Abstract
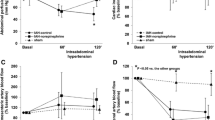
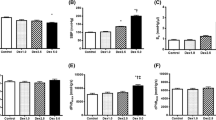
The objective of this study was to determine the effect of systemic MgSO4 infusion on subendocardial and subepicardial perfusion. Seventeen spontaneously breathing piglets were examined. Myocardial perfusion was measured using radiolabeled microspheres at baseline, 30 and 60 min after either MgSO4 (80 mg/kg) or saline infusion. Blood pressure, heart rate, and cardiac output were also measured at these time intervals. Comparison of the magnesiuminduced changes in systemic blood pressure and on subendocardial and subepicardial perfusion at 30 and 60 min with values obtained with saline solution at 30 and 60 min, yielded no statistically significant difference (Tables 1–3). The ratio of subendocardial/subepicardial blood flow and subendocardial and subepicardial coronary vascular resistance at 30 and 60 min revealed no statistically significant differences between the magnesium and the control group (Table 3). There were no statistically significant difference in cardiac output and heart rate during any of the measured periods (Table 2). Our results suggest that the administration of MgSO4 does not alter the ratio of subendocardial/subepicardial blood flow and the ratio of subendocardial/subepicardial coronary vascular resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. R. Levine, T. J. Crowlry, and H. A. Hai, Hypomagnasemia and ventricular tachycardia,Chest 81, 244–247 (1982).
D. Tzivoni, S. Banai, C. Schuger, J. Benhorin, A. Keren, S. Gottlieb, S. Stern, Treatment of torsade de points with magnesium and sulfate,Circulation 77, 392–397 (1988).
K. L. Woods, S. Fletcher, C. Roffe, and Y. Haider, Intravenous magnesium sulphate in suspected acute myocardial infarction: results of the second Leicester Intravenous Magnesium Intervention Trial (LIMIT-2),Lancet 339, 1553–1558 (1992).
K. L. Woods, and S. Fletcher, Long-term outcome after intravenous magnesium sulphate in suspected acute myocardial infarction: the second Leicester Intravenous Magnesium Intervention Trial (LIMIT-2),Lancet 343, 816–819 (1994).
ISIS collaborative group, ISIS-4: randomized study of intravenous magnesium in over 50,000 patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction,Lancet 345, 669–685 (1995).
C. W. Christensen, M. A. Rieder, E. L. Silverstein, and N. E. Gencheff, Magnesium sulfate reduces myocardial infarct size when administered before but not after coronary reperfusion in a canine model,Circulation 92, 2617–2621 (1995).
W. R. Herzog, M. L. Schlossberg, K. S. MacMurdy, L. R. Edenbaum, M. J. Gerber, R.A. Vogel, and V. L. Serebruany, Timing of magnesium therapy affects experimental infarct size,Circulation 92, 2622–2626 (1995).
E. M. Antman, Magnesium in acute MI. Timing is critical,Circulation 92, 2367–2372 (1995).
C. Vigorito, A. Giordano, P. Ferraro, D. Acanfora, L. De Caprio, C. Naddeo, and F. Rengo, Hemodynamic effects of magnesium on the normal human heart,Am. J. Cardiol. 67, 1435–1437 (1991).
J. Leor, and R. A. Kloner, An experimental model examining the role of magnesium in the therapy of acute myocardial infarction,Am. J. Cardiol. 72, 1292–1293 (1995).
M. A. Heymann, B. D. Payne, J. I. Hoffman, and A. M. Rudolph, Blood flow measurements with radionuclide-labeled particles,Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 55–59 (1977).
G. D. Buckberg, J. C. Luck, B. Payne, J. I. E. Hoffman, J. P. Archie, and D. E. Fixier, Some sources of error in measuring regional blood flow with radioactive microspheres,J. Appl. Physiol. 31, 598–604 (1971).
I. Kobrin, M. B. Kardon, W. Oigman, B. L. Pegram, and E. D. Frohlich. Role of site of microsphere injection and catheter position on systemic and regional hemodynamics in rat,Am. J. Physiol. 247, H35-H39 (1984).
G. D. Schrock, R. L. Krahmer, and J. L. Ferguson, Coronary flow by left atrial and left ventricular microsphere injection in therapy,Am. J. Physiol. 259, H635–638 (1990).
P. O. Iversen, Evidence for long-term fluctuations in regional blood flow whithin the rabbit left ventricle,Acta Physiol. Scand. 146, 329–339 (1992).
R. B. King, J. B. Bassingthwaighte, J. R. S. Hales, and L. B. Rowell, Stability of heterogeneity of myocardial blood flow in normal awake baboons,Cir. Res. 57, 285–295 (1985).
J. B. Bassingthwaighte, M. A. Malone, T. C. Moffet, R. B. King, S. E. Little, J. M. Link, and K. A. Krohn, Validity of microsphere depositions for regional myocardial flows,Am. J. Physiol. 253, H184-H193 (1987).
R. E. Austin, G. S. Aldea, D. L. Coggins, A. E. Flynn, and J. I. E. Hoffman, Profound spatial heterogeneity of coronary reserve. Discordance between patterns of resting and maximal myocardial blood flow,Cir. Res. 67, 319–331 (1990).
D. Franzen, R. S. Conway, and H. Zhang, E. H. Sonnenblick, C. Eng, Spatial heterogeneity of local blood flow and metabolic content in dogs hearts,Am. J. Physiol. 254, H344-H353 (1988).
J. B. Bassingthwaighte, R. B. King, and S. A. Roger, Fractal nature of regional myocardial blood flow heterogeneity,Cir. Res. 65, 578–590 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fantidis, P., Stiris, T.A., Blanco, D. et al. Effect of magnesium sulfate administration on subendocardial and subepicardial perfusion. Biol Trace Elem Res 60, 227–234 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784442