Abstract
Objective
To summarize the experience in diagnosing and treating parathyroid adenoma.
Methods
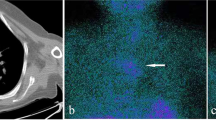
Twenty —four patients were diagnosed with parathyroid adenoma and received parathyroidectomy in our hospital. Sixteen of them presented with hyperparathyroidism. The patients received ultrasounography, CT or99mTc —MIBI to locate the tumor site. Serum concentrations of PTH and calcium were checked before the operation. All operations were performed under general anesthesia. The adenomas were resected and the four glands explored.
Results
All of the patients were cured and there was no mortality in our group. The symptoms of hyperparathyroidism remitted to various degrees after the operation. PTH dropped to the normal range 2 days after operation. Serum calcium concentrations declined to different levels from the first day after operation. Seven patients developed hypocalcemia post-operation but recovered by injection of calcium gluconate. Only one of the patients with parathyroid adenoma recurred 2 years after the operation and was found to have malignancy of the parathyroid adenoma.
Conclusion
Not all the patients with parathyroid adenoma had clinical manifestations. The CT and99mTc —MIBI were more accurate than ultrasounography in locating the adenoma. The four glands should be explored during the operation. Protecting the recurrent laryngeal nerve from being injuried and maintaning secure hemastasis were most important.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Courtney M Townsend. Sabiston Textbook of Surgery. Phyiladelphia: W. B. Sanders Company. 2001; 629–645.
Lioyd M Nyhus. Mastery of Surgery. Boston: Little, Brown and Company. 1992; 225–235.
Chen X, Cai WY, Yang WP, et al. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of primary parathyroidism. Clin J Gen Surg. 2003;18:225–226.
Xu SM, Wang P, Zheng YX, et al. Clinical research of primary hyperparathyroidism. Natl Med J China. 2001 ;81: 1453–1455.
Zhang H, Ji ZB, Ding H, et al. Value of high-frequency ultrasonography in diagnosing primary parathyroid diseases. Clin J Ultrasongr. 2002;ll:550–552.
Tang L, Wang RF, Huo L. Clinical value of radionuclide parathyroid imaging in hyperthyroidism. Clin J Med Imaging Technol. 2003;19:863–865.
Xu HZ, Li Y, Zhao YF, et al. Diagnosis and treatment of osteopathic parathyroid adenoma. Chin J Reparative and Reconstr Surg. 2003; 17:446–449.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhang, J., Zhu, D. et al. Diagnosis and surgical treatment of parathyroid adenoma (24 case report). Chin. J. Clin. Oncol. 2, 492–495 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739738
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02739738