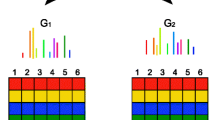
Abstract
Differential display of mRNA (DD) is a technique in which mRNA species expressed by a cell population are reverse transcribed and then amplified by many separate polymerase chain reactions (PCR). PCR primers and conditions are chosen so that any given reaction yields a limited number of amplified cDNA fragments, permitting their visualization as discrete bands following gel electrophoresis. This robust and relatively simple procedure allows identification of genes that are differentially expressed in different cell populations. Here we review DD including some recent modifications, and compare it with other techniques for analyzing differential mRNA expression.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fields, C., Adams, M. D., White, O., and Venter, J. C. (1994) How many genes in the human genome?Nature Genet. 7, 345,346.
Liang, P., and Pardee, A. B. (1992) Differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA by means of the polymerase chain reaction.Science 257, 967–971.
Sompayrac, L., Jane, S., Burn, T. C., Tenen, D. G., and danna, K. J. (1995) Overcoming limitations of the mRNA differential display technique.Nucleic Acids Res..23, 4738, 4739.
Sager, R., Anisowicz, A., Neveu, M., Liang, P., and Sotiropoulou, G. (1993) Identification by differential display of alpha 6 integrin as a candidate tumor suppressor gene.FASEB J. 7, 964–970.
Sun, Y., Hegamyer, G., and Colburn, N. H. (1994). Molecular cloning of five messenger RNAs differentially expressed in preneoplastic or neoplastic JB6 mouse epidermal cells: one is homologous to human tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-3.Cancer Res. 54, 1139–1144.
Chang, A. C.-M., Janosi, J., Hulsbeek, M., De Jong, D., Jeffrey, K. J., Noble, J. R., and Reddel, R. R. (1995) A novel human cDNA highly homologous to the fish hormone stanniocalcin.Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 112, 241–247.
Francia, G., Mitchell, S. D., Moss, S. E., Hanby, A. M., Marshall, J. F., and Hart, I. R. (1996) Identification by differential display of annexin-VI, a gene differentially expressed during melanoma progression.Cancer Res. 56, 3855–3858.
Chen, S.-L., Maroulakou, I. G., Green, J. E., Romano-Spica, V., Modi, W., Lautenberger, J., and Bhat, N. K. (1996) Isolation and characterization of a novel gene expressed in multiple cancers.Oncogene 12, 741–751.
Schleicher, R. L., Hunter, S. B., Zhang, M., Zheng, M., Tan, W., Bandea, C. I., Fallon, M. T., Bostwick, D. G., and Varma, V. A. (1997) Neurofilament heavy chain-like messenger RNA and protein are present in benign prostate and down-regulated in prostatic carcinoma.Cancer Res. 57, 3532–3536.
Joshi, C. P. and Nguyen, H. T. (1996) Differential display-mediated rapid identification of different members of a multigene family, HSP 16.9 in wheat.Plant Mol. Biol. 31, 575–584.
Linskens, M. H. K., Feng, J., Andrews, W. H., Enlow, B. E., Saati, S. M., Tonkin, L. A., Funk, W. D., and Villeponteau, B. (1995) Cataloging altered gene expression in young and senescent cells using enhanced differential display.Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 3244–3251.
Donohue, P. J., Alberts, G. F., Guo, Y., and Winkles, J. A. (1995) Identification by targeted differential display of an immediate early gene encoding a putative serine/threonine kinase.J. Biol. Chem. 270, 10,351–10,357.
Zhu, Y., Carroll, M., Papa, F. R., Hochstrasser, M., and D'Andrea, A. D. (1996) DUB-1, a deubiquitinating enzyme with growth-suppressing activity.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 3275–3279.
Hagen, H.-E., Kläger, S. L., McKerrow, J. H., and Ham, P. J. (1997)Simulium damnosum s. 1.: isolation and identification of prophenoloxidase following an infection with Onchocerca spp. using targeted differential display.Exp. Parasitol. 86, 213–218.
Liang, P., Averboukh, L., Keyomarsi, K., Sager, R., and Pardee, A. B. (1992) Differential display and cloning of messenger RNAs from human breast cancer versus mammary epithelial cells.Cancer Res. 52, 6966–6968.
Doss, R. P. (1996) Differential display without radioactivity—a modified procedure.Bio Techniques 21, 408–410.
Zhao, S., Ooi, S. L., and Pardee, A. B. (1995) New primer strategy improves precision of differential display.Bio Techniques 18, 842–848.
Chen, Z., Swisshelm, K., and Sager, R. (1994) A cautionary note on reaction tubes for differential display and cDNA amplification in thermal cycling.Bio Techniques 16, 1002–1006.
