Abstract
Sea breeze characteristics around Kalpakkam tropical coastal site are studied using an Advanced Regional Prediction System (ARPS) mesoscale model, which is non-hydrostatic, compressible atmospheric prediction model following the terrain coordinate system. Various options such as surface physics, atmospheric radiation physics, Coriolis force, microphysics, cumulus parameterization and 1.5 level TKE closure scheme for diffusion are included in the model.
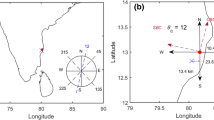
A joint meteorological field experiment was carried out by IITM-Pune and IGCAR at Kalpakkam by deploying state-of-the-art sensors and tether balloon systems for observing the height profiles of meteorological parameters. The data obtained from the field experiment are used here to compare the results from numerical simulations. From the simulated results, it is seen that duration of the sea breeze is 6 hours which agrees well with the observations. The height of the Thermal Internal Boundary Layer (TIBL) is also simulated from the vertical profiles of potential temperature. Simulated wind speed and wind directions are compared with the 50 m tower data and potential temperature profiles are compared with the kytoon data. Results are in good agreement with the observed values except during night time wherein a small difference is seen in the wind speed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arrit W R 1987 The effect of water surface temperature on lake breezes and Thermal Internal Boundary Layers;Boundary Layer Meteor.,40 101–125
Batchvarova E and Gryning S E 1998 Wind climatology, atmospheric turbulence and internal boundary-layer development in Athens during the MEDCAPHOTTRACE experiment;Atmos. Environ.,32(12) 2055–2069
Bechtold P J, Pinty P and Mascart P 1991 A numerical investigation of the influence of large-scale winds on sea breeze and inland-breeze-type circulations;J. Appld. Met. 30 1268–1279
Cai X M and Steyn D G 2000 Modelling study of sea breezes in a complex coastal environment;Atmos. Environ.,34 2873–2885
Carissimo B, Dupont E and Marchand O 1996 Local simulations of land-sea breeze cycles in Athens based on large-scale operational analyses;Atmos. Environ. 30(15) 2691–2704
Estoque M A 1962 The sea breeze as a function of the prevailing synoptic situation;J. Atmos. Sci.,19 244–250
Gross G 1986 A numerical study of the land and sea breeze including cloud formation;Beitr. Phys. Atmosph. 59(1) 97–114
Gryning S E and Batchvarova E 1990 Analytical model for the growth of the coastal internal boundary during onshore flow;Q. J. R. Met. Soc. 116 187–203
Jamima P, Venkatesan R and Aswatha Narayana P A 2001 An examination of the surface energy budget for various soil conditions and comparison with field data;Proceedings of TROPMET, 2001. 357–364
Klara F 1998 Inland and offshore propagation speeds of sea breeze from simulations and measurements;Boundary Layer. Meteor. 87 307–329
Liu H C, Johnny L, and Cheng AYS 2001 Internal boundary layer structure under sea breeze conditions in Hong Kong;Atmos. Environ.,35 683–692
Ma J 1997 Numerial modeling of a sea breeze circulation over Cleveland Bay;Aust. Met. Mag. 46 1–13
Mahrer Y and Pielke R A 1977 The effects of topography on sea and land breezes in a two-dimensional numerical model;Mon. Weather Rev. 105 1151–1162
Melas D, Ziomas I C and Zerefos C S 1995 Boundary layer dynamics in an urban coastal environment under sea breeze conditions.Atmos. Environ. 29(24) 3605–3617
Melas D, Ziomas I C, Klemm O and Zerefos C S 1998a Flow dynamics in Athens area under moderate large-scale winds;Atmos. Environ. 32(12), 2209–2222
Melas D, Ziomas I C, Klemm O, and Zerefos C S, 1998b Anatomy of the sea breeze circulation in Athens area under weak large-scale ambient winds;Atmos. Environ. 32(12) 2223–2237
Melas D and Kambezidis H D 1992 The depth of the internal boundary layer over an urban area under sea breeze conditions;Boundary Layer. Meteor.,61 247–264
Neumann J and Mahrer Y 1971 A theoretical study of the land and sea breeze circulation;J. Atmos. Sci. 28 532–542
Novitsky M, Reible D D and Corripio B M 1992 Modeling the dynamics of the land-sea breeze circulation for air quality modeling;Boundary Layer Meteor. 59 163–175
Ogawa Y, Ohara T, Wakamatsu S, Diosey P G and Uno I 1986 Observation of lake breeze penetration and subsequent development of the thermal internal boundary layer for the NANTICOKE II shoreline diffusion experiment;Boundary Layer Meteor. 35 207–230
Osamu C, Naito G, Kobayashi F and Toritani H 1994 Wave trains over the sea due to sea breezes;Boundary Layer Meteor. 70 329–340
Simpson J E 1995Sea breeze and local winds. (Cambridge University Press) 234pp
Sivaramakrishnan S and Venkatesan R 2002 Coastal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Experiment (CABLE)-2001, A Report submitted to AERB, Mumbai, India.
Thara V P, Anandakumar K, Venkatesan R and Somayaji K M 2000 Coastal Atmospheric Boundary Layer Experiment (CABLE-98); IGC-213 Report on site specific parameters. Health and Safety Division, IGCAR, Kalpakkam. (Available from L&IS, IGCAR, Kalpakkam, 603 102, India)
Thara V P, Venkatesan R and Sitaraman V 1999 Simulation of meteorological fields over a land-water-land terrain and comparison with observations;Boundary Layer Meteor. 91 227–257
Thara V P, Venkatesan R, Mursch-Radlgruber E, Rengarajan G and Jayanthi N 2002 Thermal Internal Boundary Layer characteristics at a tropical coastal site as observed by a mini-SODAR under varying synoptic conditions;Proc. Indian Acad. Sci. (Earth Planet. Sci.) 111(1) 63–77
Xian Z and Pielke R A 1991 The efeects of width of landmasses on the development of sea breezes;J. Appld. Meteor.,30(9) 1280–1304
Xue M, Droegemeier K K, Wong V, Shapiro A and Brewster K 1995 ARPS Version 4.0 User’s Guide.
Xue M, Droegemeier K K and Wong V 2000 The Advanced Regional Prediction System (ARPS) — A multiscale nonhydrostatic atmospheric simulation and prediction tool. Part I: Model dynamics and verification;Meteor. Atmos. Physics. 75 161–193
Xue M, Droegemeier K K, Wong V, Shapiro A, Brewster K, Carr F, Weber D, Liu Y and Wang D H 2001 The Advanced Regional Prediction System (ARPS)-A multiscale nonhydrostatic atmospheric simulation and prediction tool. Part II: Model physics and applications;Meteor. Atmos. Physics. 76 134–165
Zambakas J D 1973 The diurnal variability and duration of the sea breeze at the National Observatory of Athens, Greece;Meteorology Magazine 102 222–228
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jamima, P., Lakshminarasimhan, J. Numerical simulation of sea breeze characteristics observed at tropical coastal site, Kalpakkam. J Earth Syst Sci 113, 197–209 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02709787
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02709787