Abstract
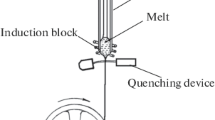
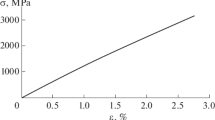
The residual internal stresses in a cylindrical wire produced in the rotating-water melt spinning process and a coated wire obtained by drawing from a melt have been calculated within the thermal viscoelasticity and structural relaxation theories. The coated wire consists of the core and the sheath with different thermal properties. The problem is considered with allowance made for the generation and the relaxation of stresses in the core and the sheath in the temperature range from initial (corresponding to the liquid state of a two-layer wire) to room temperature. The distributions of the residual stresses have been calculated for the free amorphous metallic wire and the amorphous wire with the sheath having a different elastic modulus and thermal expansion coefficient. The influence of preparation conditions and thermal properties of materials on the calculated parameters is analyzed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chiriac, H. and Ovari, T.A., Amorphous Glass-Covered Magnetic Wires: Preparation, Properties, Applications,Prog. Mater. Sci., 1996, vol. 40, no. 5, pp. 333–407.
Velazquez, J., Vazquez, M., Hernando, A.,et al., Magne- toelastic Anisotropy in Amorphous Wires Due to Quenching,J. Appl. Phys., 1991, vol. 70, no. 10, pp. 6525–6527.
Mori, K., Use of Amorphous Alloys in Detectors and Converters, inRapidly Quenched Metallic Alloys, Schtib, S. and Warlimont, G., Eds., New-York: McGraw- Hill, 1986. Translated under the titleBystrozakalennye metallicheskie splavy, Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1989, pp. 345–350.
Usov, N., Antonov, A., Dykhne, A. and Lagar’kov, A., Stress Dependence of the Loops of Co-Rich Amorphous Wires,J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1998, vol. 10, no. 11, pp. 2453–2463.
Liu, J. Malmhall, R., Arnberg, L., and Savage, S., Theoretical Analysis of Residual Stress Effects on the Magnetostrictive Properties of Amorphous Wires,J. Appl. Phys., 1990, vol. 67, no. 9, pp. 4238–4240.
Madurga, V. and Hernando, A., Radial Stress Distribution Generated during Rapid Solidification of Amor- phous Wires,J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 1990, vol. 2, no. 9, pp. 2127–2132.
Aleksandrov, I.V., Zhabotinskii, M.E., and Shush- panov, O.E., Some Problems of Mechanical Reliability of Optical Fibers,Radiotekh., 1982, vol. 37, no. 5, pp. 26–32.
Wysocki, J.B., Colborn, M.N., Alam, S.N.,et al, Low Cycle Fatigue Behavior of Metal-Coated Silica Fibers,J. Non-Cryst. Solids, 1980, vol. 42, no. 1, pp. 261–268.
Christensen, R.,Theory of Viscosoelasticity, New York: Academic, 1972. Translated under the titleVvedenie v teoriyu vyazkouprugosti, Moscow: Mir, 1974.
Lee, E.H., Rogers, T.G. and Woo, T.C., Residual Stresses in a Glass Plate Cooled Symmetrically from Both Surfaces,J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 1965, vol. 48, no. 9, pp. 480–487.
Gardon, R., Thermal Tempering of Glass, inGlass Science and Technology, Uhlman, D.R. and Kreidl, N.J., Eds., New York: Academic, 1980, vol. 5, pp. 145–216.
Gonchukova, N.O., Calculations of Stresses in Heat- Treated Glass,Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 1979, vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 425–430.
Gonchukova, N.O., Zolotarev, S.N. and Tolochko, O.V., Calculations of Stresses in Metallic Glass Ribbon,Fiz. Khim. Stekla, 1990, vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 928–931.
Rekhson, S.M. and Scherer, G.W., Visco-Elastic Com- posites: Bead Seal,J. Am. Ceram. Soc, 1982, vol. 65, no. 9, pp. 419–425.
Amorfhye metallicheskie splavy (Amorphous Metallic Alloys), Lyuborskii, F.E., Ed., Moscow: Metallurgiya, 1987.
Davies, H.A., Rapidly Quenching Techniques and Formation of Metallic Glasses,Proc. Int. Conf. on Rapidly Quenched Metals, Cantor, B., Ed., 1979, vol. 1, pp. 1– 21.
Chen, H.S., A New Aspect of the Glass Transition Process and Structural Relaxation in Metallic Glasses,Proc. IVInt. Conf. on Rapidly Quenched Metals, Sendai, 1981, vol. 1, pp. 495–500.
Zaveta, K., Springman, B.,et al, Relaxation Effects in Fe5Co75B20 Metallic Glass,Proc. IV Int. Conf. on Rapidly Quenched Metals, Sendai, 1981, vol. 1, pp. 523- 527.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antonov, A.S., Borisov, V.T., Borisov, O.V. et al. Calculation of residual stresses in amorphous wires. Glass Phys Chem 26, 353–358 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02731999
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02731999