Summary
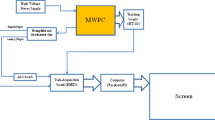
The data of measurements taken near Elbrus in the (600÷1000) mb atmospheric-depth range are used to study the angular distribution and the altitude dependence of the cosmic-ray general and muon components. The measurements were taken with a system of scintillation telescopes at 0°, 30°, 45° and 60° zenith angles and at 100°, 80°, 65° and 40° apertures, respectively. The muon component was isolated with a 10 cm thick lead screen. The angular distribution was set in the formI(θ,h)=I 0(h)[cos θ]n(h), where θ is the zenith angle,h is the atmospheric depth. Relations have been obtained which permit the parametern(h) to be plotted on the basis of the measured values of cosmic-ray intensity at various depths by using the above-mentioned four telescopes. It has been found that, ash varies from 600 to 1000 mb,n varies from 0.6 to 1.6 for the muon component and from 1.2 to 1.9 for the general component. The found altitude dependences permit the barometric coefficients to be determined for the various detection directions as functions of the pressure at the observation level.
Riassunto
I dati delle missurazioni effettuate nei pressi dell'Elbrus nell'intervallo di profondità atmosferica tra 600 e 1000 mb sono usati per studiare la distribuzione angolare e la dipendenza dall'altezza delle componenti generali e muoniche dei raggi cosmici. Le misurazioni sono state fatte con un sistema di telescopi a scintillazione, con angoli zenitali di 0°, 30°, 45° e 60° con rispettive aperture di 100°, 80°, 65° e 40°. La componente muonica è stata isolata per mezzo di uno schermo di piombo di 10 cm di spessore. La distribuzione angolare è stata posta nella formaI(θ,h)=I 0(h)[cos θ]n(h), dove θ è l'angolo zenitale,h è la profondità atmosferica. Si sono ottenute relazioni che permettono al parametron(h) di essere posto in diagramma sulla base dei valori dell'intensità dei raggi cosmici misurati alle varie profondità atmosferiche, usando i suddetti quattro telescopi. Si è trovato che, al variare dih da 600 a 1000 mb,n varia da 0.6 a 1.6 per la componente muonica e da 1.2 a 1.9 per la componente generale. La dipendenza dall'altezza che si è trovata ci permette di determinare i coefficienti barometrici per le varie direzioni di rilevazione in funzione della pressione ai livelli di osservazione.
Резюме
Данные измерений, проведенных недалеко от Эльбруса в области атмосферных толщин (600÷1000) мб, используются для исследования углового распределения и высотной зависимости общей и мюонной компонент космических лучей. Измерения проведены с помощью системы сцинтилляционных телескопов при зенитных углах 0°, 30°, 45° и 60° и при апертурах соответственно 100°, 80°, 65° и 40°. Мюонная компонента выделяется с помощью толстого свинцового экрана 10 см. Угловое распределение можно представить в видеI(θ,h)=I 0(h)[cos θ]n(h), где θ—зенитный угол,h-атмосферная толщина. Получены соотнощения, которые позволяют табулировать параметрn(h) на основе измеренных эначений интенсивности космических лучей при различных толщинах, испольэуя четыре вышеукаэанных телескопа. Установлено, что при измененииh от 600 до 1000 мб,n изменяется от 0.6 до 1.6 для мюонной компоненты и от 1.2 до 1.9 для общей компоненты. Полученные зависимости от высоты позволяют определить барометрические коэффициенты для различных направлений детектирования, как функции давления на уровне наблюдения. Подробно исседуется угловое распределение мюонной компоненты на уровне моря и на малых глубинах под землей. В то же время угловая зависимость интенсивности космически лучей на различных высотах изучена недостаточно.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
N. A. Dobrotin:Cosmic Rays (Moscow, 1954).
L. I. Dorman:Meteorological Effects in Cosmic Rays (Moscow, 1972).
A. I. Kuzmin, G. F. Krymaky andG. V. Skripin:Trans. Yahutsk Branch Acad. Sci. USSR,4, 22 (1961).
V. N. Aleksandrov, Ya. L. Blokh, I. V. Dorman, I. Ia. Libin, V. L. Kachevazov, J. I. Sorokin, Y. Ch. Chalachov andH. Hamirsov: Col. papersCosmic Rays, No. 15 (Moscow, 1975).
E. George:Cosmic-Ray Physics (Moscow, 1954).
Ya. L. Blokh, L. I. Dorman andI. Ya. Libin: Col. PapersCosmic Rays, No. 14 (Moscow, 1974), p. 141.
S. N. Vernov andA. M. Kulikov:Dokl. Akad. Nauk SSSR,73, 483 (1950).
I. E. Allen:Proc. Roy. Soc.,265 A, 117 (1961).
S. A. Azikhov:Trudy FIAN,4, 315 (1949).
C. A. Randoll andW. T. Hazen:Phys. Rev.,81, 144 (1951).
A. S. Baigubekov andV. M. Ivanenko:High-Energy and Cosmic-Ray Physics (Alma-Ata, 1971).
K. I. Greisen:Phys. Rev.,63, 323 (1943).
L. I. Dorman, V. G. Yanke, M. B. Bagdasarian, R. T. Guchina andJ. A. Pimenov: Col. papersCosmic Rays, No. 14 (Moscow, 1974), p. 57.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Traduzione a cura della Redazione.
Переведено редакцией.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blokh, Y.L., Dorman, L.I. & Libin, I.Y. Studies of the angular distribution and of the altitude dependence of the cosmic-ray muon and general components using scintillation telescopes. Nuov Cim B 37, 198–202 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726317
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02726317