Abstract
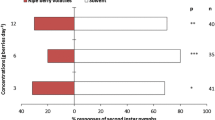
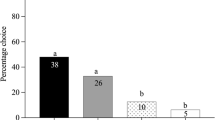
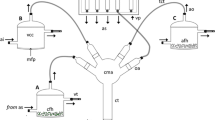
In an earlier study we documented attraction of the specialist parasitoidMacrocentrus grandii Goidanich to odors of com, potato, and snap bean. In the present study the chemical bases of the parasitoid’s attraction to these food plants of its European corn borer host were compared. Volatile compounds from corn leaves were isolated using Tenax and identified by capillary gas chromatographic-mass spectrometry. Twenty-one compounds including aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, esters, and sesquiterpenes were present in corn. These were separated into fractions by column chromatography on Florisil. Wind-tunnel bioassays of the fractions indicated thatM. grandii was attracted to fractions containing nonpolar and slightly polar compounds including sesquiterpenes, aldehydes, a ketone, and esters. More polar compounds in corn, like alcohols, were not attractive. Attraction to potato odor was based on the presence of the same classes of compounds that were attractive in corn, but more polar compounds were involved in attraction to snap bean odor. This study indicated that only some compounds in each of the three odor complexes tested were attractive. It also documented that different compounds were involved in attraction ofM. grandii to different plant odors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altieri, M.A., Annamalai, S., Katiyar, K.P., andFlath, R.A. 1982. Effects of plant extract on the rates of parasitization ofAnagasta kuehniella (Lep.: Pyralidae) eggs byTrichogramma pretiosum (Hym.: Trichogrammatidae) under greenhouse conditions.Entomophaga 27:431–438.
Becker, R.A., Chambers, J.M., andWilks, A.R. 1988. The New ‘S’ Language: A Programming Environment for Data Analysis and Graphics. Wadsworth and Brooks/Cole Computer Science Series, Pacific Grove, California.
Buttery, R.G., andLino, L.C. 1984. Corn leaf volatiles: Identification using Tenax trapping for possible insect attractants.J. Agric. Food Chem. 32:1104–1106.
Camors, F.B., {jrJr.}, andPayne, T.L. 1972. Response ofHeydenia unica (Hymenoptera: Pteromalidae) toDendroctonus frontalis (Coleoptera: Scolytidae) pheromones and a host tree terpene.Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 65:31–33.
Clausen, C.P. 1956. Biological control of insect pests in the continental United States. U.S. Dept. Agric. Tech. Bull. 1139.
Devore, J., andPeck, R. 1986. Statistics: The Exploration and Analysis of Data. West Publishing Company, New York.
Dickens, J.C. 1989. Green leaf volatiles enhance aggregation pheromone of boll weevil,Anthonomous grandis.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 52:191–204.
Ding, D., Swedenborg, P.D., andJones, R.L. 1989a. Chemical stimuli in host seeking behavior ofMacrocentrus grandii Goidanich (Hymenoptera: Braconidae).Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 82:232–236.
Ding, D., Swedenborg, P.D., andJones, R.L. 1989b. Plant odor preferences and learning inMacrocentrus grandii Goidanich (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a larval parasitoid of the European corn borer,Ostrinia nubilalis.J. Kans. Entomol. Soc. 62:164–176.
Elzen, G.W., Williams, H.J., andVinson, S.B. 1983. Response by the parasitoidCampoletis sonorensis (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae) to chemicals (synomones) in plants: Implications for host habitat location.Environ. Entomol. 12:1873–1877.
Elzen, G.W., Williams, H.J., andVinson, S.B. 1984. Isolation and identification of cotton synomones mediating searching behavior by the parasitoidCampoletis sonorensis.J. Chem. Ecol. 10:1251.
Fienberg, S.A. 1989. The analysis of cross-classified categorical data. MIT Press, Cambridge, Massachusetts.
Guthrie, W.D., Russell, R.E., andJennings, C.W. 1971. Resistance of maize to second-brood European corn borer, pp: 165–179,in J.I. Sutherland, and R.J. Falasca (eds.). Report of 26th Annual Corn and Sorghum Research Conference, Chicago, American Seed Trade Association, Washington, D.C.
