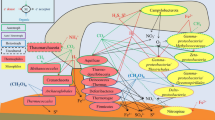
Abstract
Authigenic carbonates in the caldera of an Arctic (72°N) submarine mud volcano with active CH4bearing fluid discharge are formed at the bottom surface during anaerobic microbial methane oxidation. The microbial community consists of specific methane-producing bacteria, which act as methanetrophic ones in conditions of excess methane, and sulfate reducers developing on hydrogen, which is an intermediate product of microbial CH4 oxidation. Isotopically light carbon (δ13Cav =−28.9%0) of carbon dioxide produced during CH4 oxidation is the main carbonate carbon source. Heavy oxygen isotope ratio (δ18Oav = 5%0) in carbonates is inherited from seawater sulfate. A rapid sulfate reduction (up to 12 mg S dm−3 day−1) results in total exhausting of sulfate ion in the upper sediment layer (10 cm). Because of this, carbonates can only be formed in surface sediments near the water-bottom interface. Authigenic carbonates occurring within sediments occur do notin situ. Salinity, as well as CO 2−3 /Ca and Mg/Ca ratios, correspond to the field of nonmagnesian calcium carbonate precipitation. Calcite is the dominant carbonate mineral in the methane seep caldera, where it occurs in the paragenetic association with barite. The radiocarbon age of carbonates is about 10000 yr.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aharon, P., Schwares, H.P., and Roberts, H.H., Radiometric Dating of Hydrocarbon Seeps in the Gulf of Mexico,Bull. Geol. Soc. Am., 1997, vol. 109, pp. 586–579.
Alperin, M.J., Blair, D.B., Albert, T.M.,et al., Factors That Control the Carbon Isotopic Composition of Methane Produced in an Anoxic Marine Sediment,Global Biogeochem. Cycles, 1992, vol. 6, pp. 271–291.
Bogdanov, Yu.A., Sagalevich, A.M., Vogt, P.R.,et al., Haakon Mosbi Mud Volcano in the Norwegian Sea: Results of Complex Studies from Deep-Water Manned Submersibles,Okeanologiya (Moscow), 1999, vol. 39, no. 3, pp. 412–419.
Carson, B., Seke, E., and Pashkevich, V, and Wolmest, M.L., Fluid Expulsion Sites on the Cascadia Accretionary Prism: Mapping Direct Diagenetic Deposits with Processed GLO-RIA,J. Geophys. Res., 1994, vol. 99, no. 11, pp. 959–969.
Chilingar, G., Bissei, H, and Wulf, K., Diagenesis and Catagenesis of Carbonate Rocks,Diagenesis in Sediments, Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1967. Translated under the titleDiagenez i katagenez osadochnykh obrazovanii, Moscow: Mir, 1971, pp. 165–290.
Esikov, A.D. and Pashkina, V.I., Study of the Process of Simultaneous Formation of Methane Gas Hydrate and Authigenic Carbonates in Bottom Sediments of the Sea of Okhotsk,Vodnye Resursy, 1990, no. 6, pp. 171–176.
Esikov, A.D.,Mass-spektrometricheskii analiz prirodnykh vod (Mass Spectrometry Analysis of Natural Waters), Moscow: Nauka, 1980.
Ginsburg, G.D. and Solov’ev, V.A.,Submarinnye gazovye gidraty (Submarine Gas Hydrates), St. Petersburg: Nedra, 1994.
Hoehler, T.M., Alperin, M.J., Albert, D.B.,et al., Field and Laboratory Studies of Methane Oxidation in an Anoxic Marine Sediments: Evidence for a Methanogen-Sulfate Reducer Consorcium,Global Geochem. Cycles, 1994, vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 451–463.
Ivanov, M.V.,Rol’ mikroorganizmov vobrazovanii i razrushenii samorodnoi sery (Role of Microorganisms in the Formation and Destruction of Native Sulfur), Moscow: Nauka, 1964.
Ivanov, M.V., Polikarpov, G.G., Lein, A.Yu.,et al., Biogeochemistry of Sulfur Cycle in the Methane Gas Emanation Region of the Black Sea,Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR, 1991, vol. 320, no. 5, pp. 1235–1238.
Katalog standartnykh obraztsov sostava mineral’nogo syr’ya. NSAM (Catalog of Standard Samples of Mineral Raw Material. NSAM), Moscow: VIMS, 1988, p. 118.
Kholodov, V.N.,Postsedimentatsionnye preobrazovaniya v elizionnykh basseinakh: na primere Vostochnogo Predkavkaz’ya (Postsedimentary Transformations in Elisional Basins: Evidence from the Eastern Ciscaucasus), Moscow: Nauka, 1983, p. 150.
Kholodov, V.N., Role of Sand Diapirism in the Interpretation of Mud Volcano Genesis,Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1987, no. 4, pp. 3–11.
Kholodov, V.N., Problem of the Genesis of Minerals in Elisional Depressions: Communication 2. Cheleken-Boyadag Hydrothermal System,Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1991, no. 2, pp. 104–123.
