Abstract
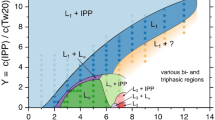
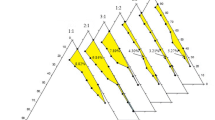
Lecithin is a natural amphiphilic molecule, the microemulsions of which are often employed as a transdermal delivery medium of drugs and cosmetics. However, it constructs a microemulsion and lamellar phase in a phase diagram without co-surfactant only at a narrow range of composition. In this study, the effect of several short-chain alcohols on pseudo-ternary phase diagrams composed of lecithin, water and dodecane containing 1.0 wt% lidocaine (local anesthetic) was investigated in relation to the application of lecithin-based microemulsion for transdermal drug delivery. The phase diagram for an aqueous solution containing 80.0 wt% ethanol showed a lamellar structure (LC) and bicontinuous isotropic regions. When the mixing ratio of lecithin to alcohols (1-propanol, 1-butanol and n-pentanol) was 2: 1, water-in-oil (L2) and oil-in-water (L1) microemulsions and LC were obtained in a certain range of compositions. The maximum solubilization of water into L2 phase was 38 wt% when the total surfactant was 43 wt% with butanol as cosurfactant.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aboofazeli, R. and Lawrence, M. J., “Investigations into the Formation and Characterization of Phospholipid Microemulsions, I. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams of Systems Containing Water-Lecithin-Alcohol-Isopropyl Myristate,”Int. J. Pharm.,93, 161 (1993).
Aboofazeli, R., Patel, N., Thomas, M. and Lawrence, M. J., “Investigations into the Formation and Characterization of Phospholipid Microemulsions. IV. Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams of Systems Containing Water-Lecithin-Alcohol and Oil; the Influence of Oil,”Int. J. Pharm.,125(1), 107 (1995).
Attwood, D. and Florence, A. T., “Surfactant Systems, Their Chemistry, Pharmacy and Biology,” Chapman and Hall, New York (1983).
Binks, B. P., Meunier, J. and Langevin, D., “Characteristic Sizes Film Rigidity and Interfacial Tensions on Microemulsion Systems,”Prog. Colloid Polym. Sci.,79, 208 (1989).
Bonina, F. P., Montenegro, L., Scrofani, N., Esposito, E., Cortesi, R., Menegatti, E. and Nastruzzi, C., “Effects of Phospholipid Based Formulations onin vitro andin vivo Percutaneous Absorption of Methyl Nicotinate,”J. of Controlled Release,34, 53 (1995).
Bourrel, M. and Schechter, R. S., “Microemulsions and Related Systems,” Surfactant Science series,30 (1988).
Burm, A. G. L. and van Kleef, J. W., “Pharmacokinetics of Local Anesthetics” in “Pharmacologic Basis of Anesthesiology: Basic Science and Practical Applications,” Bowdle, T. A. ed., Churchill Livingstone, New York (1994).
Choi, S. Y., Oh, S. G. and Lee, J. S., “Effect of Lidocaine Compounds on the Expansion of Lipid Monolayer at Air/Water Interface,”J. of Korean Ind. & Eng. Chemistry,9(7), 1090 (1998).
Cornell, B. A., Middlehurst, J. and Separvoic, F., “Small Unilamellar Phospholipid Vesicles and the Theory of Membrane Formation,”Faraday Disc. Chem. Soc.,81, 163 (1986).
De Gennes, P. G. and Toupin, C., “Microemulsions and the Flexibility of Oil/Water Interfaces,”J. Phys. Chem.,86, 2294 (1982).
Garti, N. and Aserin, A., “Pharmaceutical Emulsions, Double Emulsions and Microemulsions,” in “Microencapsulation” ed. Simon, Benita, Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York (1996).
Israelachvili, J. N., Mitchell, D. J. and Ninham, B. W., “Theory of Self-Assembly of Hydrocarbon,”J. Chem. Soc. Fraraday Trans. II,72, 1525 (1976).
Kabalnov, A., Tarara, T., and Weers, J., “Phospholipids as Emulsion Stabilizers: 2. Phase Behavior versus Emulsion Stability,”J. Colloid Interface Sci.,184, 227 (1996).
Ruth, S. H. and Attwood, D., Ktistis, G. and Taylor, C. J., “Phase Studies and Particle Size Analysis of Oil-in-Water Phospholipid Microemulsions,”Int. J. Pharm.,116, 253 (1995).
Shinoda, K., Araki, M. and Sadoghiani, A., “Lecithin-Based Microemulsions: Phase Behavior and Mcirostructure,”J. Phys. Chem.,95, 989 (1991).
Trotta, M., Ugazio, E. and Rosacasco, M., “Pseudo-Ternary Phase Diagrams of Lecithin-Based Microemulsions; Influence of Monoalkylphosphates,”J. Pharm. Pharmacol.,47, 451 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, SY., Oh, SG., Bae, SY. et al. Effect of short-chain alcohols as co-surfactants on pseudo-ternary phase diagrams containing lecithin. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 16, 377–381 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707128
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02707128