Abstract
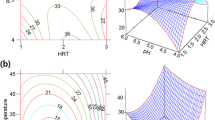
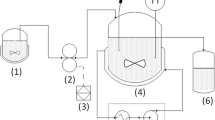
The effect of operating parameters (temperature and time) and various reaction modes(batch, semi-batch and continuous flow) on the behavior of amino acid production from hydrothermal decomposition of fish-derived wastes was investigated. The amino acids obtained in batch experiments at 523 K were mainly alanine (Ala) and glycine (Gly) at maximum yield of 65 and 28 mg/g-dry fish, respectively. At a relatively lower temperature of 473 K, the relative concentration of high-molecular-weight amino acids such as aspartic acid (Asp) and serine (Ser) is significantly high, but decreases as temperature increases. It is likely that high-molecular-weight amino acids decompose faster than low-molecular ones. Semi-batch and continuous flow modes of reaction suppressed decomposition of amino acids into organic acids (or volatile materials) by continuously removing the products from the reaction zone as soon as they were formed. Thus, a large amount of high-molecular-weight amino acids such as Asp and Ser at these reaction modes was observed. This increases the yield of total amino acids at short reaction time and at temperature relatively higher than 523 K. It was also observed that the composition of the resulting products also depends on the modes of reaction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adschiri, T., Sato, O., Machida, K., Saito, N. and Arai, K., “Recovery of Terephthalic Acid by Decomposition of PET in Supercritical Water,”KagakuKogaku,23, 505 (1997).
Daimon, H., Kang, K., Sato, N. and Fujie, K., “Development of Marine Waste Recycling Technologies using Sub- and Supercritical Water,”J. Chem. Eng. Japan,34, 1091 (2001).
Goto, M., Nada, T., Kawajiri, S., Kodama, A. and Hirose, T., “Kinetic Analysis for Destruction of Municipal Sewage Sludge and Alcohol Distillery Wastewater by Supercritical Water Oxidation”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,38, 1863 (1999).
Kang, K., Quitain, A. T., Daimon, H., Noda, R., Goto, N., Hu, H. and Fujie, K., “Optimization of Amino Acids Production from Waste Fish Entrails by Hydrolysis in Sub- and Supercritical Water“,Can. J. Chem. Eng.,65, 79 (2001).
Kang, K., Quitain, A. T., Urano, S., Daimon, H. and Fujie, K., “Rapid Sample Injection in Semi-batch Hydrothermal Treatment of Solid Waste,”Ind. Eng. Chem. Res.,40, 3717 (2001).
Kang, K. Y. and Chun, B. S., “Behavior of Hydrothermal Decomposition of Silk Fibroin to Amino Acids in Near-critical Water”,Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21, 654 (2004).
Kim, Y J., Hong, W H. and Wozny, G., “Effect of Recycle and Feeding Method on Batch Reactive Recovery System of Lactic Acid,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 808 (2002).
Meyer, J. C., Marrone, P. A. and Tester, J. W., “Acetic Acid Oxidation and Hydrolysis in Supercritical Water,”AIChEJ.,41, 2108 (1995).
Park, J. H. and Park, S. D., “Kinetics of Cellobiose Decomposition under Subcritical and Supercritical Water in Continuous Flow System,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 808 (2002).
Sasaki, M., Kabyemela, B., Malaluan, R., Hirose, S., Takeda, N., Adschiri, T. and Arai, K., “Cellulose Hydrolysis in Subcritical and Supercritical Water”,J. Supercrit. Fluids,13, 261 (1998).
Savage, P.E., “Organic Chemical Reactions in Supercritical Water,”Chem. Rev.,99, 603 (1999).
Seo, Y., Hong, W H. and Hong, T. H., “Effects of Operation Variables on the Recovery of Lactic Acid in a Batch Distillation Process with Chemical Reactions,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,16, 556 (1999).
Shanableh, A., “Production of Useful Organic Matter from Sludge using Hydrothermal Treatment,”Wat. Res.,34, 945 (2000).
Shaw, R.W., Brill, T. B., Clifford, A. A., Eckert, C. A. and Franck, E. U., “Supercritical Water: A Medium for Chemistry,”Chem. Eng. News,12, 26 (1991).
Yoshida, H., Terashima, M. and Takahashi, Y., “Production of Organic Acids and Amino Acids Production from Fish Meat by Subcritical Water Hydrolysis”,KagakuKougyou,50, 57 (1999).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, KY., Chun, BS. Behavior of amino acid production from hydrothermal treatment of fish-derived wastes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 21, 1147–1152 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02719486
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02719486