Summary
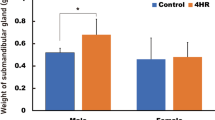
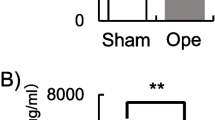
The effect of salivary epidermal growth factor (EGF) on the growth and metabolism of gastrointestinal mucosa was examined by comparing DNA synthesis, DNA and RNA content, and weight of mucosa of salivarectomized and sham operated male rats. DNA synthesis of gastric mucosa was suppressed at 2 days after salivarectomy. Both weight and DNA content of oxyntic mucosa in the salivarectomized group were significantly lower than that of the sham operated group. Although salivarectomy suppressed DNA synthesis of jejunal mucosa, the difference was not significant statistically. The effect of salivarectomy on colonic mucosa was least in the gastrointestinal tract. Such a result suggested that the gradient-oriented antitrophic effect was brought about by salivarectomy. Urinary EGF excretion after salivarectomy was examined by radioreceptor assay. Although the antitrophic effect of salivarectomy on oxyntic mucosa was highest on day 2, no significant difference of urinary EGF concentration was detected on day 2. From these results it is suggested that the effect of salivarectomy on the gastrointestinal tract was not due to the change of EGF in systemic circulation but due to the change of luminal EGF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen S, Taylor JM: Epidermal growth factor: chemical and biological characterization. Recent Prog Horm Res 1974;30: 533–550
Cohen S, Savage CR: Part II Recent studies on the chemistry and biology of epidermal growth factor. Recent Prog Horm Res 1974;30:551–574
Scheving LA, Yeh Y, Tsai T, et al: Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the tongue, esophagus and stomach of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology 1979;105:1475–1480
Scheving LA, Yeh Y. Tsai T, et al: Circadian phase-dependent stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, colon and rectum of the adult male mouse. Endocrinology 1980;106:1498–1503
Al Nafussi Al, Wright NA: The effect of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on cell proliferation of the gastrointestinal mucosa in rodents. Virchows Arch B 1982;40;63–69
Chabot JG, Payet N, Hugon JS: Effects of epidermal growth factor (EGF) on adult mouse small intestine in vivo and in organ culture. Comp Biochem Physiol 1983;74A:247–252
Johnson LR, Guthrie PD: Stimulation of rat oxyntic gland mucosal growth by epidermal growth factor. Am J Physiol 1980;238:G45-G48
Cohen S: Isolation of a mouse submaxillary gland protein accelerating incisor eruption and eyelid opening in the new-born animal. J Biol Chem 1962;237:1555–1562
Heitz PU, Kasper M, Van Noorden S, et al: Immunohistochemical localization of urogastrone to human duodenal and submandibular gland. Gut 1978;19:408–413
O’Keefe E, Hollenberg MD, Cuatrecasas P: Epidermal growth factor; Characteristics of specific binding in membrane from liver, placenta, and other target tissues. Arch Biochem Biophys 1974;164:518–526
O’Loughlin EV, Chung M, Hayden J, et al: Effect of epidermal growth factor on ontogeny of the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol 1985;248:G674-G678
Thornburg W, Matrisian LM, Magun BE, et al: Gastrointestinal absorption of epidermal growth factor in suckling rats. Am J Physiol 1984;246:G80-G85
Thornburg W, Rao Rk, Matrisian LM, et al: Effect of maturation on gastrointestinal absorption of epidermal growth factor in rat. Am J Physiol 1987;253:G68-G71
Dembinski A, Gregory H, Konturek SJ, et al: Trophic action of epidermal growth factor on the pancreas and gastroduodenal mucosa in rats. J Physiol 1982;325:35–42
Li AK, Shattenkerk ME, Hoffman RG, et al: Hypersecretion of submandibular saliva in male mice: Trophic response in small intestine. Gastroenterology 1983;84:949–955
Burton H: A Study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribouncleotic acid. Biochem J 1956;62:315–323
Giles KW, Meyers A: An improved diphenylamine method for the estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Nature 1975;206: 93
Olsen PS, Poulsen PK, Kirkegaard P, et al: Role of submandibular saliva and epidermal growth factor in gastric cytoprotection. Gastroenterology 1984;87;103–108
Skinner KA, Tepperman BL: Influence of desalivation on acid secretory output and gastric mucosal integrity in the rat. Gastroenterology 1981;81:335–339
Goodlad RA, Wilson TJG, Lenton W, et al: Intravenous but not intragastric urogastrone-EGF is trophic to the intestine of parenterally fed rats. Gut 1987;28:573–582
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamaguchi, T., Takahashi, T. Effect of salivarectomy on the growth of gastrointestinal mucosa and urinary secretion of epidermal growth factor in rats. Gastroenterol Jpn 24, 626–631 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774160
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02774160