Summary
By considering Hamiltonian actions of real Lie groupsG (respectively real Lie algebrasg and complex Lie algebrasg o) not necessarily semi-simple on a real sympletic manifold, the suitable liftings into the Lie algebra of complex-valued functions defined on the manifold are examined. The analysis is centred on complex Cartan subalgebrash o⊂g o and the corresponding vector subspacese c spanned by the common eigenvectors arising from the restricted adjoint action on the root spaces ofg o. Some new insight about the structure of these algebras are obtained, which lead to the following main result:any (essential) action is Poissonian (i.e. the corresponding cohomology classes are null) on h o×e o.
Riassunto
Considerando azioni hamiltoniane di grupi di Lie realiG (rispettivamente algebre di Lie realig e algebre di Lie complesseg o) non necessariamente semisemplici su una varietà reale simplettica, si esaminano sollevamenti adeguati all’interno dell’algebra di Lie di funzioni e valori complessi sulla varietà. L’analisi è centrata su subalgebre complesse di Cartanh o⊂g o ed i corrispondenti sottospazi vettorialie o estesi dagli autovettori comuni che derivano dall’azione aggiunta ristretta sugli spazi originali dig o. Si ottengono alcufile nuove osservazioni riguardo la struttura di queste algebre, che portano al seguente importante risultato:qualsiasi azione (essenziale) è poissoniana (cioè le corrispondenti classi di coomologia sono nulle) su J o×e o.
Резюме
Рассматривая гамильтоновы действия для вещественных групп ЛиG (соответственно, вещественные алгебры Лиg, комплексные алгебры Лиg o), не обязательно полупростые на вещественном симплексном множестве, исследуются соответствующие поднимания в алгебре Ли комплексных функций, определенных на множестве. Проводится анализ комплексных субалгебр Картанаh o⊂g o и соответствующих векторных подпространствe o, сканируемых обшими собственными векторами, возникаюцими из ограниченного сопряженного действия на пространствахg o. Получаются некоторые новые представления, касаюшиеся этих алгебр, которые приводят к следующему основному реультату: любое (существенное) действие является пуассоновым (т.е. соответствующие когомологические классы являются нулевыми) наh o×e o.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. Abraham andJ. E. Marsden:Foundations of Mechanics, 2nd Edition (London, 1978).
V. Arnold:Les méthodes mathématiques de la mécanique classique (Paris, 1969).
G. Godbillon:Geometrie differentielle et mécanique analytique (Paris, 1969).
J. M. Souriau:Structure des systèmes dynamiques (Paris, 1970).
N. Mukunda andE. C. Sudarshan:Classical dynamics: a Modern Perspective (New York, N.Y., 1974).
F. Bunchaft:Lett. Nuovo Cimento,16, 399 (1976).
A complex tensor field is a section of the suitable complexified tensor bundle (over a real manifold) constructed, in a canonical way, through theC ∞ differentiable function ⊗C. A (real or complex) Lie algebra action on (M, w⊗lc) is a Lie-algebra homomorphism:
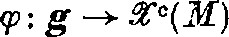 . ClearlyG (respectivelyg) actions on (M, w ⊗ 1c) and (M, w) can be naturally identified (6).
. ClearlyG (respectivelyg) actions on (M, w ⊗ 1c) and (M, w) can be naturally identified (6).For (M, w ⊗1c), notation follows (6). otherwise (1)R. Abraham andJ. E. Marsden:Foundation of Mechanics, 2nd Edition (London, 1978).
In the directiong→G, this last assertion is necessarily true only locally onG andM, otherwise simply connectedness onG and compactness onM must be required. Besides, whenM is simply connected, any action is Hamiltonian (there will be a momentum).
g o=g ⊗C is a particular case.
V. Bárgmann:Z. Phys.,99, 576 (1936).
D. J. Winter:Abstract Lie Algebras (London, 1972).
V. S. Varadarajan:Lie Groups, Lie Algebras and their representations (Englewood, N. J., 1974).
Y. Chow:General Theory of Lie Algebras (New York, N.Y., 1978).
Clearly the construction becomes trivial ifg is Abelian.
Canonical identificationE ** withE, for any finite-dimensional vector spaceE, will always be considered.
There can be more than one common eigenvector for the same root αc, soe o includes all of them.
F. Bunchaft:Proceedings of the I Seminario de Pesquisas em Andamento (Salvador, Brasil, 1983).
As already made clear, the analysis is essentially referred to complex Lie algebras, so hereafter we will omit the corresponding superscript c every time it will be possible.
e βcan also bee β=e'α≠e α, see (17).
N. Mukunda:J. Math. Phys. (N. Y.),8, 1069 (1967).
P. B. Guest:Nuovo Cimento A,61, 593 (1969).
G. Caratú, G. Marmo, A. Simoni, B. Vitale andF. Zaccaria.Nuovo Cimento B,19, 1228 (1974).
F. Bunchaft:Nuovo Cimento A,25, 110 (1975).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Traduzione a cura della Redazione.
Переведено редакцией.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bunchaft, F. Some determinations on the lifting problem of Hamiltonian actions on sympletic manifolds. Nuov Cim B 85, 149–160 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02721556
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02721556



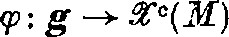 . ClearlyG (respectivelyg) actions on (M, w ⊗ 1c) and (M, w) can be naturally identified (6).
. ClearlyG (respectivelyg) actions on (M, w ⊗ 1c) and (M, w) can be naturally identified (6).