Abstract
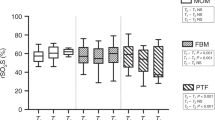
The differences between breast milk and infant formulas have been a popular subject of many recent studies. Most concern the chemical and biological characteristics of breast milk and infant formulas, but little work has been done about hemodynamic changes in the splanchnic circulation. In term neonates (n=22) we evaluated the effect of breast milk, adapted cow’s milk formula, and nucleotide supplemented cow’s milk formula on intestinal blood flow. To determine the blood flow velocity and estimate volume flow, pulsed Doppler ultrasound of the superior mesenteric artery (SMA) was performed prefeeding and 15, 45, and 90 minutes following feeding. When pre-and postprandial blood flow features of babies were compared among in their groups according to nutrition post prandial blood flow velocity and volume flow were increased significantly over baseline in all three groups. While there was no significant difference between the postprandial blood flow parameters of the breast milk and adapted cow’s milk formula-fed groups, the nucleotide supplemented cow’s milk formula-fed group had significantly higher postprandial blood flow velocity and volume flow.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson HG. Human milk feeding.Ped Clin North Am 1985; 32: 335–53.
Goldman AS, Goldblum RM, Hanson LA. Anti-inflammatory aspects of human milk. In: Xanthous M, ed.New Aspects of Nutrition in Pregnancy, Infancy and Prematurity. Amsterdam, Elsevier Science Publishers, 1987, pp 157–66.
Lawrence RA. Breast feeding.Pediatr Rev 1989; 11: 163–171
Barness LA. Infant feeding: formula, solids.Ped Clin North Am 1985; 31: 355–162.
Gallavan RH, Jacobson ED. Intestinal blood flow. In Berk Je, (ed).Gastroenterology, Fourth edn. Philadephia: W.B. Saunders Company, 1985; pp 1900–1914.
Van Bel F, Van Zwieten PHT, Guit GL, Schipper J. Superior mesenteric artery blood flow velocity an estimated volume flow: Duplex doppler US study of preterm and term neonates.Radiology 1990; 174: 165–169.
Daneman A, Bobyn P, Garcia P, Stringer DA, Hellman J. Doppler sonography of intraadbominal vessels in premature infants.Pediatr Radiol 1987; 17: 342.
Leidig E. Pulsed doppler ultrasound blood flow measurements in the superior mesenteric artery of the newborn.Pediatr Radiol 1989; 19: 169–172.
Leiding E. Doppler analysis of superior mesenteric artery blood flow in preterm infants.Arch Dis Child 1989; 64: 476–480.
Uauy R. Dietary nucleotides and requirements in early life. In: Lebvernthal E, ed.Textbook of Gastroenterology and Nutrition in Infancy 2 edn. New York: Raven Press, 1989: pp 265–280.
Quan R, Barness LA, Uauy R: Do Infants need nucleotide supplemented formula for optimal nutrition?J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1990; 11: 429–434.
Janas LM, Picciano MF. The nucleotide profile of human milk.Pediatr Res 1982; 16: 659–662.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Özkan, H., Ören, H., Erdag, N. et al. Breast milk versus infant formulas: Effects on intestinal blood flow in neonates. Indian J Pediatr 61, 703–709 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02751984
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02751984