Abstract
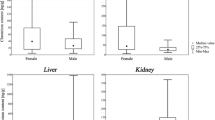
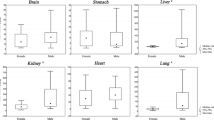
Concentrations of Cu, Mn, Zn, and Cd were measured in 13 different tissues collected at autopsy from 55 New Zealanders, aged 1 week to 74 years. All analyses were done by atomic absorption spectrophotometry. In general, concentrations of Mn and Zn were similar to those reported elsewhere but Cu levels were slightly lower. Concentrations of Cd were low in all tissues except kidney. Median values were in accordance with those reported for other “unexposed” populations. A significant trend of increasing concentrations with age was found for Cu in cartilage, Zn in kidney cortex and medulla, and Cd in all tissues except bone, fat, and hair. Declines with age were observed for Cu in liver, aorta, and skeletal muscle, for Mn in heart, aorta, and cartilage and for Zn in lung and muscle. There were no obvious relationships between tissue trace element levels and cause of death assigned according to three groups: sudden accidental, cardiovascular, or respiratory.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
H. Gautier du Défaix, R. Puente, B. Vidal, E. Pérez, and H. Vidal,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33, 133 (1980).
International Atomic Energy Agency,Trace Elements in Relation to Cardiovascular Diseases, Technical Report No. 157, IAEA, Vienna, 1973.
E. Vuori, A. Huunan-Seppälä, and J. O. Kilpiö,Scand. J. Work Environ. Hlth. 4, 167 (1978).
C. A. Johnson,Anal. Chim. Acta 81, 69 (1976).
N. E. Kowal, D. E. Johnson, D. F. Kraemer, and H. R. Pahren,J. Toxicol. Environ. Hlth. 5, 995 (1979).
E. B. Davies,J. N. Z. Instit. Chem. 30, 32 (1966).
C. D. Thomson and M. F. Robinson,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 33, 303 (1980).
J. M. McKenzie,N. Z. Med. J. 79, 1016 (1974).
J. M. McKenzie,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 31, 470 (1978).
G. V. Iyengar, W. E. Kollmer, and H. J. M. Bowen,The Elemental Composition of Human Tissues and Body Fluids, Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, 1978.
H. A. Schroeder, A. P. Nason, I. H. Tipton, and J. J. BalassaJ. Chron. Dis. 19, 1007 (1966).
I. H. Tipton and M. J. Cook,Health Phys. 9, 103 (1963).
R. A. Schor, S. G. Prussin, D. L. Jewett, J. J. Ludowieg, and R. S. Bhatnagar,Clin. Orthopaed. Related Res. 93, 346 (1973).
H. A. Schroeder, J. J. Balassa, and I. H. Tipton,J. Chron. Dis. 19, 545 (1966).
A. Forssen,Ann. Med. Exp. Biol. Fenn. 50, 99 (1972).
G. Brückmann and S. G. Zondek,Biochem. J. 33, 1845 (1939).
H. A. Schroeder, A. P. Nason, I. H. Tipton, and J. J. Balassa,J. Chron. Dis. 20, 179 (1967).
T. L. M. Syverson, T. K. Stray, G. B. Syverson, and J. Olfstad,Scand J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 36, 251 (1976).
J. M. Janes, J. T. McCall, and L. R. Elveback,Mayo Clin. Proc. 77, 476 (1972).
E. Vuori, A. Huunan-Seppälä, J. O. Kilpiö, and S. S. Salmela,Scand. J. Work Environ. Hlth. 5, 16 (1979).
C.-G. Elinder, T. Kjellström, L. Friberg, B. Lind, and L. Linnman,Arch. Environ. Hlth. 31, 292 (1976).
L. Pickston,N. Z. Med. J. 93, 10 (1981).
K. S. Mason,J. Nutr. 109, 1979 (1979).
R. Masironi,Bull. World Hlth. Org. 40, 305 (1969).
P. O. Wester,Atherosclerosis 13, 395 (1971).
N. W. Solomons,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 32, 856 (1979).
I. D. Capel, M. H. Pinnock, H. M. Dorrell, D. C. Williams, and E. C. G. Grant,Clin. Chem. 27, 879 (1981).
R. A. Jacob, L. M. Klevay, and G. M. Logan,Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 31, 477 (1978).
J. M. McKenzie,Am. J. Clin. Nutr.,32, 570 (1979).
E. J. Underwood,Trace Elements in Human and Animal Nutrition, 4th ed., Academic Press, New York, 1977.
B. E. Guthrie and M. F. Robinson,N. Z. Med. J. 87, 3 (1978).
B. E. Guthrie,N. Z. Med. J. 82, 418 (1975).
J. A. Halsted, J. C. Smith, and M. I. Irwin,J. Nutr. 104, 345 (1974).
M. Piscator and B. Lind,Arch. Environ. Hlth. 24, 426 (1972).
G. P. Lewis, W. J. Jusko, L. L. Coughlin, and S. Hartz,Lancet i, 291 (1972).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casey, C.E., Guthrie, B.E. & Robinson, M.F. Copper, manganese, zinc, and cadmium in tissues from New Zealanders. Biol Trace Elem Res 4, 105–115 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783251
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02783251