Abstract
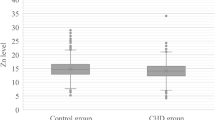
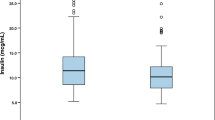
Concentrations of 14 trace elements (Bi, Cd, Co, Cs, Cu, Hg, Mn, Pb, Rb, Sb, Sn, Sr, Tl, and Zn) were determined by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) in 120 whole-blood and 121 plasma samples of 56 patients with angiographically documented coronary heart disease (CHD). One serum and two wholeblood reference materials were analyzed for quality control. At baseline, patients had elevated Co plasma as well as diminished Cu blood concentrations compared to healthy adults. The Zn concentrations in whole blood were below or at the lower end of the normal range, but the concentrations in plasma were elevated. All other trace elements were within the normal concentration ranges for healthy adults. After initial investigations, patients were randomly assigned to an experimental group (N = 27) and to a usual care group (N = 29). Experimental group patients were prescribed a lifestyle program that included a low-fat diet and a weekly moderate exercise. Patients were examined at baseline, after 6 and 12 mo for clinical assessment and fasting venous blood samples. No significant time-course changes in concentrations of trace elements in blood and plasma during the clinical treatment in both groups of patients could be observed. The experimental group patients lost weight and had lower blood pressure after 12 mo compared to baseline. The interventional therapy reduced the need for further revascularization procedures.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. C. Arzenius, D. Kromhout, and J. D. Barth,N. Engl. J. Med. 312, 805–811 (1985).
G. F. Watts, B. Lewis, J. N. H. Brunt, E. S. Lewis, D. J. Coltart, L. D. R. Smith, J. I. Mann, and A. V. Swan,Lancet 339, 563–569 (1992).
R. A. Floyd and J. M. Carney,Toxicol. Ind. Health 9, 197–214 (1993).
J. J. Strain,Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 51, 241–251 (1994).
M. Krachler, S. Habersack-Wallner, M. Lindschinger, and K. J. Irgolic, inMengen- und Spurenelemente, 15. Arbeitstagung 1995, M. Anke et al., eds., Verlag H. Schubert, Leipzig, pp. 109–115 (1995).
M. Krachler and K. J. Irgolic,J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 8, 89 (1995).
H. Vanhoe,J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 7, 131–139 (1993).
M. Krachler, G. Wirnsberger, and K. J. Irgolic,Biol. Trace Element Res. 58, 209–222 (1997).
M. Krachler, H. Radner, and K. J. Irgolic,Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 355, 120–128 (1996).
S. Pucheau, C. Coudray, G. Vanzetto, A. Favier, J. Machecourt, and J. De Leiris,Biol. Trace Element Res. 47, 171–181 (1995).
B. Halliwell,Biochem. J. 205, 461–463 (1982).
B. Halliwell and J. Gutteridge, inMethods in Enzymology, Vol. 186, L. Packer and A Glazer, eds., Academic, San Diego, pp. 1–85 (1990).
J. S. Striffler, M. M. Polanski, and R. A. Anderson,J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 6, 75–81 (1993).
Y. Schechter,Diabetes 39, 1–5 (1990).
J. J. Strain,Proc. Nutr. Soc. 50, 591–604 (1991).
D. J. O’Reilly,J. Endocrinol. 118, 349–351 (1988).
K. A. Woeber,N. Engl. J. Med. 327, 94–98 (1992).
J. K. Friel, C. S. Skinner, S. E. Jackson, and H. P. Longerich,Analyst 115, 269–273 (1990).
M. D. Mingorance, M. L. Perez-Vazquez, and M. Lachica,J. Anal. At. Spedrom. 8, 853–858 (1993).
P. Quevauviller, J. L. Imbert, and M. Olle,Mikrochim. Acta 112, 147–154 (1993).
M. Champell, G. Vermeir, R. Dams, and P. Quevauviller,J. Anal. At. Spedrom. 7, 617–621 (1992).
O. Oster, M. Dahm, H. Oelert, and W. Prellwitz,Clin. Chem. 35, 851–856 (1989).
S. Caroli, A. Alimonti, E. Coni, F. Petrucci, F. Senofonte, and N. Violante,Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 24, 363–398 (1994).
S. N. Khan, M.A. Rahman, and A. Samad,Clin. Chem. 30, 644–688 (1984).
L. M. Klevar,J. Trace Elem. Electrolytes Health Dis. 7, 63–69 (1993).
J. Manthey, M. Stoeppler, W. Morgenstern, E. Missel, D. Opherk, A. Weintraut, H. Wesch, and W. Kubier,Circulation 64, 722–729 (1981).
S. Wallner, M. Lindschinger, N. Watzinger, K. H. Smolle, H. Toplak, T. C. Wascher, I. Elmadfa, W. Klein, and G. J. Kreijs,Ann. Intern. Med., submitted.
D. Ornish, S. H. Brown, L. W. Scherwitz, J. H. Billings, W. T. Armstrong, T. A. Ports, S. M. McLanahan, R. L. Kirkeeide, R. J. Brand, and K. L. Gould,Lancet 336, 129–133 (1990).
M. Krachler, S. Habersack-Wallner, B. Eber, M. Lindschinger, N. Watzinger, and K. J. Irgolic, inMetal Ions in Biology and Medicine, vol. 4, P. Collery, J. Corbella, J. L. Domingo, J.-C. Etienne, J. M. Liobet, eds., John Libbey Eurotext, Paris, pp. 560–562 (1996).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krachler, M., Lindschinger, M., Eber, B. et al. Trace elements in coronary heart disease. Biol Trace Elem Res 60, 175–185 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784438
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02784438