Summary
Evidence is present that plasma contains non-specific factors which interfere with the 30K glucagon assays. A correction can be made for these interference factors because the factors can be quantitated following absorption of glucagon with charcoal-dextran. Using a correction factor the range of fasting plasma immunoreactive glucagon (IRG) in 12 totally pancreatectomized patients was below detectable limit.
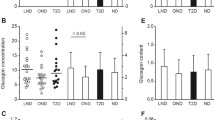
Fasting levels of IRG were determined on the plasma from 25 liver cirrhotics complicated by abnormal GTT, 13 pancreatic diabetics with chronic calcified pancreatitis (CCP), 25 adult-onset primary diabetics and 25 healthy subjects. When all samples were measured using no correction factor, the mean levels of IRG were 358 ± 24 (mean ± SE), 170 ± 26, 178 ± 16 and 178 ± 7 pg/ml, respectively. Using a correction factor the mean levels of IRG were 177 ± 26, 16 ± 4, 39 ± 9 and 20 ± 4 pg/ml, respectively. The mean values of the interference factor were not significantly different among all five groups. During an arginine infusion the interference factor remained unchanged despite an increase in IRG.
It is available but not always necessary to apply a correction factor for 30K glucagon radioimmunoassay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Eisentraut A, et al: Immunologic discrimination between pancreatic glucagon and enteric glucagon-like immunoreactivity (GLI) in tissues and plasma. Diabetes 17 (Suppl 1): 321, 1968
Heding LG: Radioimmunological determination of pancreatic and gut glucagon in plasma. Diabetologia 7: 10, 1971
Faloona GR: The structure-function relationships of pancreatic glucagon, in “Glucagon”, by Lefebvre PJ, Unger RH. Pergamon Press Inc. Elmsford, New York, 1972, p 201
Krause U, et al: Glucagon secretion in four duodenopancreatectomized patients after arginine and glucose load. Horm Metab Res 12: 364, 1980
Boden G, et al: Glucagon deficiency and hyperaminoacidemia after total pancreatectomy. J Clin Invest 65: 706, 1980
Muller WA, et al: Studies of glucagon secretion in pancreatectomized patients. Diabetes 23: 512, 1974
Weir GC, et al: Glucagon radioimmunoassay using antiserum 30K: Interference by plasma. Horm Metab Res 5: 241, 1973
Valverde I, et al: Presence of glucagon immunoreactivity in the globulin fraction of human plasma (“Big plasma glucagon”). J Clin Endocrinol Metab 39: 1090, 1974
Unger RH, et al: Glucagon antibodies and their use for immunoassay for giucagon. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 102: 621, 1959
Muller WA, et al: Glucagon immunoreactivities and amino acid profile in plasma of duodenÒpancreatectomized patients. J Clin Invest 63: 820. 1979
Hayakawa T, et al: Plasma pancreatic glucagon and insulin responses to oral glucose load in chronic pancreatitis. Jpn J Gastroenterol 74: 130, 1977
Marco J, et al: Elevated plasma glucagon levels in cir rhosis of the liver. N Engl J Med 289: 1107, 1973
Sherwin RS, et al: Hyperglucagonemia in cirrhosis: Altered secretion and sensitivity to glucagon. Gastroenterology 74: 1224, 1978
Okumura N, et al: Pancreatic endocrine function in chronic liver diseases: Plasma insulin, C-peptide and glucagon responses to intravenous administration of arginine. Acta Hepatologica Jpn 22: 837, 1981
Valverde I, et al: Heterogeneity of plasma immunoreactive glucagon. Metabolism 25 (Suppl 1): 1393, 1976
Shurberg JL, et al: Serum lipids, insulin and glucagon after portacaval shunt in cirrhosis. Gastroenterology 72:301, 1977
Okumura N, et al: Plasma insulin, C-peptide and pancreatic glucagon responses to oral glucose load in chronic liver diseases. Jpn J Gastroenterol 79: 38, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This study was supported by a research grant of Intractable Pancreatic Disease from the Intractable Division, Public Health Bureau, Ministry of Health and Welfare, Japan.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okumura, N., Hayakawa, T., Yasui, K. et al. Plasma pancreatic glucagon in pancreatic and primary diabetes, and liver cirrhosis: Application of a correction to the radioimmunoassay for pancreatic glucagon. Gastroenterol Jpn 17, 347–352 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774581
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774581