Abstract
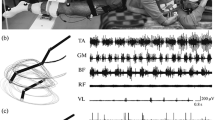
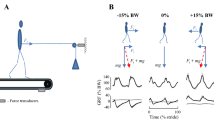
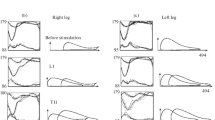
The influence of the Jendrassik maneuver on the generation of the locomotor rhythmicity was studied under conditions of the “suspension” of legs in a horizontal plane. It was shown that during Jendrassik’s maneuver, passive movements of one limb trigger stepping with the participation of both limbs. The Jendrassik’s maneuver also notably facilitates the vibration-induced locomotion. The kinematics of the evoked stepping movements did not differ from the kinematics of the voluntary “air-stepping,” reciprocal electromyographic activity being observed in antagonistic muscles. It seems likely that the generation of cyclic movements during the Jendrassik maneuver occurs due to the activation of the same stepping automatism as in normal stepping. The experimental results suggest that an increase in the level of tonic readiness of the tonogenic CNS structures, which participate in realization of the locomotor program, is a necessary condition for the activation of the spinal mechanisms of the stepping generation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gurfinkel’, V.S., Levik, Yu.S., Kazennikov, O.V., and Selionov, V.A., Involuntary Air-stepping Induced by the Increase of the Level of Tonic Readiness: Evidence for CPG in Human,Brain and Movement. Proceedings of International Symposium, Gurfinkel, V.S. and Levik, Yu.S., Eds., Moscow, 1997, p. 86.
Gurfinkel’, V.S., Levik, Yu.S. Kazennikov, O.V., and Selionov, V.A., Locomotor-like Movements Evoked by Leg Muscle Vibration in Humans,Eur. J. Neurosci., 1998, vol. 10, p. 1608.
Gurfinkel', V.S., Levik, Yu.S., and Lebedev, M.A., Postural Automatisms Revealed by Augmentation of Tonicity,Dokl. AN SSSR, 1989, vol. 305, no. 5, p. 1266.
Mori, S., Kawahara, K., Sakamoto, T.,et al., Setting and Resetting of Level of Postural Muscle Tone in Decerebrated Cat by Stimulation of Brain Stem,J. Neurophysiol., 1982, vol. 48, p. 737.
Mori, S., Matsui, T., Kuze, B.,et al., Cerebellar-induced Locomotion: Reticulospinal Control of Spinal Rhythm Generating Mechanisms in Cats,Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci., 1998, vol. 860, p. 94.
Rossignol, S., Neural Control of Stereotypic Limb Movement,Handbook of Physiology. Section 12: Exercise: Regulation and Integration of Multiple Systems, Rowell, L.B. and Shepherd, J.T., Eds., Oxford: Oxford Univ. Press, 1996, p. 171.
Bussel, B., Morin, C., and Pierrot-Deseilligny, E., Mechanism of Monosynaptic Reflex Reinforcement during Jendrassik Maneuver in Man,J. Neurosurg. Psychiatry, 1978, vol. 41, no. 1, p. 44.
Kameyma, O., Hayes, K. C., and Wolfe, D., Methodological Considerations Contributing to Variability of the Quadriceps H-Reflex,Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil., 1989, vol. 68, no. 6, p. 277.
Pereon, Y., Genet, R. and Guiheneuc, P., Facilitation of Motor Evoked Potentials: Timing of Jendrassik Maneuvre Effects,Muscle and Nerve, 1995, vol. 18, p. 1427.
Young, R.R. and Hagbarth, K.E., Physiological Tremor Enhanced by Manoeuvre Affecting the Segmental Stretch Reflex,J. Physiol. (London), 1980, vol. 302, p. 171.
Delwaide, P.J. and Toulouse, P., Jendrassik Maneuver vs. Controlled Conditioning the Excitability Soleus Monosynaptic Reflexes,Arch. Phys. Med., Rehabil., 1980, vol. 61, no. 11, p. 505.
Dowman, R. and Wolpow, J.R., Jendrassik Maneuvre Facilitates Soleus H-Reflex without Change in Average Soleus Motoneuron Pool Membrane Potential,Exp. Neurol., 1988, vol. 101, no. 2, p. 288.
Surguladze, T.D. and Gurfinkel', V.S., Trace Changes in Excitability of the Spinal Cord after Termination of Rhythmic Movements,Biofizika, 1973, vol. 18, p. 947.
Gurfinkel' V.S. and Ivanenko, Yu.P., Low-threshold Reactions of Human Muscles in the State of Rest,Fiziol. Chel., 1987, vol. 13, no. 2, p. 317.
Lundberg, A.,Reflex Control of Stepping. The Nansen Memorial Lecture, Oslo: Universitetsforlaget, 1969.
Kiehn, O. and Eken, T., Prolonged Firing in Motor Units: Evidence of Plateau Potentials in Human Motoneurons?,J. Neurophysiol., 1997, vol. 78, p. 3061.
Bernshtein, N.A.,Issledovanie po biodinamike khod'by, bega, pryzhka (Study on Biodynamics of Walking, Running, and Jumping), Moscow: Fizkul'tura i Sport, 1940.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gurfinkel’, V.S., Levik, Y.S., Kazennikov, O.V. et al. Jendrassik’s maneuver creates conditions for triggering involuntary stepping. Hum Physiol 26, 187–192 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760090
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02760090