Callard, D., Lescure, B., and Mazzolini, L. (1994) A method for the elimination of false positive generated by the mRNA differential display technique.Bio Techniques 16, 1096,1097.
Zhang, L., Zhou, W., Velculescu, V. E., Kern, S. E., Hruban, R. H., Hamilton, S. R., Vogelstein, B., and Kinzler, K. W. (1997) Gene expression profiles in normal and cancer cells.Science 276, 1268–1272.
Graf, D., Fisher, A. G., and Merkenschlager, M. (1997) Rational primer design greatly improves differential display-PCR (DD-PCR).Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 2239,2240.
Bertioli, D. J., Schlichter, U. H. A., Adams, M. J., Burrows, P. R., Steinbiss, H.-H., and Antoniw, J. F. (1995) An analysis of differential display shows a strong bias towards high copy number mRNAs.Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 4520–4523.
Ikonomov, O. C. and Jacob, M. H. (1996) Differential display protocol with selected primers that preferentially isolates mRNAs of moderate- to low-abundance in a microscopic system.Bio Techniques 20, 1030–1042.
Welsh, J., Chada, K., Dalal, S. S., Cheng, R., Ralph, D., and McClelland, M. (1992) Arbitrarily primed PCR fingerprinting of RNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 20, 4965–4970.
Guimarães, M. J., Lee, F., Zlotnik, A., and McClanahan, T. (1995) Differential display by PCR: novel findings and applications.Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 1832,1833.
Haag, E. and Raman, V. (1994) Effects of primer choice and source of Taq DNA polymerase on the banding patterns of differential display RT-PCR.Bio Techniques 17, 226–228.
Liang, P. and Pardee, A. B., eds. (1997).Methods in Molecular Biology, vol. 85: Differential Display Methods and Protocols, Humana Press, Inc., Totowa, NJ.
Bauer, D., Müller, H., Reich, J., Riedel, H., Ahrenkiel, V., Warthoe, P., and Strauss, M. (1993) Identification of differentially expressed mRNA species by an improved display technique (DDRT-PCR).Nucleic Acids Res. 21, 4272–4280.
Liang, P., Zhu, W., Zhang, X., Guo, Z., O'Connell, R. P., Averboukh, L., Wang, F., and Pardee, A. B. (1994) Differential display using one-base anchored oligo-dT primers.Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 5763–5764.
Sokolov, B. P. and Prockop, D. J. (1994) A rapid and simple PCR-based method for isolation of cDNAs from differentially expressed genes.Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 4009–4015.
Favia, G., Mariotti, G., Mathiopoulos, K. D., and della Torre, A. (1996) Rapid, nonradioactive differential display using Tth polymerase.Trends Genetics 12, 396,397.
Rompf, R. and Kahl, G. (1997) mRNA differential display in agarose gels.Bio Techniques 23, 28.
Averboukh, L., Douglas, S. A., Zhao, S., Lowe, K., Maher, J., and Pardee, A. B. (1996) Better gel resolution and longer cDNAs increase the precision of differential display.Bio Techniques 20, 918–921.
Trentmann, S. M., van der Knaap, E., and Kende, H. (1995) Alternatives to35S as a label for the differential display of eukaryotic messenger RNA.Science 267, 1186,1187.
Chen, J. J. W. and Peck, K. (1996) Non-radioisotopic differential display method to directly visualize and amplify differential bands on nylon membrane.Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 793,794.
Lohmann, J., Schickle, H., and Bosch, T. C. G. (1995) REN display, a rapid and efficient method for nonradioactive differential display and mRNA isolation.Bio Techniques 18, 200–202.
An, G., Luo, G., Veltri, R. W., and O'Hara, S. M. (1996) Sensitive, nonradioactive differential display method using chemiluminescent detection.Bio Techniques 20, 342–344.
Ito, T. and Sakaki, Y. (1997) inMethods in Molecular Biology, vol. 85: Differential Display Methods and Protocols (Liang, P. and Pardee, A. B., eds.), Humana, Totowa, NJ, pp. 37–44.
Luehrsen, K. R., Marr, L. L., van der Knaap, E., and Cumberledge, S. (1997) Analysis of differential display RT-PCR products using fluorescent primers and GENESCAN software.Bio Techniques 22, 168–174.
Corton, J. C. and Gustafsson, J.-Å. (1997) Increased efficiency in screening large numbers of cDNA fragments generated by differential display.Bio Techniques 22, 802–804.
Ross, R., Kumpf, K., and Reske-Kunz, A. B. (1997) PCR-amplified cDNA probes for verification of differentially expressed genes.Bio Techniques 22, 894–897.
