Abstract
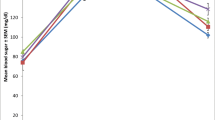
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a multi-factorial disease which is characterized by hyperglycaemia, lipoprotein abnormalities and oxidative stress. This study evaluated effect of oral vitamin C administration on basal metabolic rate and lipid profile of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Vitamin C was administered at 200 mg/kg body wt. by gavage for four weeks to diabetic rats after which the resting metabolic rate and plasma lipid profile was determined. The results showed that vitamin C administration significantly (P<0.01) reduced the resting metabolic rate in diabetic rats; and also lowered plasma triglyceride, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. These results suggest that the administration of vitamin C in this model of established diabetes mellitus might be beneficial for the restoration of basal metabolic rate and improvement of lipid profile. This may at least in part reduce the risk of cardiovascular events seen in diabetes mellitus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BMR:
-
Basal metabolic rate
- DM:
-
diabetes mellitus
- HDL:
-
high density lipoprotein
- LDL:
-
low density lipoprotein
References
Anderson J W, Gowri M S and Turner J 1999 Antioxidant supplementation effects on low-density lipoprotein oxidation for individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus;J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 18 451–461
Avesani C M, Cuppari L, Silva A C, Sigulem D M, Cendoroglo M, Sesso R and Draibe S A 2001 Resting energy expenditure in pre-dialysis diabetic patients;Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 16 556–560
Betteridge D J 1994 Diabetic dyslipidemia;Am. J. Med. (Suppl. 6A)96 255–315
Bhakdi S, Lackner K K, Han S R, Torzewski M and Husmann M 2004 Beyond cholesterol: The enigma of atherosclerosis revisited;Thromb. Haemost. 91 639–645
Caballero A E, Srora S, Saouaf R, Lim S C, Smakowscki P, Park J Y, King G L, Lo Gerfo F W, Horton E S and Veves A 1999 Microvascular and macrovascular reactivity is reduced in subjects at risk for type 2 diabetes;Diabetes 48 1856–1862
Ceriello A and Motz E 2004 Is oxidative stress the pathogenic mechanism underlying insulin resistance, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease? The common soil hypothesis revisited;Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 24 816–823
Franssila-Kallunki A and Groop L 1992 Factors associated with basal metabolic rate in patients with type II diabetes melliltus;Diabetologia 35 962–966
Felmeden D C, Spencer C G, Blann A D, Beevers D G and Lip G Y 2003 Low-density lipoprotein subfraction and cardiovascular risk in hypertension: Relationship to endothelial dysfunction and effects of treatment;Hypertension 41 528–533
Fontvielli A M, Lillioja S, Ferraro R T, Schulz L O, Rising R and Ravussin E 1992 Twenty four hour energy expenditure in Pima Indians with type II (non insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus;Diabetologia 35 753–759
Guyton A C and Hall J E 2006Textbook of medical physiology 11th edition (Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunder) pp 884–888
Hoar WS, Hickman Jr G P 1975A laboratory comparison for general and comparative physiology 2nd edition (Prentice-Hall)
Kamata K and Yamashita K 1999 Insulin resistance and impaired endotheliium-dependent renal vasodilation in fructose-fed hypertensive rats;Res. Commun. Mol. Pathol. Pharmacol. 103 195–200
Kamata K, Kanie N and Inose A 2001 Mechanisms underlying attenuated conntractile respoonse of aortic rings to noradrenaline in fructose-fed mice;Eur. J. Pharmacol. 428 241–249
Kaviarasan K, Arjunan M M and Pugalendi K V 2005 Lipid profile, oxidant-antioxidant status and glycoprotein components in hyperlipidemic patients with/without diabetes;Clin. Chim. Acta 362 49–56
Kurowska E M, Spence J D, Jordan J, Wetmore S, Freeman D J, Piche L A and Serratore P 2000 HDL-cholesterol-raising effect of orange juice in subjects with hypercholesterolemia;Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 72 1095–1100
Nawata K, Sohmiya M, Kawaguchi M, Nishiki M and Kato Y 2004 Increased resting metabolic rate in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus accompanied by advanced diabetic nephropathy;Metabolism 531395–1398
Osim E E, Owu D U, Isong E U and Umoh I B 1994 Influence of chronic consumption of thermoxidized and fresh palm oil diets on basal metabolic rate, body weight and morphology of tissues in rats;Discovery Innovation 6 389–396
Paolisso G, D’Amore A, Balbic V, Volpe C, Galzerano D, Guigliano D, Sgambato S, Varricchio M and D’Onofrio F 1994 Plasma Vitamin C affects glucose homeostasis in healthy subjects and in non-insulin-dependent diabetics;Am. J. Physiol. 266 E261-E268
Regensteiner J G, Sippel J, McFarling E T, Wolfel E E and Hiatt W R 1995 Effects of non-insulin dependent diabetes on maximal exercise performance;Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 27 875–881
Regensteiner J G, Bauer T A, Reusch J E B, Brandenburg S L, Sippel J M, Vogelsong A M, Smith S, Wolfel E E, Eckel R H and Hiatt W R 1998 Abnormal oxygen uptake kinetic responses in women with type 11 diabetes mellitus,J. Appl. Physiol. 85 310–317
Roy T M, Peterson H R, Snider H L, Cyrus J, Vasti L B, Fell R D and Rothchild E 1989 Autonomic influence on cardiovascular performance in diabetic subjects;Am. J. Med. 87 382–388
Scoppola A, Montecchi F R, Mezinger G and Lala A 2001 Urinary mevalonate excretion rate in type 2 diabetes: role of metabolic control;Atherosclerosis 156 357–361
Shahar E, Chambless L E, Rosamond W D, Boland L L, Ballantyne C M, McGovern P G and Sharnett A R 2003 Atherosclerosis risk in community study, plasma lipid profile and incident ischaemic stroke: the atherosclerosis risk in communities (ARIC) study;Stroke 34 623–631
Sheweita S A, Newairy A A, Mansour H A and Yousef M I 2002 Effect of some hypoglycemic herbs on the activity of phase I and II drug-metabolising enzymes in alloxan-induced diabetic rat;Toxicology 174 131–139
Simoneau JA and Kelley D E 1997 Altered glycolytic and oxidative capacities of skeletal muscle contribute to insulin resistance in NIDDM;J. Appl. Physiol. 83 166–171
Sowers J R and Melvin A L 1999 Diabetes and cardiovascular disease;Diabetes Care 22 c14-c20
Unwin N, Sobngwi E and Alberti K G M M 2001 Type 2 diabetes: The challenge of preventing a global epidemic;Diabetes Int. 11 4–8
White A, Handler P, Smith E L, Hill R L and Lehman I R 1994Principles of biochemistry 7th edition (Tokyo: McGrawHill Kogakusha Ltd) pp 619–630
Young I S and Woodside J V 2001 Antioxidants in health and disease;J. Clin. Pathol. 54 176–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Owu, D.U., Antai, A.B., Udofia, K.H. et al. Vitamin C improves basal metabolic rate and lipid profile in alloxan-induced diabetes mellitus in rats. J. Biosci. 31, 575–579 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708409
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708409