Kholodov, V.N., Kuleshov, V.N., and Nedumov, R.I., Catagenetic Transformations and Isotopic Composition of Carbonates in Tertiary Sediments: Evidence from Kuban Superdeep Boreholes (SAS-1 and SAS-2),Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1999, no. 1, pp. 46–57.
Lazarenko, E.K.,Kurs mineralogii (Course of Mineralogy), Moscow: Vysshaya Shkola, 1971.
Le Pichon, X., Foucher, J.P., and Bouleque, J.,et al., Mud Volcano Field Seaward of the Barbados Accretionary Comlex: A Submersible Survey,J. Geoph. Res., 1990, vol. 95, pp. 8931–8943.
Lein, A.Yu., Logvinenko, N.V., Sulerzhitsskii, L.D., and Volkov, I.I., Source of Carbon and Age of Diagenetic Carbonate Concretions in the Gulf of California,Litol. Polezn. Iskop., 1979, no. 1, pp. 23–35.
Lein, A.Yu., Gal’chenko, V.F., and Pokrovskii, B.G., Marine Carbonate Concretions As a Result of Microbial Oxidation of Gas-Hydrate Methane in the Sea of Okhotsk,Geokhimiya, 1989, no. 10, pp. 1396–1406.
Lein, A.Yu., Vogt, P.R., Krein, K.,et al, Geochemical Features of CH4-Bearing Sediments from Underwater Mud Volcano in the Norwegian Sea,Geokhimiya, 1998, no. 3, pp. 230–249.
Lein, A.Yu., Pimenov, N.V., Savvichev, A.S.,et al., Methane As a Source of Organic Matter and Carbon Dioxide in Carbonates from Cold Seeps of the Norwegian Sea,Geokhimiya, 2000, no. 3, pp. 268–281.
Minert, J. and Posewang, J., Flach und Tiefwassergashydrate in Sediments Polares Kontinental-Rander des Nordatlantiks, Geophysikalicshe Signaturen des Instabilitat,Geowissenschatten, 1997, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 287–291.
Nechiporenko, G.O. and Bondarenko, G.P.,Usloviya obrazovaniya morskikh karbonatov (Formation Conditions of Marine Carbonates), Moscow: Nauka, 1988.
Pimenov, N.V., Savichev, A.S., and Rusanov, I.I., Microbial Processes of the Carbon Cycle at the Base of the Food Chain of the Haakon Mosbi Mud Vulcano Benthic Community,EOS, 1997, vol. 29, OS41A11.
Reeburg, W.S., Anaerobic Methane Oxidation: Rate Depth Distributions in Skan Bay Sediments,Earth Planet. Sci. Lett., 1980, vol. 47, pp. 345–352.
Reeburg, W.S. and Alperin, M.J., Stages of Anaerobic Methane Oxidation,Transport of Carbon and Minerals in Major World Rivers, Lakes, and Estuaries, Degens, E.T.et al., Eds., Hamburg, 1988, part 5.
Shishkina, O.V.,Geokhimiya morskikh i okeanicheskikh ilovykh vod (Geochemistry of Marine and Oceanic Mud Waters), Moscow: Nauka, 1972.
Suess, E., Bohrmann, G., Linke, P.,et al., Gas Hydrates and Fluid Venting from the Cascadia Accreationary Margin,EOS Transactions of the American Geophysical Union Supplement, 1998, vol. 77, pp. 321–323.
Taft, W.H., Physical Chemistry of Carbonate Formation,Development in Sedimentology 9B. Carbonate Rocks. Physical and Chemical Aspects, Chilingar, G., Bissei, H., and Fairbridge R., Eds., Amsterdam: Elsevier, 1967. Translated under the titleKarbonatnye porody, Moscow: Mir, 1971, pp. 112–123.
Vogt, P.R., Cherkashev, G.A., Ginsburg, G.D.,et al., Haakon Mosbi Mud Vulkano: A Warm Methane Seep with Seafloor Hydrates and Chemosynthesis Based Ecosystem in Late Quaternary Slide Valley, Bear Island Fan, Barents Sea Passive Margin,EOS, 1997, vol. 78, no. 48, pp. 556–557.
Von Rad, U., Rosch, H., and Berner, H.,et al., Authigenic Carbonates Derived from Oxidized Methane Vented from the Makran Accretionary Prism of Pakistan,Mar. Geol., 1996, vol. 136, pp. 55–77.
Zehnder, A.J.B. and Brock, T.D., Methane Formation and Methane Oxidation by Methanogenic Bacteria,J. Bacteriol, 1979, no. 39, pp. 420–432.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lein, A.Y., Gorshkov, A.I., Pimenov, N.V. et al. Authigenic carbonates in methane seeps from the Norwegian sea: Mineralogy, geochemistry, and genesis. Lithol Miner Resour 35, 295–310 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782686
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782686