Abstract
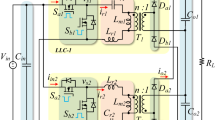
Operation and characteristics of resonant converters on the utility line are presented. Series-parallel (LCC-type) resonant converter operating with discontinuous current mode and continuous current mode (variable frequency control as well as fixed-frequency) are considered. Design examples are presented. SPICE simulation and experimental results obtained for the designed converters (rated at 150 W) are presented to verify the theory. It is shown that high line power factor (>0.95) and line current total harmonic distortion (THD) of <25% are obtained for the LCC-type converter for a wide load range (from full load to 10% rated load) without any active control, and the switch peak current decreases with the load current. With active line current control, low distortion and zero voltage switching for the entire cycle are realized.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Belaguli V 1996Series-parallel and parallel-series resonant converters operating on the utility line — analysis, design, simulation and experimental results. Ph D dissertation, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of Victoria, Canada
Belaguli V, Bhat A K S 1995 Characteristics of fixed frequency series-parallel resonant converter operating on the utility line with and without active control.IEEE Power Electronics and Drive Systems (PEDS ’95) Conference Record, pp 168–173
Bhat A K S 1991 A unified approach for the steady-state analysis of resonant converters.IEEE Trans. on Ind. Electron. 38: 251–259
Chambers D 1983 A new high frequency resonant technique for dynamic correction of off-line converter input current waveforms.Proceedings of Powercon 10, paper # F-1, pp 1–7
He J, Mohan N 1987 Input-current shaping in line-rectification by resonant converters.IEEE Industry Applications Society Conference Records, pp 990–995
Kataoka T, Mizumachi K, Miyairi T 1979 A pulse-width controlled AC to DC converter to improve power factor and waveform of AC line current.IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 15: 670–675
Keraluwala M H, Steigerwald R L, Gurumoorthy R 1991 A fast-response high power factor converter with a single power stage.IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference Record, pp 769–779
Kocher M J, Steigerwald R L 1983 Anac todc converter with high quality input waveforms.IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 19: 586–599
Nijhof E B G 1986 Resonant power supply (RPS) converters: The solution for mains/line pollution problems.Proc. Power Conversion Int. Conf. Rec. pp 104–139
Schlecht M F, Miwa B A 1987 Active power factor correction for switching power supplies.IEEE Trans. Power Electron. PE-2: 273–281
Schutten M J, Steigerwald R L, Keraluwala M H 1991 Characteristics of load resonant converters in a high power factor mode.IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference Record, pp 5–16
Steigerwald R L 1988 A comparison of half-bridge resonant converter topologies.IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 3: 174–182
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhat, A.K.S., Belaguli, V. High power factor operation of resonant converters on the utility line. Sadhana 22, 733–752 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02745843
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02745843