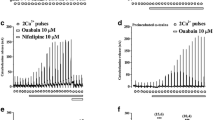
Summary
To solve many problems in other in-vitro methods such as perfusion and static incubation, perifusion of isolated rat pancreatic acini was established. Continuous stimulation by carbamylcholine induced a biphasec secretory response, a sharp initial phase and a slow-varying second phase. The junction of these two phases occurred at almost the same time (in about 7 min of stimulation) at any concentration of carbamylcholine. The slow-rising former part of a second phase indicated that a biphasic pattern is produced by overlapping of two kinds of real phases and the beginning of a real second phase occurs at the time of the junction. The concentration dependence of amylase release showed a bell-shaped pattern and the maximal amylase release at an optimal concentration (10-6M) was 5.43±0.24% total/30 min. The sustained latter part of a second phase showed a slow decline at optimal or less concentrations but a plateau at supraoptimal concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Amsterdam A, Jamieson JD: Structural and functional characterization of isolated pancreatic exocrine cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci US 1972;69:3028–3032
Amsterdam A, Jamieson JD: Studies on dispersed pancreatic exocrine cells. I. Functional characteristics of separated cells. J Cell Biol 1974;63:1057–1073
Williams JA, Korc M, Dormer RL: Action of secretagogues on a new preparation of functionally intact, isolated pancreatic acini. Am J Physiol 1978;235:E517-E524
Peikin SR, Rottman AJ, Batzri S, et al: Kinetics of amylase release by dispersed acini prepared from guinea pig pancreas. Am J Physiol 1978;235:E743-E749
Saito A, Williams JA, Kanno T: Potentiation of cholecystokinin-induced exocrine secretion by both exogenous and endogenous insulin in isolated and perfused rat pancreata. J Clin Invest 1980;65:777–782
Petersen OH, Ueda N: Secretion of fluid and amylase in the perfused rat pancreas. J Physiol 1977;264:819–835
Kanno T, Shibya I, Asada N: The role of extracellular calcium and other ions in the secretory responses of the exocrine pancreas to cholecysotkinin. Biomedical Res 1983;4:295–302
Lacy PE, Walker MM, Fink CJ: Perifusion of siolated rat islets in vitro. Participation of the microtublar system in the biphasic release of insulin. Diabetes 1972;21:987–998
Lowry PJ: A sensitive methods for the detection of corticotrophin releasing factor using a perfused pituitary cell column. J Endocrinol 1974;62:163–164
Yeo T, Thorner MO, Jones A, et al: The effects of dopamin, bromocriptine, lergotrile, and metoclopramide on prolactin release from continuously perfused columns of isolated rat pituitary cells. Clin Endocrinol 1979;10:123–130
Foster R, Rasmussen H: Angiotensin-mediated calcium efflux from adrenal glomerulosa cells. Am J Physiol 1983;245:E281-E287
Uchikawa T, Borle AB: Studies of calcium-45 desaturation from kidney slices in flow through chambers. Am J Physiol 1978;234:R34-R38
Ceska M, Birath K, Brown B: A new rapid method for the clinical determination of alpha-amylase activities in human serum and urine. Optimal conditians. Clin Chim Acta 1969;26:437–444
Ceska M, Brown B, Birath K: Ranges of alpha-amylase activities in human serum and urine and correlations with some other alpha-amylase methods. Clin Chim Acta 1969;26:445–453
Scheele G, Tartakoff A: Exit of nonglycosylated secretory proteins from the rough endoplasmic reticulum is asynchronous in the exocrine pancreas. J Biol Chem 1985;260:926–931
Kojima I, Lippes H, Kojima K, et al: Aldosteron secretion: effects of A23187 and phorbol ester. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1983;116:555–562
Delbeke D, Kojima I, Dannies PS, et al: Synergistic stimulation of prolactin release by phorbol ester, A23187 and forskolin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1984;123:735–741
Gorelick FS, Cohn JA, Freedman SD, et al: Calmodulinstimulated protein kinase activity from rat pancreas. J Cell Biol 1983;97:1294–1295
Burnham DB, Williams JA: Activation of protein kinase activity in pancreatic acini by calcium and cAMP. Am J Physiol 1984;246:G500-G508
Williams JA: An in vitro evaluation of cholinergic and adrenergic receptors affecting pancreatic amylase secretion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 1975;150:513–516
Kanno T: The electrogenic sodium pump in the hyperpolarizing and secretory effects of pancreozymin in the pancreatic acinal cell. J Physiol 1975;245:599–616
D’Doherty J, Stark RJ: Stimulation of pancreatic acinar secretion: increase in cytosolic calcium and sodium. Am J Pysiol 1982;242:G513-G521
Savion N, Selinger Z: Inhibition of enzyme secretion and autophagy of secretory granules caused by action of high concentration of secretory hormones on rat pancreatic slices. Meth Cell Biol 1981;23:359–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagai, M., Oka, H. Perifusion of isolated rat pancreatic acini: Carbamylcholine-induced biphasic amylase release. Gastroenterol Jpn 24, 393–397 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774345
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774345