Abstract
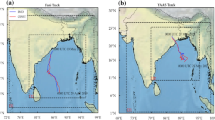
The present study is carried out to examine the performance of a regional atmospheric model in forecasting tropical cyclones over the Bay of Bengal and its sensitivity to horizontal resolution. Two cyclones, which formed over the Bay of Bengal during the years 1995 and 1997, are simulated using a regional weather prediction model with two horizontal resolutions of 165 km and 55 km. The model is found to perform reasonably well towards simulation of the storms. The structure, intensity and track of the cyclones are found to be better simulated by finer resolution of the model as compared to the coarse resolution. Rainfall amount and its distribution are also found to be sensitive to the model horizontal resolution. Other important fields, viz., vertical velocity, horizontal divergence and horizontal moisture flux are also found to be sensitive to model horizontal resolution and are better simulated by the model with finer horizontal grids.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anthes R A 1977 A cumulus parameterization scheme utilizing a one-dimensional cloud model;Mon. Weather Rev. 105 270–286
Bhaskar Rao D V and Ashok K 1999 Simulation of tropical cyclone circulation over Bay of Bengal using the ArakawaSchubert cumulus parameterization. Part I — Description of the model, initial data and results of the control experiment;Pure and Applied Geophysics 156 525–542
Braun S A and Tao W -K 2000 Sensitivity of high-resolution simulations of hurricane Bob (1991) to planetary boundary layer parameterizations;Mon. Weather Rev. 128 3941–3961
Giorgi F and Marinucci M R 1996 An investigation of sensitivity of simulated precipitation to model resolution and its implication for climate studies;Mon. Weather Rev. 124 148–166
Gupta Akhilesh and Bansal R K 1997 Performance of a Global Spectral Model in predicting the track of a hurricane in the Bay of Bengal using synthetic vortex;Dept. of Sci. & Tech., New Delhi (NCMRWF) Tech. Report,August, 1997.
Iwasaki T, Nakano H and Sugi M 1987 The performance of typhoon track prediction model with cumulus parameterization;J. Meteor. Soc. Japan 65 555–570
Karyampudi V M, Lai G S and Manobianco J 1998 Impact of initial condition, rainfall assimilation and cumulus parameterization on simulation of Hurricane Florance (1988);Mon. Weather Rev. 126 3077–3101
Krishnamurti T N 1990 Monsoon prediction a different resolution with a global spectral model;Mausam 41 234–240
Kuo H L 1974 Further studies of parameterization of the influence of cumulus convection on large-scale flow;J. Atmos. Sci. 31 1232–1240
Kurihara Y, Bender M A, Tuleya R E and Ross R J 1993 Hurricane forecasting with GFDL automated prediction system; Preprints 20th Conf. Hurr. Trop. Meteor., Amer. Meteor. Soc., Boston, MA02 108 323–326
Kurihara Y, Bender M A, Tuleya R E and Ross R J 1995 Improvements in the GFDL hurricane prediction system;Mon. Weather Rev. 123 2791–2801
Liu Y, Zhang D -L and Yau M K 1997 A multi-scale numerical simulation of hurricane Andrew (1992). Part-I: Explicit simulation and verification;Mon. Weather Rev. 125 3073–3093
Liu Y, Zhang D -L and Yau M K 1999 A multi-scale numerical simulation of hurricane Andrew (1992). Part-II: Kinematics and inner core structure;Mon. Weather Rev. 127 2597–2616
Madala R V 1978 Efficient time integration schemes for atmosphere and ocean. Finite difference techniques for the vectorized fluid dynamics calculations;Springer Verlag 56–74
Madala R V, Chang S W, Mohanty U C, Madan S C, Paliwal R K, Sarin V B, Holt T and Sethu Raman 1987 Description of Naval Research Laboratory Limited Area Dynamical Weather Prediction Model;N.R.L. Tech. Report 5992, Washington D.C., 131 pp.
Mathur M B 1991 The National Meteorological Center’s quasi-Lagrangian model for hurricane prediction;Mon. Weather Rev. 109 1419–1447
Mohanty U C and Mandal M 2003 Simulation of Orissa super cyclone (1999) using Psu/NCAR mesoscale model;Natural Hazards (in press)
Patra K, Prabir Santhanam M S, Potty K V J, Tewari M and Rao P L S 2000 Simulation of tropical cyclones using regional weather prediction models;Current Science 79 1, 70–78
Perkey D J and Krietzberg W 1976 A time dependent lateral boundary scheme for limited area primitive equation models;Mon. Weather Rev. 104 744–755
Prasad K 1990 Synthetic observations for representation of tropical cyclones in NWP data assimilation systems;Proc. International symposium on assimilation of observations in Meteorology and Oceanography, ClermountFerrand, France, July, 9–13.
Prasad K, Singh B V and Hatwar H R 1992 Objective analysis and track prediction of tropical cyclones with synthetic data;Physical Processes in atmospheric models. (ed) D R Sikka and S S Singh (Wiley Eastern Ltd.) 349–363
Prasad K, Rama Rao Y V and Sanjib Sen 1997 Tropical cyclone track prediction by a high resolution limited area model using synthetic observation;Mausam 48 3, 351–366
Puri K, Davidson N E, Leslie L M and Lagan L W 1992 The BMRC tropical limited area model;Aust. Meteor. Mag. 40 81–104
Yu Zhongbo, Lakhatakia M N and Barron E J 1999 Modeling of the river-basin response to single-storm events simulated by a mesoscale meteorological model at various resolutions;J. Geo. Res. 104 D16 19675–19689
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, M., Mohanty, U.C., Potty, K.V.J. et al. Impact of horizontal resolution on prediction of tropical cyclones over Bay of Bengal using a regional weather prediction model. J Earth Syst Sci 112, 79–93 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02710045
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02710045