Abstract
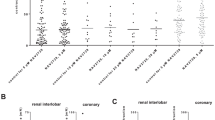
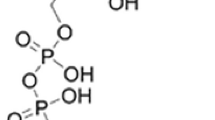
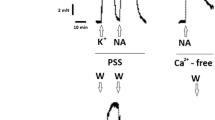
We studied the effects of trace elements, Mn, Mo, and Si, on vasoconstriction induced by norepinephrine (NE) or electrical field stimulation in isolated porcine right coronary arteries. α1-Adrenoceptor (AR) antagonist prazosin dose-despondently suppressed vasoconstriction in response to NE or field stimulation indicating an α1-AR mediated response. Mn, Mo, and Si at 0.3-3 μmol/L dosedespondently inhibited NE mediated contraction (allp < 0.05). In contrast, Mn, Mo, and Si at the same concentrations (0.3-3 μmol/L) enhanced the maximal contractile response to field stimulation in a dose-dependent manner (allp < 0.05), but these elements at 10 μmol/L suppressed the vasoconstrictive response. The results indicate that in porcine right coronary arteries, the α1-AR-mediated vasoconstriction by NE or electrical field stimulation was affected differently by micromolar concentrations of Mn, Mo, and Si and that the elements might facilitate NE release presynaptically but inhibit the contractile response postsynaptically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. Baumgart and G. Heusch, Neuronal control of coronary blood flow,Basic Res. Cardiol. 90, 142–159 (1995).
C. Indolfi, F. Piscione, B. Villari, and E. Russolillo, Identification of an α2-adrenoceptors in normal and atherosclerotic human coronary arteries circulation,Circulation 86, 1116–1124 (1992).
J. P. Hieble, D. B. Bylund, D. E. Clarke, D. C. Eikenberg, S. Z. Langer, R. J. Lefkowitz, K. P. Minneman, and R. R. Ruffolo, Jr., International union of pharmacology X. recommendation for nomenclature of α1-adrenoceptors: consensus update,Pharmacol. Rev. 47, 267–270 (1995).
C. Han and K. P. Minneman, α1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle,Nature 329, 333–335 (1987).
K. P. Minneman, α1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates and sources of cell calcium,Pharmacol. Rev. 40, 87–119 (1988).
D. B. Bylund, D. C. Eikenberg, J. P. Hible, S. Z. Langer, R. J. Lefkowitz, K. P. Minneman, P. B. Molinoff, R. R. Ruffolo, Jr., and U. Trendelenburg, Nomenclature of adrenoceptors.Pharmacol. Rev. 46, 121–136 (1994).
G. M. Berkenboom, M. Abramovi, P. Vandermoten, and S. G. Deger, Role of adrenergic coronary tone in exercise-induced angina pectoris,Am. J. Cardiol. 57, 195–198 (1986).
A. C. Bonham, D. D. Gutterman, J. M. Arthur, M. L. Marcus, Neurogenic regulation of coronary blood flow: evidence for a central nervous system pathway,Circ. Res. 61 (suppl. II), II-42–II-46 (1987).
T. W. Clarkson, Molecular and ionic mimiery of toxic metals,Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 32, 545–571 (1993).
R. S. Goodhart and M. E. Shiles, The biochemical and nutritional roles of trace elements, in:Modern Nutrition in Health and Disease, 1st ed., Henry Kimpton Publishers, London, pp. 428–437 (1978).
B. Thomas and D. B. Clayton, The trace elements, in:Manual of Dietetic Practice, 1st ed.,Blackwell Science Ltd, London, pp. 180–183 (1994).
B. L. Vallee and K. A. Falchuk, The biochemical basis of Zinc physiology,Physiol. Rev. 73, 79–118 (1993).
B. Katz and R. Miledi, The effects of divalent cations on transmission in the squid giant synapse,Publ. Stn. Zool. Napoli. 37, 303–310 (1969).
R. R. Linnas, Calcium and transmitter release in squid synapse,Soc. Neurosci. Symp. 2, 139–160 (1977).
M. Bechern, H. G. Glitsch, and L. Pott, Facilitation of acetylcholine release from cardiac parasympathetic nerve endings. Effect of stimulation pattern and Mn ions,Pfliigers Arch. 391, 105–111 (1981).
P. Drapeau and D. Nachshen, Manganese fluxes and manganese-dependent neurotransmitter release in presynaptic nerve endings isolated from rat brain,J. Physiol. 348, 493–510 (1984).
S. Hagiwara and S. Miyazak, Ca and Na Spikes in egg cell membrane, in:Cellular Neurobiology, 1st ed., Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 147–158 (1977).
C. Edwards, The selectivity of ion channels in nerve and muscle,Neuroscience 7, 1335–1366 (1982).
T. J. Williams and D. E. Clarke, Characterization of mediating vasoconstriction to noradrenaline and nerve stimulation in the isolate perfused mesentery of rat,Br. J. Pharmac. 114, 431–536 (1995).
L. J. Sullivan and A. H. Briggs, Effects of manganese on response of aortic strips to angiotensin and norepinephrine contraction,J. Pharmac. Exp. Ther. 161, 205–209 (1968).
R. Kuribayashi, Effects of Mn and Zn ions contraction of smooth muscle of guinea pig taenia coli,Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 98, 241–247 (1969).
G. A. Collins, M. C. Sutter, and J. C. Teiser, The effects of manganese on the rabbit anterior mesenteric portal vein,Can. J. Physiol. Pharmac.50, 300–309 (1972).
G. B. Weiss and P. Kutsky, Effects of manganese on45Ca mobilization and contractile responses in rabbit aortic smooth muscle,Gen. Pharmacol.16, 97–102 (1985).
R. Inoue, Effects of Cd2+ and other divalent cations on cabachol-activated non-selective cation channels in guinea pig ileum,J. Physiol. 442, 447–463 (1991).
R. K. Murray and M. I. Kotlikoff, Receptor-activated calcium influx in human airway smooth muscle cells,J. Physiol. 435, 123–144 (1991).
Q. Chen and C. Van Breemen, The superficial buffer barrier in venous smooth muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum refilling and unloading,Br. J. Pharmac. 109, 336–343 (1993).
E. Haberman and G. Richardt, Intracellular calcium binding proteins as targets for heavy metal ions,Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 7, 298–300 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, M., Lu, Z., Du, XJ. et al. Effects of micromolar concentrations of Mn, Mo, and Si on α1adrenoceptor-mediated contraction in porcine coronary artery. Biol Trace Elem Res 64, 75–87 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783326