Abstract
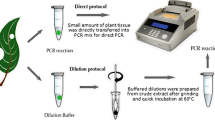
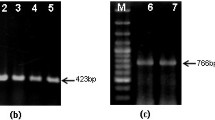
A protocol is described, for the rapid screening of a large number of putative transgenic shoots. Genomic DNA is isolated and screened by PCR. To validate the purity of the DNA, PCR amplification is done with primers homologous to an endogenous gene. Multiplex PCR is used to screen for the transgenic shoots with two sets of primers, one set against the endogenous gene (internal control) and the other set against the gene used in transformation. This protocol has been successfully used on maize, melon, oil-seed rape, pepper, petunia, potato, squash, sugar beet and tobacco.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CTAB:
-
hexadecyltrimethylammonium bromide
- nad5 :
-
gene encoding NADH dehydrogenase
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- uidA :
-
β-glucuronidase
- surA/surB :
-
acetolactate synthase
References
Dellaporta, S.L., J. Wood and J.B. Hicks. 1983. A plant DNA minipreparation: Version II, Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 1:19–21.
Ecke, W., W. Schmitz and G. Michaelis. 1990. The mitochondrialnad5 gene of sugar beet (Beta vulgaris) encoding a subunit of the respiratory NADH dehydrogenase. Curr. Genet. 18:133–139.
Edwards, K., C. Johnstone and C. Thompson. 1991. A simple and rapid method for the preparation of plant genomic DNA for PCR analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 19:1349.
Giebel, L.B. and R.A. Spritz. 1990. Site-directed mutagenesis using a double-stranded DNA fragment as a PCR primer. Nucleic Acids Res. 18:4947.
Guillemaut, P and L. Marèchal-Drouard. 1992. Isolation of Plant DNA: A fast, inexpensive and reliable method. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 10:60–65.
Gyllensten, U.B. and H.A. Erlich. 1988. Generation of single-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction and its application to direct sequencing of theHLA-DQA locus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85:7652–7656.
Hamill, J.D., S. Rounsley, A. Spencer, G. Todd and M.J. Rhodes. 1991. The use of polymerase chain reaction in the plant transformation studies. Plant Cell Rep. 10:221–224.
Haughn, G.W and C. Sommerville. 1986. Sulfonylurea-resistant mutants ofArabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Gen. Genet. 204:430–434.
Jefferson, R.A., S.M. Burgess and D. Hirsh. 1986. β-Glucuronidase fromEscherichia coli as a gene-fusion marker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 83:8447–8451.
Jefferson, R.A. 1987. Assaying chimeric genes in plants: The GUS gene fusion system. Plant. Mol. Biol. Reptr. 5:387–405.
Katterman, F.R.H., and V.I. Shattuck. 1983. A effective method of DNA isolation from the mature leaves ofGossypium species that contain large amounts of phenolic tarpenoids and tannins. Prep. Biochem. 13:347–359.
Lodhi, M.A., G.-N. Ye, N.F. Weeden and B.I. Reisch. 1994. A simple and efficient method for DNA extraction from grapevine cultivars andVitis species. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 12:6–13.
Luo, G., A.G. Hepburn and J.M. Widholm. 1992. Preparation of plant DNA for PCR analysis: A fast, general and reliable procedure. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 10:319–323.
Maliyaki, E.J. 1992. An efficient method for isolation of RNA and DNA from plants containing polyphenolics. Nucleic Acids Res. 20:2381.
Murray, H.C, and W.F. Thompson. 1980 Rapid isolation of high molecular weight DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 8:4321–4325.
Padegimas, L., O.A. Shul’ga, and K.G. Skryabin. 1993. Screening of transgenic plants with polymerase chain reaction. Mol. Biol. 27:583–585.
Saghai-Maroof, M.F., K.M. Soliman, R.A. Jorgensen and R.W. Allard. 1984. Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance chromosomal location and population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81:8014–8018.
Scharf, S.J., G.T. Horn and H.A. Erlich. 1986. Direct cloning and sequence analysis of enzymatically amplified genomic sequences. Science 233:1076–1078.
Tai, T.H., and S.D. Tanksley. 1991. A rapid and inexpensive method for isolation of total DNA from dehydrated plant tissue. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 8:297–303.
Varadarajan, G.S., and C.S. Prakash. 1991 A rapid and efficient method for the extraction of total DNA from sweet potato and its related species. Plant Mol. Biol. Reptr. 9:6–12.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mannerlöf, M., Tenning, P. Screening of transgenic plants by multiplex PCR. Plant Mol Biol Rep 15, 38–45 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772111
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02772111