Abstract
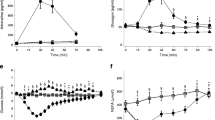
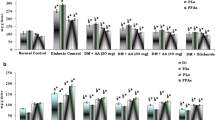
Intraperitoneal administration of lipoic acid (10 mg/100 g) does not effect changes in serum insulin levels in normal and alloxan diabetic rats, while normalising increased serum pyruvate, and impaired liver pyruvic dehydrogenase characteristic of the diabetic state. Dihydrolipoic acid has been shown to participate in activation of fatty acids with equal facility as coenzyme A. Fatty acyl dihydrolipoic acid however is sparsely thiolyzed to yield acetyl dihydrolipoic acid. Also acetyl dihydrolipoic acid does not activate pyruvate carboxylase unlike acetyl coenzyme A. The reduced thiolysis of Β-keto fatty acyl dihydrolipoic acid esters and the lack of activation of pyruvic carboxylase by acetyl dihydrolipoic acid could account for the antiketotic and antigluconeogenic effects of lipoic acid
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CoA:
-
Coenzyme A
- DTO:
-
dihydrolipoic acid
- DTNB:
-
5, 5′ dithiobis (2 nitrobenzoic acid)
- DTT:
-
dithiothreitol
- NAD:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide
- PD:
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- PC:
-
pyruvate carboxylase
References
Burch, R. E. and Wertheim, A. R. (1973)Am. J. Clin. Nutr.,26, 814.
Carreau, J. P., Lapous, D. and Raulin, J. (1977)Biochimie,59, 487.
Carreau, J. P. (1979)Methods Enzymol.,62, 152.
Cate, R. L. and Roche, T. E. (1983)J. Biol. Chem.,258, 4771.
Chiba, T. (1969)Yakugaku Zasshi,89, 248.
Dang, A. Q., Faas, F. M. and Carter, W. J. (1984) Lipids,19, 578.
Drummond, G. I. and Stern, J. R. (1957)J, Am. Chem. Soc.,79, 2657.
Drummond, G. I. and Stern, J. R. (1961)J. Biol. Chem.,236, 2886.
Gunsalus, I. C., Barton, L. S. and Gruber, W. (1956)J. Am. Chem. Soc.,78, 1763.
Haugaard, N. and Haugaard, E. S. (1970)Biochim. Biophys. Acta,222, 583.
Herbert, A. A. and Guest, J. R. (1975)Arch. Microbiol.,106, 259.
Herbert, V., Lan, K. S., Gottlieb, C. W. and Bleicher, S. J. (1965)J. Clin. Endocrinol.,25, 1375.
Hers, H. G. and Hue, L. (1983)Ann. Rev. Biochem.,52, 617.
Hughes, W. A., Brownsey, R. W. and Denton, R. M. (1980)Biochem. J.,192, 469.
Kerbey, A. L., Randle, P. J., Cooper, R. H., Whitehouse, S., Pask, A. T. and Denton, R. M. (1976)Biochem. J.,154, 327.
Lavis, V. R. and Williams, R. H. (1970)J. Biol. Chem.,245, 23.
Linn, T. C, Pelley, J. W., Pettit, F. H., Hucho, F., Randall, D. D. and Reed, L. J. (1972)Arch. Biochem. Biophys.,148, 327.
Lipmann, F. and Tuttle, L. C. (1945)J. Biol. Chem.,159, 21.
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L. and Randall, R. J. (1951)J. Biol. Chem.,193, 265.
Martin, B. R. and Denton, R. M. (1970)Biochem. J.,117, 861.
May, J. M. and Mikulecky, D. C. (1983)J. Biol. Chem.,258, 4771.
McClure, W. R. and Lardy, H. R. (1971)J. Biol. Chem.,246, 3591.
Natraj, C. V., Gandhi, V. M. and Menon, K. K. G. (1984)J. Biosci.,6, 37.
O’Connor, T. P., Roche, T. E. and Paukstelis, J. V. (1982)J. Biol. Chem.,257, 3110.
Ohgaku, S., Brady, P. S., Schumann, W., Bartsch, G. E., Margolis, J. M., Kumaran, K., Landau, S. B. And Landau, B. R. (1983)J. Biol. Chem.,257, 9283.
Randle, P. J. (1966)Symp. Med. Hoechst,12, 97.
Reed, L. J. (1974)Acc. Chem. Res.,7, 40.
Rudermann, N. B., Aoki, T. T. and Cahill, G. F. Jr., (1976) inGluconeogenesis—Regulation in Mammalian Species (eds R. W. Hanson and M. A. Mehlman) (New York: Academic Press) p. 515.
Sauer, F. and Erfle, J. D. (1966)J. Biol. Chem.,241, 30.
Scrutton, M. C, Olmsted, M. R. and Utter, M. F. (1969)Methods Enzymol.,13, 235.
Segal, H. L. and Menon, K. K. G. (1961)J. Biol. Chem.,236, 2872.
Somogyi, M. (1952)J. Biol. Chem.,195, 19.
Spoto, G., Dupre, S. and Cavallini, D. (1982)IRCS Med. Sci.,10, 626.
Stepp, L. R., Bleile, D. M., Mcrorie, D. K., Pettit, F. H. and Reed, L. J. (1981)Biochemistry,20, 4555.
Stern, J. R., Drummond, G. I., Coon, M. J. and Delcampillo, A. (1960)J. Biol. Chem.,235, 234.
Stern, J. R. and Drummond, G. I. (1961)J. Biol. Chem.,236, 2892.
Utter, M. F., Keech, D. B. and Scrutton, M. C. (1964)Adv. Enzyme Regul.,2, 49.
Varley, H., Gowneloch, A. H. and Bell, M. (1976)Practical Clinical Chemistry, 5th Edition (London: William Heineman) p. 226.
Walker, P. G. (1954)Biochem. J.,58, 699.
Weinberg, M. B. and Utter, M. F. (1980)Biochem. J.,188, 601.
Wieland, O., Seiss, E., Shulze-WethmarII, F. A., Von Funcke, H. G. and Winton, B. (1971)Arch. Biochem. Biophys.,143, 593.
Williamson, J. R., Browning, E. T. and Scholz, R. (1969)J. Biol. Chem.,244, 4607.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandhi, V.M., Wagh, S.S., Natraj, C.V. et al. Lipoic acid and diabetes II: Mode of action of lipoic acid. J Biosci 9, 117–127 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02716838
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02716838