Abstract
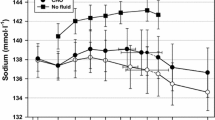
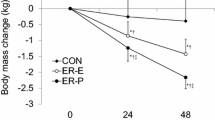
The objective of this investigation was to determine whether urinary and plasma potassium changes developed during prolonged hypokinesia (HK) (decreased number of km/d) in endurance-trained subjects could be minimized or reversed with a daily intake of fluid and salt supplementation (FSS). The studies were performed on 30 endurance-trained male volunteers aged 23–26 yr with an average peak oxygen uptake of 65 mL/kg min during 364 d of HK. All volunteers were on an average of 13.8 km/d prior to their exposure to HK. All volunteers were randomly divided into three groups: 10 volunteers were placed continuously under an average of 14.0 km/d (control subjects), 10 volunteers were subjected continuously to an average of 2.7 km/d (unsupplemented hypokinetic subjects), and 10 volunteers were submitted continuously to an average of 2.7 km/d, and consumed daily an additional amount of 0.1 g sodium chloride (NaCl)/kg body wt and 30 mL water/kg body wt (supplemented hypokinetic subjects). During the prehypokinetic period of 60 d and during the hypokinetic period of 364 d, potassium loading tests were performed with 1.5–1.7 mEq potassium chloride/kg body wt, and potassium, sodium, and chloride excretion in urine and potassium, sodium, and chloride in plasma were determined. In the unsupplemented hypokinetic volunteers, urinary excretion of electrolytes and concentrations of electrolytes in plasma increased significantly as compared to the control and supplemented hypokinetic groups of volunteers. It was concluded that daily intake of fluid and salt supplementation had a favorable effect on regulation of urinary and plasma potassium changes in trained subjects during prolonged HK.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye. A. Kovalenko and N. N. Gurovskiy,Hypokinesia, Meditsina, Moscow (1980).
F. V. Fedorov,Metabolism Under Hypodynamic Conditions. Izdatel'stvo Nauka, Moscow (1982).
Y. G. Zorbas and N. B. Alekseyev, Physiological reactions of man under hypokinesia and physical exercise with fluid and salt supplementation,Modelling Simulation Control 19, 31–46 (1989).
N. Ye. Panferova,Hypodynamia and Cardiovascular System. Meditsina, Moscow (1977).
K. H. Hyatt, P. C. Johnson, G. V. Hoffler, et al., Effect of potassium depletion in normal males: An Apollo 1-simulation,Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 46, 11–15 (1975).
Y. G., Zorbas, A. L. Ivanov, and Y. F. Federenko, Biochemical changes in physically conditioned subjects after exposure to hypokinesia and chronic hyperhydration,Materia Medica Polona,4, 300–308 (1990).
I. S. Balakhovskiy, R. K. Kiselev, M. A. Kaplan, et al., Changes in total body potassium, hemoglobin and bromine space in the crew of Soyuz-14,Kosmicheskaya Biol. 3, 11–15 (1978).
Y. G. Zorbas, N. I. Abratov, and C. B. Stoikolescu, Renal excretion of potassium in men under hypokinesia and physical exercise with chronic hyperhydration,Urologia,3, 229–238, (1988).
L. I. Kakurin, G. S., Arzamov, and A. I. Grigor'yev, Kaliuretic renal function in man as related to different degrees of exercise during bed rest,Kosmicheskaya Biol. 4, 13–17 (1978).
J. Durnin and M. Rahaman, The assessment of the amount of fat in the human body from measurements of skinfold thickness,Br. J. Med. 21, 681–689, (1967).
Y. G. Zorbas, Y. F. Federenko, and K. N. Naexu, Effect of daily hyperhydration on fluid electrolyte changes in endurance trained volunteers during prolonged restriction of muscular activity,Biol. Trace Element Res. 50, 57–78 (1995).
J. E. Greenleaf, V. A. Convertino, R. W. Stremel, et al., Plasma (Na+), (Ca2+), and volume shifts and thermoregulation during exercise in man,J. Appl. Physiol. 43, 1026–1032 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zorbas, Y.G., Federenko, Y.F. & Naexu, K.A. Potassium changes in trained subjects after potassium loading and during restriction of muscular activity and chronic hyperhydration. Biol Trace Elem Res 53, 95–112 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784548
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784548