Abstract
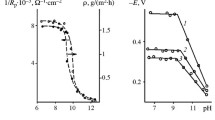
The influence of heavy metal oxides on the chloride induced corrosion of steel reinforcement in concrete was studied. Significant inhibition and stimulation of chloride induced corrosion have been observed. Basicity and acidity of the relevant metal ions, and their ability to form complexes are considered as the main factors of the observed effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berke N S and Weil T G 1992World-wide review of corrosion inhibitors in concrete, InAdvances in concrete technology (ed.) V M Malhotra (Canada: CANMET) pp 889–924
Boyd W K and Tripler A 1988Mater. Protect. 7 40
Craig R J and Wood L E 1970 Effectiveness of corrosion inhibitors and their influence on the physical properties of Portland cement mortars, Highway Research records328 Highway Research Board
Diamond S 1986Concentrations in concrete pore solutions resulting from calcium and nitrium chloride admixtures, Cement and concrete aggregates (Philadelphia PA: American Society of Testing and Materials)Vol. 8, pp 97–102
Dreeman S, Osroff T, Dillard J, Glanville J and Weyers R1991A screening test for rebar corrosion inhibitors (Washington DC: Transportation Research Board)
Gaidis J M and Rosenberg A M 1979Materials performance (Houston: NACE)Vol. 18 p. 45
Remy H 1961Inorganic chemistry II (Leipzig: Akademische Verlagsgeselschaft Gest & Portig)(in German)
Rosenberg A, Grace W R and Co 1993Mechanism of corrosion of steel in concrete, InConcrete science IV (ed.) J Skalny (Westerville, OH: The American Ceramic Society)
Tashiro C 1984Effect of zinc oxide admixture on corrosion inhibition of iron in cement mortar containing sea water, Proc 8th int. congress on the chemistry of cement (Rio de Janeiro: Abla Grafica e Editora Ltda) pp 226–230
Tashiro C, Takashi H, Kanaya M, Hirakida I and Yosida R 1979Cement & Concr. Res. 3 283
Tashiro C, Ueoka C and Tashibana K 1985Effect of heavy metal on corrosion of iron in cement mortar, Proc. SILICONF (Budapest: Magyar Tudomanyos Akademia) pp 281–291
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Živica, V. Electrochemical activity of heavy metal oxides in the process of chloride induced corrosion of steel reinforcement. Bull Mater Sci 25, 371–373 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708012
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02708012