H. E. Stromberg, A. Rindby, and G. Hallmans,Acta Derm. Venerol. 66, 237–240 (1986).
Diabetes Mellitus: Report of a WHO Study Group (1985) WHO Geneva.
E. Raabo and T. C. Terkildsen,Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 12, 402–407 (1960).
J. Rubeška and B. Moldan,Atomova apsorčni spectrofotometrie, S. N. T. L., Praha (1967).
Perkin-Elmer Analytical Methods for Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (1971), Perkin-Elmer, Norwalk.
B. Štraus,Medicinska biokemija, JUMENA, Zagreb, 1988, pp. 1010–1011.
S. Barić,Agronomski glasnik 14, 787 (1964).
J. L. Schlienger, F. Grunengerger, E. A. Maier, C. Simon, G. Chabrier, and M. J. F. Leroy,Presse Med. 17, 1076–1079 (1988).
C. D'Ocon, A. De Armino, and I. Frasquet,Revista Española De Fisiología 3, 335–338 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Car, N., Car, A., Granić, M. et al. Zinc and copper in the serum of diabetic patients. Biol Trace Elem Res 32, 325–329 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784618
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784618