Vögeli-Lange, R., Bürckert N., Boller, T., and Wiemken, A. (1996) Rapid selection and classification of positive clones generated by mRNA differential display.Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 1385,1386.
Kester, H. A., van der Leede, B. M., van der Saag, P. T., and van der Burg, B. (1997) Novel progesterone target genes identified by an improved differential display technique suggest that progestin-induced growth inhibition of breast cancer cells coincides with enhancement of differentiation.J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16,637–16,643.
Wadhwa, R., Duncan, E., Kaul, S. C., and Reddel, R. R. (1996) An effective elimination of false positives isolated from differential display of mRNAs.Mol. Biotechnol. 6, 213–218.
Mou, L., Miller, H., Li, J., Wang, E., and Chalifour, L. (1994) Improvements to the differential display method for gene analysis.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 199, 564–569.
Zhang, H., Zhang, R., and Liang, P. (1996) Differential screening of gene expression difference enriched by differential display.Nucleic Acids Res. 24, 2454–2455.
Fischer, A., Saedler, H., and Theissen, G. (1995) Restriction fragment length polymorphism-coupled domain-directed differential display: a highly efficient technique for expression analysis of multigene families.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5331–5335.
Matz, M., Usman, N., Shagin, D., Bogdanova, E., and Lukyanov, S. (1997) Ordered differential display: a simple method for systematic comparison of gene expression profiles.Nucleic Acids Res. 25, 2541,2542.
Ralph, D., McClelland, M., and Welsh, J. (1993) RNA fingerprinting using arbitrarily primed PCR identifies differentially regulated RNAs in mink lung (My 1Lu) cells growth arrested by transforming growth factor b1.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10,710–10,714.
Sargent, T. D. (1987) Isolation of differentially expressed genes.Methods Enzymol. 152, 423–432.
Lisitsyn, N., Lisitsyn, Na., and Wigler, M. (1993) Cloning the differences between two complex genomes.Science 259, 946–951.
Lisitsyn, N. A., Lisitsina, N. M., Dalbagni, G., Barker, P., Sanchez, C. A., Gnarra, J., Linehan, W. M., Reid, B. J., and Wigler, M. H. (1995) Comparative genomic analysis of tumors: detection of DNA losses and amplification.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 151–155.
Schutte, M., Da Costa, L. T., Hahn, S. A., Moskaluk, C., Hoque, A. T. M. S., Rozenblum, E., Weinstein, C. L., Bittner, M., Meltzer, P. S., Trent, J. M., Yeo, C. J., Hruban, R. H., and Kern, S. E. (1995) Identification by representational difference analysis of a homozygous deletion in pancreatic carcinoma that lies within the BRCA2 region.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92, 5950–5954.
Hubank, M. and Schatz, D. G. (1994) Identifying differences in mRNA expression by representational difference analysis of cDNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 22, 5640–5648.
Siebert, P. D., Chenchik, A., Kellogg, D. E., Lukyanov, K. A., and Lukyanov, S. A. (1995) An improved PCR method for walking in uncloned genomic DNA.Nucleic Acids Res. 23, 1087,1088.
Diatchenko, L., Lau, Y.-F. C., Campbell, A. P., Chenchik, A., Moqadam, F., Huang, B., Lukayanov, S., Lukyanov, K., Gurskaya, N., Sverdlov, E. D., and Siebert, P. D. (1996) Suppression subtractive hybridization: a method for generating differentially regulated or tissue-specific cDNA probes and libraries.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 6025–6030.
Velculescu, V. E., Zhang, L., Vogelstein, B., and Kinzler, K. W. (1995) Serial analysis of gene expression.Science 270, 484–487.
Velculescu, V. E., Zhang, L., Zhou, W., Vogelstein, J., Basrai, M. A., Bassett, D. E., Jr., Hieter, P., Vogelstein, B., and Kinzler, K. W. (1997) Characterization of the yeast transcriptome.Cell 88, 243–251.
Polyak, K., Xia, Y., Zweier, J. L., Kinzler, K. W., and Vogelstein, B. (1997) A model for p53-induced apoptosis.Nature 389, 300–305.
Schena, M., Shalon, D., Davis, R. W., and Brown, P. O. (1995) Quantitative monitoring of gene expression patterns with a complementary DNA microarray.Science 270, 467–470.
Schena, M., Shalon, D., Heller, R., Chai, A., Brown, P. O., and Davis, R. W. (1996) Parallel human genome analysis: microarray-based expression monitoring of 1000 genes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 10,614–10,619.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.S., Duncan, E.L., Chang, A.C.M. et al. Differential display of mRNA. Mol Biotechnol 10, 155–165 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760862
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760862