Abstract
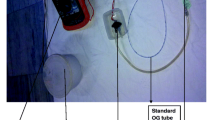
In non-trachestomised patients of tetanus neonatorum adoption of semiprone position and continuous intragastric drip led to a marked decrease in the rate of aspiration and a six-fold decrease in the rate of chest infections as compared with the patients managed in supine position and given bulk feeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodman RI, Marton HJV, Thomas ET: Treatment of tetanus with chlorpromazine and nitrous oxide. Lancet 2: 230, 1955.
Kelly RE, Lawrence DR: Effect of chlorpromazine on convulsions of experimental and clinical tetanus. Lancet I: 118, 1956
Wright R, Sykes MK, Jackson BG, Mann NM, Adams EB: Intermittent positive pressure ventilation in tetanus neonatorum. Lancet 2: 678, 1961
Varma YS, Varma JMS, Kohli JB: Conservative management of tetanus. Arch Anaesth and Resus Under Publication
Deaty RN, Petersdrop PG: Tetanus.In Harrison’s Principles of Internal Medicine, McGraw Hill. 7 edn: 1974. p. 847.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, Y.S., Verma, J.S. & Dattal, M.S. Semiprone position and continuous intragastric drip in conservative management of tetanus neonatorum. Indian J Pediatr 47, 385–387 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02759834
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02759834