Abstract
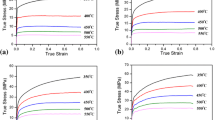
An experimental study of the constitutive response of the oxide dispersion-strengthened (ODS) superalloy MA 956, which consists of an Fe-Cr-Al matrix dispersion strengthened with yttria, has been performed.Single-crystal specimens of MA 956 having remarkably simple initial microstructures have been tested in compression in the temperature range of 900 °C to 1200 °C and in the axial strain-rate range of 1.8 x 10-4 s-1 to 10-2 s-1. The deformation response of the material has been examined by performing constant true strain-rate tests, strain-rate jump tests, and stress relaxation tests. The orientation dependence of the stress-strain response of the single crystals has been compensated for by determining the operative slip systems and resolving the stresses and strains accordingly. These experiments, together with electron-microscopic observations of deformed and quenched specimens, allow a number of conclusions to be drawn about the physics of particle strengthening in this simple ODS alloy at high temperatures. Further, drawing on this physical understanding, a set of phenomenological internal variable constitutive equations which model the high-temperature deformation behavior of this alloy is also developed. These equations reasonably well model not only the temperature and strain-rate sensitivity of the flow stress but also the strain-hardening behavior of the material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L.M. Brown and R.K. Ham:Strengthening Methods in Crystals, A. Kelly and R.B. Nicholson, eds., Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1971, p. 9.
R.S.W. Shewfelt and L.M. Brown:Phil. Mag., 1977, vol. 35, pp. 945–62.
R.W. Lund and W.D. Nix:Acta Metall., 1976, vol. 24, pp. 469–81.
J.H. Hausselt and W.D. Nix:Acta Metall., 1977, vol. 25, pp. 1491–1502.
J.D. Whittenberger:Metall. Trans. A, 1979, vol. 10A, pp. 1285–95.
J.D. Whittenberger:Metall. Trans. A, 1981, vol. 12A, pp. 845–51.
J.D. Whittenberger:Metall. Trans. A, 1984, vol. 15A, pp. 1753–62.
T.E. Howson, J.E. Stulga, and J.K. Tien:Metall. Trans. A, 1980, vol. 11A, pp. 1599–1607.
A.H. Cooper, V.C. Nardone, and J.K. Tien:Superalloys 1984: Proc. 5th Int. Conf. on Superalloys, TMS-AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1984, p. 357.
D.J. Srolovitz, R. Petkovic-Luton, and M.J. Luton:Scripta Metall., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 1401–06.
S.M. Allen:Phil. Mag. A, 1981, vol. 43 (2), pp. 325–35.
M. Haghi: M.S. Thesis, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, MA, 1986.
L. Anand:J. Eng. Mater. Technol., 1982, vol. 104, pp. 12–17.
S.B. Brown, K.H. Kim, and L. Anand:Int. J. Plas., 1989, vol. 5, pp. 95–130.
E.E. Underwood:Quantitative Stereology, Addison-Wesley Publishing Company, Reading, MA, 1970, pp. 172–78.
E. Artz and M.F. Ashby:Scripta Metall., 1982, vol. 16, pp. 1285–90.
D.J. Srolovitz, M.J. Luton, R. Petkovic-Luton, D.M. Barnett, and W.D. Nix:Acta Metall., 1984, vol. 32, pp. 1079–88.
J.H. Schröder and E. Artz:Scripta Metall., 1985, vol. 19, pp. 1129–34.
E. Artz and D.S. Wilkinson:Acta Metall., 1986, vol. 34, pp. 1893–98.
P.B. Hirsch and F.J. Humphreys:Physics of Strength and Plas ticity, A.S. Argon, ed., MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1969, pp. 189–216.
J.P. Hirth and J. Lothe:Theory of Dislocations, John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York, NY, 1982, p. 263.
M.F. Ashby:Physics of Strength and Plasticity, A.S. Argon, ed., MIT Press, Cambridge, MA, 1969, pp. 113–31.
J.W. Martin:Micromechanisms in Particle Hardened Alloys, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1980, p. 44.
H.J. Frost and M.F. Ashby:Deformation-Mechanism Maps: the Plasticity and Creep of Metals and Ceramics, Pergamon Press, 1982.
W.R. Manning and O. Hunter:J. Am. Chem. Soc., 1969, vol. 52, pp. 492–96.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haghi, M., Anand, L. High-temperature deformation mechanisms and constitutive equations for the oxide dispersion-strengthened superalloy MA 956. Metall Trans A 21, 353–364 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782415
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02782415