Abstract
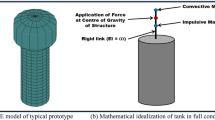
The current designs of supporting structures of elevated water tanks are extremely vulnerable under lateral forces due to an earthquake and the Bhuj earthquake provided another illustration when a great many water tank stagings suffered damage and a few collapsed. The more popular shaft type stagings suffer from poor ductility of thin shell sections besides low redundancy and toughness whereas framed stagings consist of weak members and poor brace-column joints. A strength analysis of a few damaged shaft type stagings clearly shows that all of them either met or exceeded the strength requirements of IS:1893-1984, however, they were all found deficient when compared with requirements of the International Building Code. IS:1893-1984 is unjustifiably low for these systems which do not have the advantage of ductility and redundancy and are currently being underestimated at least by a factor of 3 and need an upward revision of forces immediately.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BIS 1976 IS:4326-1976 Earthquake resistant design and construction of buildings—Code of practice, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
BIS 1993 IS:13920-1993 Ductile detailing of reinforced concrete structures subjected to seismic forces—Code of Practice, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
BIS 1984 IS:1893-1984 Criteria for earthquake resistant design structures, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
BIS 1985 IS:11682-1985 Criteria for design of RCC staging for overhead water tanks, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
BIS 2000 IS:456-2000 Indian standard for plain and reinforced concrete—Code of practice, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
IBC 2000 International Building Code, International Conf. of Building Officials, Whittier, CA.
Jain S K and Sameer S U 1993 A review of requirements of Indian codes for aseismic design of elevated water tanks;Bridge & Structural Engineer Vol.XXIII No. 1
Rao M L N 2000 Effect of confinement on ductility of RC hollow circular columns, a masters' thesis submitted to Dept. of Earthquake Engg, Univ. of Roorkee, Roorkee, India
Zahn F A, Park R and Priestley M J N 1990 Flexural strength and ductility of circular hollow reinforced concrete columns without reinforcement on inside face;ACI Structural Journal,87(2), 156–166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rai, D.C. Performance of elevated tanks inM w 7.7 Bhuj earthquake of january 26th, 2001. J Earth Syst Sci 112, 421–429 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02709269
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02709269