Summary
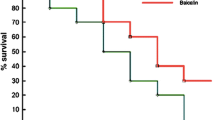
When heat-killedPropionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) and a small amount of endotoxin lipopolysaccharide (LPS) were intravenously injected into mice at a week’s interval, most of them died of massive hepatic cell necrosis. This experimentally-induced acute liver injury was significantly inhibited by cyclosporin A (CsA), resulting in a remarkable improvement of the survival rate. This protective effect of CsA on acute liver injury was also histopathologically confirmed. To study the mechanism by which CsA protected the mice from fatal hepatic injury, adherent cells prepared from the murine liver 7 days afterP. acnes injection were incubated with LPS in the presence of CsA, and the effect of CsA on the production of the cytotoxic factor from the adherent cells was estimated. As a result, CsA inhibited the activation of liver adherent cells and suppressed the release of the cytotoxic factor.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tsutsui H, Mizoguchi Y, Yamamoto S, et al: Studies on experimentally-induced acute hepatic failure: Possible involvement of activated liver adherent cells, in “Cells of the hepatic sinusoid” vol. 1 by Kirn A, et al, The Kupffer Cell Foundation, Netherlands. 1986; 307–314
Tsutsui H, Miyajima K, Mizoguchi Y, et al: Studies on experimentally-induced acute hepatic failure in mice. Characteristics of the hepatocytotoxic factors released from the activated liver adherent cells. Jpn J Gastroenterol 1986; 83: 1161–1167 (Jpn)
Mochizuki M: Effects of cyclosporin on the efferent limb of the immune response. Transplantation 1983; 35: 148
Bunjes D, Hatdt C, Solbach W, et al: Studies on the mechanism of action of Cyclosporin A in the murine and human T-cell response in vitro, in “Cyclosporin A” by White DJG, Elsevier Biomedical Press, Amsterdam. 1982; 261–280
Drath DB, Kahan BD: Alterations in rat pulmonary macrophages function by the immunosuppressive agents cyclosporin, azathioprine and prednisolone. Transplantation 1983; 35: 588–592
Bellemann P, Gebhardt R, Mecke D, et al: An improved method for the isolation of hepatocytes from liver slices. Anal Biochem 1977; 81: 408–415
Ferluga J, Allison AC: Role of mononuclear infiltrating cells in pathogenesis of hepatitis. Lancet 1978; II:610–611
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mizoguchi, Y., Kuboi, H., Kodama, C. et al. The protective effect of cyclosporin a on experimentally-induced acute hepatic injury in mice. Gastroenterol Jpn 22, 743–747 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02776748
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02776748