Summary
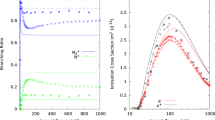
Low-energy elastic cross-sections of positrons and electrons colliding with alkali atoms are calculated in a simple approach which makes use of i) the pseudopotential formalism to reduce the many-electron alkali atom to an effective one-electron model atom, ii) the Stone variational formulation of the polarized orbital method (POM) to calculate the polarization potentials, and iii) the JWKB semi-classical approximation to determine the phase shifts. The calculations are straightforward and the results encouraging. The cross-sections for both positron and electron scattering are plotted for energies of the incoming particle ranging from 0.8 eV to 6.8 eV, and compared to pertinent calculations and measurements available in the literature. The present approach may result of considerable use in scattering problems involving many-electron atoms, where, as a rule, great computational difficulties must be overcome.
Riassunto
Si calcolano sezioni d’urto di collisione elastica a bassa energia di positoni ed elettroni con atomi alcalini, seguendo un semplice approccio che fa uso: 1) del formalismo, dello pseudopotenziale per ridurre l’atomo alcalino ad un atomo modello con un solo elettrone (quello di valenza), 2) delle formulazione variazionale di Stone del metodo dell’orbitale polarizzato per calcolare i potenziali di polarizzazione, e 3) dell’approssimazione semiclassica JWKB per determinare gli spostamenti di fase. I calcoli sono molto semplici e i risultati incoraggianti. Le sezioni d’urto sono riportate graficamente per un intervallo di energia della particella incidente che va da 0.8 eV a 6.8 eV, e confrontate con dati teorici e sperimentali presenti nella letterature. II presente approccio può risultare utile in problemi di collisioni che coinvolgono atomi a molti elettroni, dove di regola occorre superare grosse difficoltà di calcolo.
Резюме
Вычисляются поперечные сечения упругого рассеяния позитронов и злектронов на щелочных атомах при низких знергиях в простом подходе, в котором использужтся: 1) псевдопотенциальный формализм, чтобы преобразовать многозлектронный щелочной атом к модельному зффективному однозлектронному атому; 2) вариационная формулировка Стоуна метода поляризованных орбиталей для вычисления поляризационных потенциалов; и 3) квази-классическое приближение для определения фазовых сдвигов. Вычисления являются прямыми и результаты обнадеживающие. Вычерчиваются поперечные сечения рассеяния злектронов и позитронов, как функции знергии падающих частиц в области от 0.8 зВ до 6.8 зВ. Полученные результаты сравниваются с вычислениями и измерениями, имеющимися в литературе. Предложенный подход может быть использован для анализа проблем рассеяния на многозлектронных атомах, где, как правило, встречаются большие вычислительные трудности.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A review article on slow positrons in gases by SirH. Massey has recently appeared onPhysics Today (29, 42, March 1976).
See, for instance,B. H. Bransden:Positron collisions, inGas Studies in Atomic-Collision Physics,1, 171 (1969)
See, for instance,J. N. Bardsley:Pseudopotentials in atomic and molecular physics, inGas Studies in Atomic-Collision Physics,4, 299 (1974).
T. D. Bui andA. D. Stauffer:Can. Journ. Phys.,49, 2527 (1971).
K. Sarkar, B. C. Saha andA. S. Ghosh:Phys. Rev. A,8, 236 (1973).
W. R. Garrett andR. A. Mann:Phys. Rev.,130, 658 (1963).
P. M. Stone andJ. R. Reitz:Phys. Rev.,131, 2101 (1963).
W. R. Garrett andR. A. Mann:Phys. Rev.,135, A 580 (1964).
W. R. Garrett:Phys. Rev.,140, A 705 (1965).
P. M. Stone:Phys. Rev.,141, 137 (1966).
L. C. Balling:Phys. Rev.,179, 78 (1969).
T. D. Bui andA. D. Stauffer:Can. Journ. Phys.,49, 1670 (1971).
Vo Ky Lan:J. Phys. B,4, 658 (1971).
E. Karule: inProceedings of the IV ICPEAC, Quebec 1965, edited byL. Kerwin andW. Fite (New York, N. Y., 1965), p. 139;Tr. Inst. Fiz. Akad. Nauk Ltv. SSR,3, 33 (1965).
E. Karule andR. Peterkop: inProceedings of the IV ICPEAC, Quebec, 1965. edited byL. Kerwin andW. Fite (New York, N. Y., 1965), p. 134.
D. L. Moores andD. W. Norcross:J. Phys. B,5, 1482 (1972).
P. G. Burke andJ. F. B. Mitchell:J. Phys. B,6, L161 (1973).
A. L. Sinfailam andR. K. Nesbet:Phys. Rev. A,7, 1987 (1973).
H. R. J. Walters:J. Phys. B,6, 1003 (1973).
A. N. Tripathi, K. C. Mathur andS. K. Joshi:Journ. Chem. Phys.,58, 1384 (1973).
T. D. Bui andA. D. Stauffer:Can. Journ. Phys.,53, 1615 (1975).
H. R. J. Walters:J. Phys. B,9, 227 (1976).
J. Perel, P. Englander andB. Bederson:Phys. Rev.,128, 1148 (1962).
R. E. Collins, B. Bederson andM. Goldstein:Phys. Rev. A,3, 1976 (1971).
P. J. Visconti, J. A. Slevin andK. Rubin:Phys. Rev. A,3, 1310 (1971).
J. A. Slevin, P. J. Visconti andK. Rubin:Phys. Rev. A,5, 2065 (1972).
B. Bederson:Comm. At. Mol. Phys.,1, 135 (1970);2, 7 (1970).
R. J. Drachman andA. Temkin:Polarized orbital approximations, inGas Studies in Atomic-Collision Physics,2, 401 (1972).
M. R. C. McDowell andJ. P. Coleman:Introduction to the Theory of Ion-Atom Collisions, Chap. 2 (Amsterdam, 1970), p. 76.
L. Landau andE. Lifchitz:Mecanique quantique, deux. ed., Chap. VII (Moscow, 1967), p. 192, 204.
G. A. Hart andP. L. Goodfriend:Journ. Chem. Phys.,53, 448 (1970).
P. Cavaliere andG. Ferrante:Nuovo Cimento,14 B, 127 (1973).
G. Ferrante andM. Zarcone: Technical Report APP-76-01, Institute of Physics, University of Palermo (in preparation).
Calculations on e+-Li, by the authors, are in progress by using nonlocal Hellmann model potentials and Slater-type wave functions.
M. Cohen andP. S. Kelly:Can. Journ. Phys.,45, 1661 (1967).
K. Rubin, quoted byMoores andNorcross, ref. (16).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
To speed up publication, the authors of this paper have agreed to not receive the proofs for correction.
Переведено редакцией.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bordonaro, G., Ferrante, G., Zarcone, M. et al. Positron- and electron-alkali atom low-energy elastic scattering by a JWKB-approximated polarized orbital method. Nuov Cim B 35, 349–362 (1976). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724070
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02724070