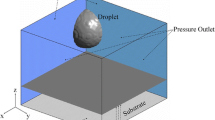
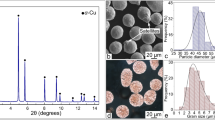
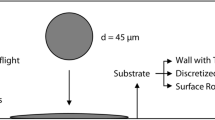
Abstract
Mechanical thermal and adhesive properties of thermal spray coating are primarily determined by the phase and microstructure of single splats, which ultimately depend on rapid solidification of each splat and on the interactions between the splats and between the splat and the substrate. Significant efforts are being made to develop a better understanding of the physical mechanisms underlying these phenomena. This paper reviews a series of work in the area of mathematical modeling of phase and microstructure formation during the rapid solidification of single splats and coatings. The model development has been complimented by special experiments. Conditions under which plantar interface solidification occurs, columnar celluar or dendritic growth takes place, or banded structure forms, have been identified. A microstructure map can therefore built using the model presented here. The process parameters that promote crystalline nucleation and grain structure formation can be isolated and the effect of interfacial heat transfer, splat substrate temperature difference, and substrate melting and resolidification can be examined using the model. The model prediction agree qualitatively well with the experimental data for alumina, yttria, partially-stabilized zirconia, and molybdenum.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aziz M J 1982 Model for solute redistribution during rapid solidification.J. Appl. Phys. 53: 1158–1168.
Baker J C, Cahn J W 1971 Thermodynamics of solidification. InSolidification (Metal Park, OH;Am. Soc. Metals pp 23–58.
Bartlett A H, Maschio R D 1995 Failure mechanisms of a zirconia-8 with yttria thermal barrier coating,J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 78: 1018–1024
Battle U P 1992 Mathematical modeling of solute segregation in solidifying methods.Int. Mater. Rev. 37: 249–270
Beckermann C, Wang C Y. 1995 Multiphase/-scale modeling of alloy solidification.Annu. Rev. Heat Transfer 6: 115–198
Boettinger W J, Coriell S R 1986 Microstructure formation in rapidly solidified alloys. InScience and technology of the undercoated melt. (eds.) P. R Sahm, H Jones, C M Adam (Martinus Nijhoff) pp 81–109.
Carrard M, Gremand M, Zimmermann M, Kurz W 1992 About the banded structure in rapidly solidified dendritic and eutectic alloys.Acta. Metall. Mater. 40: 983–996.
Clyne T W 1982 Numerical modeling of directional solidification of metallic alloys.Metal Sci. 16: 441–450
Clyne T W 1984 Numerical treatment of rapid solidification.Metall. Trans. B15: 369–381
Feuerbacher B 1989Phase formation in metastable solidification of metals.Mater. Sci. Rep. 4: 1–40
Flood S C, Hutt J D 1987 Columnar and equiaxed growth, I. A model of a columnar front with a temperature dependent velocity.J. Crystal Growth 82: 543–551
Gansert R V 1996 Plasma-spray processing of alumina-based free-forms using water-stabilized plasma. Ph D thesis, State University of New York at Stony Brook, Stony Brook
Giovanola B, Kurz W 1990 Modeling of microsegregation under rapid solidification conditions,Metall. Trans. A21: 260–263.
Goswami R, Wang G-X, Sampath S, Herman H 1999 Synthesis of zirconia-8wt.% yttria nanocomposites by thermal spray. 1999TMS Annual Meeting, San Diego, CA (Warrendale, PA: TMS)
Granasy L, Ludwig A 1992 Impact of casting conditions of the dendritic solidification in single roller quencing methods (simulation). InMelt-spinning and strip casting: Research and implementation (ed.) E F Matthys (Warrendale PA: TMS), pp 53–68.
Jacobson L A, McKittrick J 1994 Rapid solidification processing.Mater. Sci. Eng. R11: 355–408.
Jiang X Y, Sampath S, Matejieck J 1999 Substrate temperature effects on splat formation, microstructure development and properties of plasma sprayed coatings, Part II: Case study for molybdenum.Mater. Sci. Eng. A272: 189–198.
Jiang X Y, Sampath S, Herman H 2000 Grain morphology of molybdenum splats plasma-sprayed on glass substrates.Mater. Sci. A (submitted).
Karma A, Sarkissian A 1993 Interface dynamics and banding in rapid solidification.Phys. Rev. 47: 513–533.
Kim S G, Shin S H, Suzuki T, Umede T 1994 Numerical analysis of the rapid solidification of gas- atomized Al-8 wt pct Fe droplets.Metall. Mater. Trans. A25: 2815–2826.
Kurz W, Fisher D J 1989Fundamentals of solidification. 3rd edn (Trans. Tech. Publ.)
Levi C G 1988 The evolution of microcrystalline structures in supercooled metal powders.Metall. Trans. A19: 699–708.
