Abstract
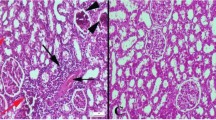
Administration of coenzyme Q10 to humans and animals has a beneficial effect on a number of cardiac diseases. The purpose of the present study was to determine if coenzyme Q10 treatment could ameliorate cardiac abnormalities associated with the carbohydrate × copper interaction in rats. Weanling male rats were provided with a copper-deficient diet (0.6 μg Cu/g) containing either 62.7% starch (S−Cu) or fructose (F−Cu) for 5 wk. Half of the rats provided with the F−Cu diet were given daily oral supplements of 300 mg coenzyme Q10/kg body weight (F−Cu+Q). Heart hypertrophy, liver enlargement, or pancreatic atrophy were not affected by, nor was body growth or anemia improved by, supplementation with coenzyme Q10 when compared to rats fed only the F−Cu diet. Hearts from rats fed the F−Cu diet had severe inflammation, degeneration, fibrosis, and giant mitochondria with abnormal cristae. Hearts from F−Cu+Q rats had similar mitochondrial changes as the F−Cu rat hearts but without any apparent degenerative changes. None of the F−Cu+Q rats, but 30% of the F−Cu rats, died during the study as a result of heart rupture. These observations show that whereas coenzyme Q10 treatment did not prevent the cardiac hypertrophy of the carbohydrate × copper interaction, it did play a role in maintaining the integrity of the heart.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. H. Gallagher,Aust. Vet. J. 33, 311–317 (1957).
D. I. Paynter, R. J. Moir, and E. J. Underwood,J. Nutr. 109, 1570–1576 (1979).
N. Rusinko and J. R. Prohaska,J. Nutr. 115, 936–943 (1985).
R. S. Redman, M. Fields, S. Reiser, and J. C. Smith, Jr.,Atherosclerosis 74, 203–214 (1988).
W. A. Burns, M. Fields, J. C. Smith, Jr., and S. Reiser,J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 3, 67–77 (1990).
D. M. Medeiros, D. Bagby, G. Ovecka, and R. McCormick,J. Nutr. 121, 815–824 (1991).
W. T. Johnson and J. T. Saari,Nutr. Res. 9, 1355–1362 (1989).
P. H. Langsjoen, K. Folkers, K. Lysons, K. Muratsu, T. Lyson and P. Langsjoen,Klin. Wochenschr. 66, 583–590 (1988).
F. Okamoto, B. S. Allen, G. D. Buckberg, J. Leaf, and H. J. Bugyi,Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 92, 573–582. (1986).
T. Yuzuriha, M. Takada, and K. Katazama,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 759, 286–291 (1983).
T. Ozawa,Coenzyme Q: Biochemistry, Bioenergetics and Clinical Applications of Ubiquione, G. Lenaz, ed. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, 1980, pp. 441–456.
R. E. Beyer, K. Nordenbrand, and L. Ernster,Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q, K. Folkers and Y. Yamamura, eds. Elsevier Science Publ. Amsterdam, Holland, 1977, pp. 17–24.
P. H. Langsjoen, K. Folkers, K. Lyson, K. Muratsu, T. Lyson, and P. Langsjoen,Int. J. Tiss. Reac. XII, 163–168 (1990).
American Institute of Nutrition: Report on the AIN ad hoc committee on standards for nutritional studies,J. Nutr. 107, 1340–1348 (1977).
American Institute of Nutrition: Second report of the AIN ad hoc committee on standards for nutritional studies.J. Nutr. 110, 1726 (1980).
C. G. Lewis, M. Fields, and T. Beal,Biol. Trace Ele. Res. 35, 239–246 (1992).
K. H. Schosinsky, H. P. Lehmann, and M. Beeler,Clin. Chem. 20, 1556–1563 (1974).
A. D. Hill, K. Y. Patterson, C. Veillon, and E. R. Morris,Anal. Chem. 58, 2340–2342 (1986).
Perkin-Elmer Inc.Analytical Methods for Atomic Absorption Spectrophotometry, Norwalk, CT. (1976).
SAS Institute Inc.SAS User's Guide: Statistcis, 5th ed., Cary, NG., (1985).
J. Scholler, T. M. Farley, and K. Folkers,Internat. Z. Vit. Forschung 38, 362–368 (1968).
J. R. Prohaska and L. J. Heller,J. Nutr. 112, 2142–2150 (1982).
J. R. Goodman, J. B. Warshaw, and P. R. Dallman,Pediat. Res. 4, 244–256 (1970).
P. R. Dallman and J. R. Goodman,Blood 35, 496–505 (1970).
S. J. Kopp, L. M. Klevay, and J. M. Feliksik,Am. J. Physiol. 245, H855-H866 (1983).
M. Gupta and P. K. Singal,Circ. Res. 64, 398–406 (1989).
W. Bohnenkamp and U. Weser,Biochim. Biophys. Acta 444, 396–406 (1976).
C. G. Taylor, W. J. Bettger, and T. M. Bray,J. Nutr. 118, 613–621 (1988).
C. Guarnieri, C. Muscari, and C. M. Caldarera,Advances in Myocardiology, P. Harris and P. A. Poole-Wilson, eds. vol. 5, Plenum Publishing Co., New York, 1985, pp. 191–199.
P. J. Quinn, H. Baun, E. J. Harris, C. S. Franklin, and P. Trivedi,Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q, vol. 2. Y. Yamamura, K. Folkers, and Y. Ito, eds. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, North-Holland, 1980, pp. 435–446.
W. G. Nayler,Biomedical and Clinical Aspects of Coenzyme Q, vol. 2, Y. Yamamura, K. Folkers, Y. Ito, eds. Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam, North-Holland, 1980, pp. 409–425.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lewis, C.G., Fields, M., Burns, W.A. et al. Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on cardiac hypertrophy of male rats consuming a high-fructose, low-copper diet. Biol Trace Elem Res 37, 137–149 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783789
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783789