Lewis, L.C. 1982. Present status of introduced parasitoids of the European corn borer,Ostrinia nubilalis (Hübner) in Iowa.Iowa State J. Res. 56:429–436.
Martin, W.R., Nordlund, D.A., andNettles, W.C. 1990. Response of parasitoidEucelatoria bryani to selected plant material in an olfactometer.J. Chem. Ecol. 16:499–508.
McLafferty, F.W., andStauffer, D.B. 1989. The Wiley/NBS Registry of Mass Spectral Data. Wiley, New York.
Miwa, T.K. 1963. Identification of peaks in gas-liquid chromatography.J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 40:309–313.
Navasero, R.C., andElzen, G.W. 1989. Responses ofMicroplitis croceipes to host and non-host plants ofHeliothis virescens in a wind tunnel.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 53:57–63.
Nordlund, D.A., andLewis, W.J. 1976. Terminology of chemical releasing stimuli in intraspecific and interspecific interactions.J. Chem. Ecol. 2:211–220.
Nordlund, D.A., Chalfant, R.B., andLewis, W.J. 1985. Response ofTrichogramma pretiosum females to volatile synomones from tomato plants.J. Entomol. Sci. 20:372–376.
Parker, H.L. 1931.Macrocentrus gifuensis Ashmead, a polyembryonic braconid parasite in the European corn borer. U.S. Dept. Agric. Tech. Bull. 230.
Peairs, F.B., andLilly, J.H. 1975. Parasites reared from larvae of the European corn borer,Ostrinia nubilalis (Hbn.) in Massachusetts, 1971–73. (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae)J. N.Y. Entomol. Soc. 33:36–37.
Ramachandran, R., andNorris, D.M. 1991. Volatiles mediating plant-herbivore-natural enemy interactions: Electroantennogram responses of soybean looper,Pseudoplusia includens, and a parasitoidMicroplitis demolitor, to green leaf volatiles.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:1665–1690.
Read, D.P., Feeny, P.D., andRoot, R.B. 1970. Habitat selection by the aphid parasiteDiaeretiella rapae and hyperparasiteCharips brassicae.Can. Entomol. 102:1567.
Sakamoto, Y., andAkaike, H. 1978. Analysis of cross classified data by AIC.Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 30:185–197.
Shahjahan, M. 1974.Erigeron flowers as food and attractive odor source forPeristenus pseudopallipes, a braconid parasitoid of the tarnished plant bug.Environ. Entomol. 3:69–72.
Sugimoto, T., Kameoka, H., Kusatani, S., Invi, O., andOtsuka, K. 1988. Foraging for patchilydistributed leaf-miners by the parasitoid,Dapsilartha rufiventris (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) V. Plant odour as a cue to long range patch location.Appl. Entomol. Zool. 23:135–143.
Turlings, T.C.J., Tumlinson, J.H., Heath, R.R., Proveaux, A.T., andDoolittle, R.E. 1991. Isolation and identification of allelochemicals that attract the larval parasitoid,Cotesia marginiventris (Cresson), to the microhabitat of one of its hosts.J. Chem. Ecol. 17:2235–2251.
Udayagiri, S. 1991. A chemically mediated interaction between plants andMacrocentrus grandii Goidanich (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a specialist parasitoid of European corn borer. PhD thesis. University of Minnesota, Minneapolis.
Visser, J.H., Straten, S. van, andMaarse, H. 1979. Isolation and identification of volatiles in the foliage of potato,Solanum tuberosum, a host plant of the Colorado beetle,Leptinotarsa decemlineata.J. Chem. Ecol. 5:13–25.
Whitman, W., andEller, F.J. 1990. Parasitic wasps orient to green leaf volatiles.Chemoecology 1:69–75.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Udayagiri, S., Jones, R.L. Role of plant odor in parasitism of European corn borer by braconid specialist parasitoidMacrocentrus grandii Goidanich: Isolation and characterization of plant synomones eliciting parasitoid flight response. J Chem Ecol 18, 1841–1855 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02751108
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02751108