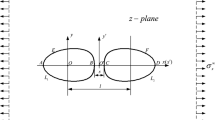
Abstract
Engineering materials are vulnerable targets for damage by chemical agents. This results in various types of irregular cavities which may subsequently change their shape under the combined action of loads and chemical attack. Such shape evolutions are subject to certain constraints. This paper explores the evolution in stresses as a result of an evolution in the shape of an isolated irregular hole in an infinite elastic plate subjected to remote uniform stress. The constraint employed here is a fixed area for the irregular hole with variable perimeter as a result of the evolution. Increase in perimeter implies decrease in strain energy on account of increased surface energy. Such phenomena could also occur in polymeric sheets on account of viscoelasticity even in the absence of chemical agents. This paper presents the evolution in boundary stresses as the cavity evolves to take different shapes. Complex variable methods are developed to tackle three cases of remote loading: (a) hydrostatic tension, (b) uniaxial tension, and (c) pure shear state. Of the above three cases, the first case of hydrostatic loading leads to a remarkably simple result for the boundary stress as shown in this paper. The last case is obtained by superposing a uniaxial tension and uniaxial compression along orthogonal directions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- σ x ,σ y :
-
normal stress inx- andy-directions respectively
- σ xy :
-
shear stress onx-plane iny-direction
- σ t :
-
tangential stress
- σ n :
-
normal stress
- σ tm :
-
mean value of tangential stress around the hole
- σ t(rms) :
-
root mean square value of tangential stress around the hole
- E, F :
-
Kolosov-Muskhellishvilli first and second complex potentials respectively
- z :
-
point on physical plane
- ζ :
-
point on complex plane
- ϑ :
-
angle in complex plane
- m :
-
coefficients ofζ-terms in mapping equation
- n :
-
powers ofζ-terms in mapping equation
- p :
-
internal pressure applied
- s :
-
distance along the hole boundary
- G :
-
shear modulus
- v :
-
Poisson’s ratio
- u, v :
-
displacements along thex- andy-directions respectively
- α :
-
coefficients ofζ-terms in the expressions forE
- α L :
-
angle of load application for uniaxial loading
References
Carrier G F, Krook M, Pearson C E 1966Functions of a complex variable (New York: McGraw-Hill)
Churchill R V 1960Introduction to complex variables (New York: McGraw-Hill)
England A H 1971Complex variable methods in elasticity (London: Wiley-Interscience)
Givoli D, Elishakoff I 1992 Stress concentration at a nearly circular hole with uncertain irregularities.Trans. ASME: J. Appl. Mech. 59: S65-S71
Kober H 1952Dictionary of conformal representations (New York: Dover)
Savin G S 1962Stress concentration around holes (New York: Pergamon)
Timoshenko S, Goodier J N 1970Theory of elasticity (New York: Mc-Graw Hill)
Vandembroucq D, Roux S 1997a Conformal mapping on rough boundaries. I. Application to harmonic problems.Phys. Rev. E-55: 6171–6185
Vandembroucq D, Roux S 1997b Conformal mapping on rough boundaries. II. Application to biharmonic problems.Phys. Rev. E-55: 6186–6196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Simha, K.R.Y., Mohapatra, S.S. Stress concentration around irregular holes using complex variable method. Sadhana 23, 393–412 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02745750
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02745750