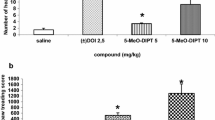
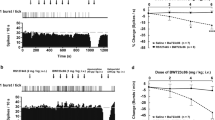
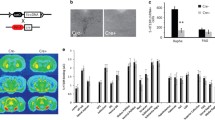
Abstract
The administration of the anorexigenic drugd,l-fenfluramine (Ponderax®) to laboratory animals results in a dose-dependent reduction in presynaptically located serotonergic reuptake transporter protein. This long-term effect may represent an altered mechanism of synthesis of the transporter (downregulation). Alternatively, fenfluramine may destroy the serotonergic terminals on which 5-HT transporters are located. To distinguish between these two alternatives, we applied an assay of neurotransmitter-specific nerve endings (α) to brain tissue from two animal models of reduced 5-HT transporter density. In Model 1, serotonergic nerve terminals were destroyed (rats received 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine [5,7-DHT] intracisternally); in Model 2, there was a loss of 5-HT transportersper se on otherwise intact serotonergic nerve terminals. The manner in which α declined as transporter density was decreased (reducingV max values) in animal Models 1 and 2 was found to be significantly different. In rats treated with fenfluramine, the association between 5-HT transporter density and α was the same as in the neurotoxic model.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel N. M., Contrera J. F., and De Souza E. B. (1989) Fenfluramine selectively and differentially decreases the density of serotonergic nerve terminals in rat brain: evidence from immunocytochemical studies.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 249, 928–943.
Appel N. M., Mitchell W. M. M., Contrera J. F., and De Souza E. B. (1990) Effects of high-dose fenfluramine treatment on monoamine uptake sites in rat brain: assessment using quantitative autoradiography.Synapse 6, 33–44.
Baumgarten G., Garattini S., Lorens S., and Wurtman R. (1992) Dexfenfluramine and neurotoxicity.Lancet 339, 359.
Biessen E. A. L., Norder J. A., Horn A. S., and Robillard G. T. (1988) Evidence for the existence of at least two different binding sites for 5HT-reuptake inhibitors within the 5HT-reuptake system from human platelets.Biochem. Pharmacol. 37, 3959–3966.
Bjorklund A., Baumgarten H. G., and Rensch A. (1975) 5,7-Dihydroxytryptamine: improvement of its selectivity for serotonin neurones in the CNS by pretreatment with desipramine.J. Neurochem. 24, 833–835.
Borroni E., Ceci A., Garattini S., and Mennini T. (1983) Differences between d-fenfluramine and d-norfenfluramine in serotonin presynaptic mechanisms.J. Neurochem. 40, 891–893.
Clinschmidt B. V., Totaro J. A., McGuffin J. C., and Pflueger A. B. (1976) Fenfluramine: long-term reduction in brain serotonin (5-hydroxy-tryptamine).Eur. J. Pharmacol. 35, 211–214.
Colado M. I., Murray T. K., and Green A. R. (1993) 5-HT loss in rat brain following 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA),p-chloroamphetamine and fenfluramine administration and effects of chlormethiazole and dizocilpine.Br. J. Pharmacol. 108, 583–589.
Curtis R., Adryan K. M., Zhu Y., Harkness P. J., Lindsay R. M., and DiStefano P. S. (1993) Retrograde axonal transport of cilliary neurotrophic factor is increased by peripheral nerve injury.Nature 365, 253–255.
Dodd P. R., Hardy J. A., Oakley A. E., Edwardson J. A., Perry E. K., and Delaunoy J. P. (1981) A rapid method for preparing synaptosomes: comparison with alternative procedures.Brain Res. 226, 107–118.
Duhault J. and Verdavainne C. (1967) Modification du taux de serotonine cerebrale chez le rat par les trifluoromethyl-phenyl-2-ethyl aminopropane (fenfluramine 768 S).Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 170, 276–286.
Frenken M. and Kaumann A. J. (1987) Interconversion into a low active state vascular 5-HT2-receptors against irreversible antagonism by phenoxybenzamine.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 335, 481–490.
Fuller R. W., Snoddy H. D., and Robertson D. W. (1988) Mechanisms of effects of d-fenfluramine on brain serotonin metabolism in rats: uptake inhibition verses release.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 30, 715–721.
Gobbi M., Presti M. L., Mancini L., Desimoni M. G., and Mennini T. (1993) Down-regulation of serotonin uptake carriers after chronic d-fenfluramine?Soc. Neurosci. Abstract 19, 1895.
Harvey J. A. and McMaster S. E. (1975) Fenfluramine: evidence for a neurotoxic action in midbrain and a long-term depletion of serotonin.Pharmacol. Commun. 1, 217–228.
Hekmatpanah C. R. and Peroutka S. J. (1990) 5-Hydroxytryptamine uptake blockers attenuate the 5-hydroxytryptamine-releasing effect of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and related agents.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 177, 95–98.
Johnson M. P. and Nichols D. E. (1990) Comparative serotonin neurotoxicity of the stereoisomers of fenfluramine and norfenfluramine.Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 36, 105–109.
Kalia M. (1991) Reversible, short-lasting, and dose-dependent effect of (+)-fenfluramine on neocortical serotonergic axons.Brain Res. 548, 111–125.
Kalia M. and O’Malley N. P. (1993)Brain serotonergic neurons demonstrate normal axonal transport following short- and long-term treatment with dexfenfluramine.Soc. Neurosci. Abstract 19, 1060.
