Abstract
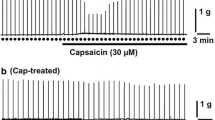
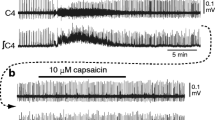
5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), injected intravenously (close to the right atrium), caused apnoea, bradycardia, hypotension and a reduction in the tidal volume in anaesthetized rats. The latency of the apnoea response was 0.61 seconds. 5-HT also produced similar effects when injected into the left ventricle (intra-arterial). The latency of the apnoea response was 0.33 s by this route. The apnoea and bradycardia evoked by intravenous and intra-arterial injections of 5-HT were abolished by bilateral vagotomy and reduced or abolished by vagal cooling. The blocking temperatures varied considerably in different animals, particularly with respect to the intravenous route of drug administration. Intravenous capsaicin caused apnoea, bradycardia and hypotension and these effects were blocked by vagal section or cooling. In contrast intra-arterial injections caused apnoea but no bradycardia and the apnoea was resistant to vagal section. The study shows that there are at least two populations of receptors; one which is chemosensitive to 5-HT and capsaicin and which is supplied by the pulmonary circulation, and one which is chemosensitive to 5-HT and which is accessible via the systemic circulation. The receptors and their vagal afferent connections may be non-myelinated since 5-HT and capsaicin are known to stimulate this type of ending in other species, and because respiratory responses were only blocked at low temperatures. In addition capsaicin also activates a non-vagal receptor, accessible from the systemic circulation, and which mediates apnoea but not bradycardia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coleridge JCG, Coleridge HM, Kaufman MP, Roberts AM, Baker DG (1982) Tracheal contraction and relaxation initiated by lung and somatic afferents in dogs. J Appl Physiol 52:984–990
Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG, Kidd C (1964) Cardiac receptors in the dog, with particular reference to two types of afferent ending in the ventricular wall. J Physiol 174:323–339
Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG, Luck JC (1965) Pulmonary afferent fibres of small diameter stimulated by capsaicin and by hyperinflation of the lungs. J Physiol 179:248–262
Coleridge HM, Roberts AM, Coleridge JCG (1981) Stimulation of bronchial C-fibres in dogs causes rapid shallow breathing. Fed Proc 40:452
Dawes GS, Mott JC (1950) Circulatory and respiratory reflexes caused by aromatic guanidines. Br J Pharmacol 5:65–76
Dawes GS, Mott JC, Widdicombe JG (1951) Respiratory and cardiovascular reflexes from the heart and lungs. J Physiol 115:258–291
Dey PK, Rao KS (1978) Visceral reflex responses following right intra-atrial injection of phenyldiguanide in rats. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 22:347–357
Franz DN, Iggo A (1968) Conduction failure in myelinated and nonmyelinated axons at low temperatures. J Physiol 199:319–345
Glogowska M, Widdicombe JG (1973) Respiratory and circulatory responses to phenyldiguanide in rabbits. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 203:313–322
Guz A, Trenchard DW (1971) The role of non-myelinated vagal afferent fibres from the lungs in the genesis of tachypnoea in the rabbit. J Physiol 213:345–371
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1982) Bronchial smooth muscle contraction induced by stimulation of capsaicin-sensitive sensory neurons. Acta Physiol Scand 116:473–476
Makara GB, Gyorgy L, Molnar J (1967) Circulatory and respiratory responses to capsaicin, 5-hydroxytryptamine and histamine in rats pretreated with capsaicin. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 170:39–45
Mills JE, Sellick H, Widdicombe JG (1969) Activity of lung irritant receptors in pulmonary microembolism, anaphylaxis and drug-induced bronchoconstriction. J Physiol 203:337–357
Mitchell HW (1983) Reflex changes in breathing to 5-HT in the anaesthetised rat. Br J Pharmacol 78:84P
Paintal AS (1955) Impulses in vagal afferent fibres from specific deflation receptors. The response of these receptors to phenyl diguanide, potato starch, 5-hydroxytryptamine and nicotine and their role in respiratory and cardiovascular reflexes. Q J Exp Physiol 40:89–111
Paintal AS (1957) The location and excitation of pulmonary deflation receptors by chemical substances. Q J Exp Physiol 42:56–71
Paintal AS (1967) A comparison of the nerve impulses of mammalian non-myelinated nerve fibres with those of the smallest diameter medullated fibres. J Physiol 193:523–533
Raybould HE, Russell NJW (1981) Pulmonary chemoflexes in the anaesthetised rat. J Physiol 315:37P
Roberts AM, Kaufman MP, Baker DG, Brown JK, Coleridge HM, Coleridge JCG (1981) Reflex tracheal contraction induced by stimulation of bronchial C-fibres in dogs. J Appl Physiol 51:485–493
Russell AJ, Lai-Fook SJ (1979) Reflex bronchoconstriction induced by capsaicin in the dog. J Appl Physiol 47:961–967
Sant’Ambrogia FB, Sant’Ambrogia G (1982) Circulatory accessibility of nervous receptors localised in the tracheobronchial tree. Respir Physiol 49:49–73
Sato A, Findone S, Eyzaguirre C (1968) Presence of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor C-fibres in the carotid nerve of the cat. Brain Res 11:459–463
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mitchell, H.W., Tomlin, J. & Ward, R.J. Reflex changes in respiration and heart rate evoked by intravenous and left ventricular injection of 5-HT and capsaicin in anaesthetized rats: a comparison of mechanisms. Lung 162, 153–163 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715643
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02715643