Abstract
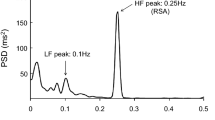
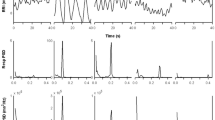
Respiration influences heart rate variability, leading to the suggestion that respiration should be controlled to assess autonomic function by using heart rate variability. Clearly, control of respiration is advantageous or even essential in several experimental circumstances. However, control of respiration, by itself, produces a small, but significant, increase in mean heart rate and a decrease in respiratory synchronous variation in heart rate. We tested whether, in some experimental situations, it may be possible to arrive at similar interpretation about autonomic function with and without using control of respiratory rate. heart rate spectral powers from nine subjects were compared between spontaneous and metronomic breathing during two sympatho-excitatory stresses, lower body negative pressure (LBNP) and head up tilt (HUT). The normalized spectral powers in supine and HUT during spontaneous breathing were: 0.43 and 0.75 in very low (VLF) and 0.28 and 0.09 in high frequency (HF) regions. The powers during metronomic breathing were: 0.36 and 0.82 (VLF) and 0.36 and 0.09 (HF). The powers in supine and LBNP during spontaneous breathing were: 0.43 and 0.81 (VLF) and 0.28 and 0.06 (HF). The powers during metronomic breathing were: 0.36 and 0.80 (VLF) and 0.36 and 0.07 (HF). All p values were <0.05. Therefore, changes in heart rate spectral powers during HUT and LBNP were similar during metronomic breathing and spontaneous breathing. These results suggest that in experimental designs such as in our study, using metronomic breathing may not provide any additional insight into autonomic function than that can be obtained during spontaneous breathing.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed, A.K., J.B. Harness, and A.J. Mearns. Respiratory control of heart rate.European Journal of Applied Physiology. 50:95–104, 1982.
Akselrod, S., D. Gordon, J.B. Madwed, N.C. Snidman, D.C. Shannon, and R.J. Cohen. Hemodynamic regulation: investigation by spectral analysis.American Journal of Physiology, 249 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology 18): H867-H875, 1985.
Bendat JS, Piersol AG. Random Data, Analysis and Measurement Procedures. 2nd Ed. New York: John-Wiley and Sons, 1986.
Brown, T.E., L.A. Beightol, J. Koh, and D.L. Eckberg. Important influence of respiration on human R-R interval power spectra is largely ignored.Journal of Applied Physiology 75:2310–7, 1993.
Eckberg, DL. Human sinus arrhythmia as an index of vagal cardiac outflow.Journal of Applied Physiology Respiratory, Environmental and Exercise Physiology. 54:961–966, 1983.
Hayano, J., S. Mukai, M. Sakakibara, A. Okada, K. Takata, and T. Fujinami. Effects of respiratory interval on vagal modulation of heart rate.American Journal of Physiology 267 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology 36): H33-H40, 1994.
Hirsch, J.A., and B. Bishop. Respiratory sinus arrhythmia in humans: how breathing pattern modulates heart rate.American Journal of Physiology 241 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology. 10): H620–H629, 1981.
Lishner M, Akselrod S, Mor Avi V, Oz O, Divon M, Ravid M. Spectral analysis of heart rate fluctuations. A non-invasive sensitive method for early diagnosis of autonomic neuropathy in diabetes mellitus.Journal of Autonomic Nervous System.: 119–125, 1987.
Malliani A, Pagani M, Lombardi F, Cerutti S. Cardiovascular neural regulation explored in the frequency domain.Circulation, 84:482–492, 1991.
Pagani M, Lombardi F, Guzzeti S, Rimoldi O, Furlan R, Pizzinelli P, Sandrone G, Malfatto G, Dell’Orto S, Piccaluga E, Turiel M, Baselli G, Cerutti S, Malliani A. Power spectral analysis of heart rate and arterial pressure variabilities as a marker of sympatho-vagal interaction in man and conscious dog.Circulation Research, 59:178–193, 1986.
Patwardhan AR, Evans JM, Bruce EN, Eckberg DL, Knapp CF. Voluntary control of respiration does not alter vagal modulation of heart rate. Journal of Applied Physiology. 78(6):2087–2094, 1995.(a).
Patwardhan AR, Evans JM, Berk MR, Knapp CF. Comparison of heart rate and arterial pressure spectra during head up tilt and a matched level of LBNP.Aviation, Space and Environmental Medicine, 66:865–71, 1995.(b).
Patwardhan AR, Vallurupalli S, Evans JM, Bruce EN, Knapp CF. Override of the spontaneous respiratory pattern generator reduces cardiac parasympathetic influence.Journal of Applied Physiology 79:1048–54, 1995.(c).
Saul J.P., R.D. Burger, P. Albrecht, S.P. Stein, M.H. Chen, and R.J. Cohen. Transfer function analysis of the circulation: unique insights into cardiovascular regulation.American Journal of Physiology 261 (Heart and Circulatory Physiology) 30:H1231–1245, 1991
Schwartz, J.B., W.J. Gibb, and T. Tran. Aging effects on heart rate variation.J. Geront., 46: M99-M106, 1991.
Tapp WN, Knox III FS, Natelson BH. The heart rate spectrum in simulated flight: reproducibility and effects of atropine.Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 61:887–892, 1990.Aviation, Space, and Environmental Medicine.
Tobin M.J., M.J. Mador, S.M. Guenther, R.F. Lodato, and M.A. Sackner. Variability of resting respiratory drive and timing in healthy subjects.Journal of Applied Physiology 65(1): 309–317, 1988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patwardhan, A., Evans, J., Bruce, E. et al. Heart rate variability during sympatho-excitatory challenges: Comparison between spontaneous and metronomic breathing. Integr. psych. behav. 36, 109–120 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734045
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02734045