Kleven M. S., Schuster C. R., and Seiden L. S. (1988) Effect of depletion of brain serotonin by repeated fenfluramine on neurochemical and anorectic effects of acute fenfluramine.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 246, 822–828.
Kouyoumdjian J. C., Gonnard P., and Belin M. F. (1979) Effect of fenfluramine administration on synaptosomal uptake of some neurotransmitters and on synaptosomal enzymes which metabolize GABA.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 309, 7–11.
Kovachich G. B., Aronson C. E., and Brunswick D. J. (1992) Effect of repeated administration of antidepressants on serotonin uptake sites in limbic and neocortical structures of rat brain determined by quantitative autoradiography.Neuropsychopharmacology 7, 317–324.
Langer S. Z., Javoy-Agid F., Raisman R., Briley M., and Agid Y. (1981) Distribution of specific high-affinity binding sites for [3H]imipramine in human brain.J. Neurochem. 37, 267–271.
Lesch K. P., Aulakh C. S., Wolozin B. L., Tolliver T. J., Hill J. L., and Murphy D. L. (1993) Regional brain expression of serotonin transporter mRNA and its regulation by reuptake inhibiting antidepressants.Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 17, 31–35.
Lorens S. A., Hata N., and Cabrera T. (1990) Comparison of the behavioral and neurochemical effects of 5,7-DHT, MDMA, and d,1-fenfluramine.NIDA Res. Monogr. Ser. 95, 347.
Markwell M. A. K., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., and Tolbert N. E. (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples.Anal. Biochem. 87, 206–210.
Mennini T., Bizzi A., Caccia S., Codegoni A., Fracasso C., Frittoli E., Guiso G., Padura I. M., Uslenghi A., and Garanttini S. (1991) Comparative studies on the anorectic activity ofd-fen-fluramine in mice, rats, and guinea pigs.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 343, 483–490.
Molliver D. C., and Molliver M. E. (1990) Anatomical evidence for a neurotoxic effect of (+)-fenfluramine upon serotonergic projections, in the rat.Brain Res. 511, 165–168.
Munson P. J. and Rodbard D. (1980) LIGAND: a versitile computer approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems.Ann. Biochem. 107, 220–239.
Opitz K. (1967) Anorexigene phenylalkylamine und serotoninstoffwechsel.Naunyn-Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. Exp. Pathol. 259, 56–65.
Pinder R. M., Brogden R. N., Sawyer, P. R., Speight T. M., and Avery G. S. (1975) Fenfluramine: a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic efficacy in obesity.Drugs 10, 241–323.
Pinto W., Guran D., Karczmar A. G., and Battaglia G. (1993) Differential dose-dependent inactivation of brain serotonin recognition sites by EEDQ: lack of inactivation of the 5-HT transporter.Soc. Neurosci. Abstract 19, 1169.
Puig de Parada M., Parada M. A., and Hoebel B. G. (1993) Long-term effects ofd-fenfluramine andd-norfenfluramine on serotonin and 5-HIAA in the rat hippocampus.Soc. Neurosci. Abstract 19, 1181.
Sarkissian C. F., Wurtman R. J., Morse A. N., and Gleason R. (1990) Effects of fluotexine of fenfluramine on serotonin release from, and levels in, rat frontal cortex.Brain Res. 529, 294–301.
Schuster C. R., Lewis M., and Seiden L. S. (1986) Fenfluramine: neurotoxicity.Psychopharmacol. Bull. 22, 148–151.
Sotelo C. (1991) Immunohistochemical study of short- and long-term effects of dl-fenfluramine on the serotonergic innervation of the rat hippocampal formation.Brain Res. 541, 309–326.
Sotelo C., and Zamora A. (1978) Lack, of morphological change in the neurones of the B-9 group in rats treated with fenfluramine.Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 6, 55–62.
Stadlin A., Choi H. L., and Tsang D. (1993) [3H]Mazindol-labelled dopamine uptake sites in the rat striatum following prenatal cocaine exposure.Brain Res. 637, 345–348.
Steranka L. R. and Sanders-Bush E. (1979) Long-term effects of fenfluramine on central serotonergic mechanisms.Neuropharmacology 18, 895–903.
Wagner J. and Peroutka S. J. (1990) Neurochemistry and neurotoxicity, of substituted amphetamines.Neuropsycpharmacology 3, 219,220.
Westphalen R. I. and Dodd P. R. (1993a) New evidence for a loss of serotonergic nerve terminals in rats treated withd,l-fenfluramine.Pharmacol. Toxicol. 72, 249–255.
Westphalen R. I. and Dodd P. R. (1993b) The regeneration of fenfluramine-destroyed serotonergic nerve terminals.Eur. J. Pharmacol. 238, 399–402.
Westphalen R. I., Dodd P. R., and Cameron D. L. (1994) Differing effects of EEDQ and phenoxybenzamine on 5-HT transporters in Wistar and Sprague-Dawley rat brain.Soc. Neurosci. Abstract 20, 1605.
Zaczek R., Battaglia G., Culp S., Appel, N. M., Contrera J. F., and De Souza E. B. (1990) Effects of repeated fenfluramine administration on indices of monoamine function in rat brain: pharmacokinetics, dose response, regional specificity and time-course data.J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 253, 104–112.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Westphalen, R.I., Dodd, P.R. The nature ofd,l-fenfluramine-induced 5-HT reuptake transporter loss in rats. Mol Neurobiol 11, 165–175 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740693
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02740693