Levi C G, Mehrabian R 1982 Heat flow during rapid solidification of undercooled metal droplets.Metall. Trans. A13: 221–234
Lu S Z, Hunt J D, Gilgien P, Kurz W 1994 Cellular and dendritic growth in rapidly solidified Al-Fe and Al-Cu alloys.Acta. Metall. Mater. 42: 1653–1660
McPherson R. 1980 On the formation of thermally sprayed alumina coatings.J. Mater. Sci. 15: 3141–3149
Moreau C, Lamontagne M, Crelo P 1992 Influence of the coating thickness on the cooling rates of plasma-sprayed particles impinging on a substrate.Surf. Coating Tech. 53: 107–114
Mostaghinu J, Pasandideh Fard M, Azar R G, Chandra S 1999 Modeling of the formation of the thermal spray coatings. Presented at the Mater. Res. Soc. Fall Meeting, Boston MA
Rappar M 1989 Modelling of microstructure formation in solidification processes;Int. Mater. Rev. 34: 93–123
Robert C, Denoirjean A, Vardelle A, Wang G-X, Sampath S 1998a Nucleation and phase selection in plasma-sprayed Al2O3: Modeling and experiments.Proc. 15th Int Thermal Spray Conference, Nice, France. pp 407–412
Robert C, Vardelle A, Wang G-X, Jiang X, Sampath S 1998b Microstructure development during plasma spraying of molybdenum, Part I: Splat solidification.Proc. 15th Int. Thermal Spray Conference, Nice, France. pp 729–734
Sampath S, Herman H 1996 Rapid solidification and microstructure development during plasma spraying.J. Thermal Spray Tech. 5: 445–456
Sampath S, Neiser R A, Herman H, Kirkland J P, Elam W T 1993 A structural investigation of a plasma sprayed Ni-Cr based alloy coating.J. Mater. Res. 8: 78–86
Sampath S, Jiang X Y, Matejicek J, Legger A C, Vardelle A 1999 Substrate temperature effects on splat formation, microstructure development and properties of plasma sprayed coatings. Part I: Case study for partially stabilized zirconia.Mater. Sci. Eng. A272: 181–188
Trapaga G, Szekely J 1991 Mathematical modeling of the isothermal impingement of liquid droplets in spraying processes.Metall. Trans. B 22: 901–914
Trivedi R, Kurz W 1986 Morphological stability of a planar interface under rapid solidification conditions.Acta Metall. 34: 1663–1670
Trivedi R., Kurz W 1994 Dendritic growth,Int. Mater. Rev. 39: 49–74
Vardelle A, Robert C, Wang G-X, Sampath S 1997 Analysis of nucleation, phase selection and rapid solidification of an alumina splat. InThermal spray: A united forum for scientific and technological advances (ed.) CC Berndt (Materials Park, OH: ASM Int.) pp. 635–643
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1991 Modeling of heat transfer and solidification during splat cooling: Effect of splat thickness and splat/substrate thermal contact.Int. J. Rapid Solidification 6: 141–174
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1992 Numerical of phase change and heat transfer during rapid solidification processes: Use of control volume intergal with element subdivision.Int. J. Heat Mars Transfer 35: 141–153
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1993 Modeling of rapid planar solidification of a binary alloy. InHeat and mass transfer in materials processing and manufacturing (New York: ASME):vol. HTD 261, pp 35–44
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1996a Modeling of surface melting and resolidification for pure metals and binary alloys: Effects of non-equilibrium kinetics.J. Heat Transfer. 118, 944–951
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1996b Experimental investigation of interfacial thermal resistance for molten metal solidification on a substrate.J. Heat Transfer. 118, 157–163
Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1996c On the heat transfer at the interface between a solidifying metal and a solid substrate. InMelt-spinning, strip casting and slab casting (eds.) E F Matthys, W G Truckner (Warrendale, PA: TMS) pp 205–236
Wang G-X, Prasad V, 2000 Rapid solidification: Fundamentals and modeling,Annu. Rev. Heat Transfer 11: 207–305
Wang G-X, Prasad V, Sampath S, Herman H 1998 A mathematical model for microsegregation in rapidly solidified alloys. InModeling casting, welding advanced solidification processes — VIII, (eds.) B G Thomas C Beckermann (Warrendale, PA: TMS) pp 219–226
Wang G-X, Prasad V, Sampath S 2000a An interated model for dendritic planar interface growth and morphology transition rapid solidification.Metall. Mater. Trans. A31: 735–746
Wang G-X, Goswami R, Sampath S, Prasad V 2000b Heat transfer and solidification analysis of splat formation in plasma-sprayed zirconia-yttrin thermal barner coatings.4th ISHMT-ASME Heat Transfer Conferrence (New Delhi Tata-McGraw-Hill) pp 1135–1140.
Wang G-X, Hang X Y, Sampath S 2000c Grain structure development in plasma-sprayed coatings: Experiment and modeling. InSurface engineering in materials science I (eds) S Sealet al (Warrendale, PA; TMS) pp 197–209
Wang S-P, Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1998 Melting and resolidification of a substrate in contact with a molten metal: Operational maps.Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 41: 1177–1188
Wang S-P, Wang G-X, Matthys E F 1999 Deposition of a molten layer of high melting point meterial: Substrate melting and resolidification,Mater. Sci. Eng. A262: 25–32
Zhang H 1999 Theoretical analysis of spreading and solidification of molten droplet during thermal spray deposition.Int. J. Heat Mass Transfer 42: 2499–2508
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, GX., Prasad, V. & Sampath, S. Rapid solidification in thermal spray deposition: Microstructure and modelling. Sadhana 26, 35–57 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02728478
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02728478