Summary
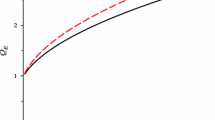
The maximum-anisotropy approximation, introduced by Baraff for the solution of the Boltzmann equation in semiconductor problems, is used here analogously for discussing the electron motion in a ionized gas. An expression for the drift velocity of electrons is derived under simplifying assumptions on the velocity dependence of the collision parameters. For the most significant ranges of these collision parameters numerical values of the drift velocity, properly normalized, are also given. The results are most useful for the case of gases, in which the fractional energy loss of electrons per collision is large.
Riassunto
L'approssimazione di massima anisotropia, introdotta da Baraff per risolvere l'equazione di Boltzmann in problemi semiconduttoristici. è qui usata in modo analogo per discutere il moto degli elettroni in un gas ionizzato. Si deriva un'espressione per la velocità di trascinamento degli elettroni, dopo aver introdotto ipotesi semplificative sulla dipendenza dalla velocità dei parametri d'urto. Per i campi più significativi di questi parametri d'urto si danno anche valori numerici della velocità di trascinamento, opportunamente normalizzata. I risultati sono particolarmente utili nel caso di gas in cui la frazione di perdita d'energia degli elettroni per urto è grande.
Резюме
В этой работе приближение максимальной анизотропии, предложенное Бараффом для решения уравнения Больцмана в проблемах полупроводников, используется для обсуждения движения электрона в ионизованном газе. Выводится выражение для скорости дрейфа электронов при упрошающих предположениях относительно зависимости скорости от параметров соударения. Приводятся нормированные соответствующим образом численные значения скорост дрейфа для наиболее существенных областей параметров соударения. Полученные результаты оказываются особенно полезными для случая газов, в которых доля энергетических потерь для электронов в результате соударений является большой.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. A. Baraff:Phys. Rev.,133, A 26 (1964).
See, for example,I. P. Shkarofsky: T. W. Johnston andM. P. Bachynski:The Particle Kinetics of Plasmas (Reading, Mass, 1966);A. L. Gilardini:Low Energy Electron Collisions in Gases (New York, N. Y., 1972).
In the opposite case,h<−1, runaway phenomena appear and there is no longer a steady-state equilibrium distribution function. SeeG. Cavalleri andS. Paveri-Fontana:Phys. Rev. A,6, 327 (1972).
See, for example,P. M. Morse andH. Feshbach:Methods of Theoretical Physics (New York, N. Y., 1953).
R. B. Dingle:Asymptotic Expansions: Their Derivation and Interpretation (London, 1973).
G. Cavalleri: private communication, to be published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Переведено редакцией.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilardini, A. Drift velocity of electrons in a gas where the electron energy loss per collision is large. Nuov Cim B 27, 59–64 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726338
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726338