Summary
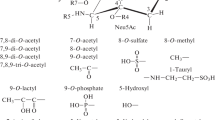
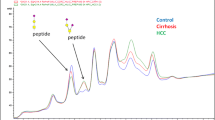
The level of serum orosomucoid, the amount of sialic acid binding to it, and the binding rate of sialic acid to orosomucoid in normal individuals and in patients with chronic hepatitis and liver cirrhosis were determined by affinity column chromatography, SDS electrophoresis and the method of Warren. Although no apparent changes in the level of serum orosomucoid or the amount of sialic acid binding to it in each group were seen, the binding rate of sialic acid to orosomucoid in chronic persistent hepatitis and chronic active hepatitis showed a remarkable increase, compared with normal individuals and patients with liver cirrhosis. Furthermore, the binding rate of sialic acid in liver cirrhosis was the lowest in each group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kawahara K, et al: The effect of the sialyl residues on the thermodynamic and hydrodynamic properties of α1-acid glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1973, 295: 505
Li YT, et al: Isolation and characterization of α1-acid glycoprotein from chimpanzee plasma. J Biol Chem 1970, 245: 825
Sarcione EJ: Synthesis of α1-acid glycoprotein by the isolated perfused rat liver. Arch Biochem Biophys 1963, 100: 516
Athineos E, et al: Biosynthesis of glycoproteins. The site of glucosamine incorporation into conine plasma α1-acid glycoprotein. Arch Biochem Biophys 1964, 106: 338
Warren R, et al: Turnover of the surface proteins and the receptor for serum asialoglycoproteins in primary cultures of rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 1981, 256: 1346
Howard DJ, et al: Asialoglycoprotein receptors in hepatic regeneration. J Biol Chem 1982, 257: 2856
Oka JA, et al: Microtubule-depolymerizing agents inhibit asialo-orosomucoid delivery to lysosomes but not its endocytosis or degradation in isolated rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1983, 763: 368
Bollet AJ: Plasma glycoproteins. Mucoproteins and mucopolysaccharides. Arch Inst Med 1959, 104: 152
Denko CW, et al: Serum proteins-transferrin, ceruloplasmin, albumin, α1-acid glycoprotein, α1-antitrypsin-in rheumatic disorder. J Rheumatol 1979, 6: 664
Serbource-Gognel N, et al: Measurement of serum α1-acid glycoprotein and α1-antitrypsin desialylation in liver disease. Hepatology 1983, 3: 356
Schmidt K: Isolation of a group of α1-acid glycoprotein from human plasma. J Am Chem Soc 1955, 77: 742
Warren L: The thiobarbituric acid assay of sialic acid. J Biol Chem 1959, 234: 1971
International Group: Acute and chronic hepatitis revisited. Lancet 1977, vol 2: 914
Chandrasekaran EW: Structures of the oligosaccharide chains of two forms of α1-acid glycoprotein purified from liver metastases of lung, colon and breast tumors. Cancer Res 1984, 44: 1557
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozeki, T., Okada, Y. & Iwaki, K. The binding rate of sialic acid to serum α1-acid glycoprotein in patients with chronic hepatic injury. Gastroenterol Jpn 22, 448–452 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02773812
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02773812