Abstract
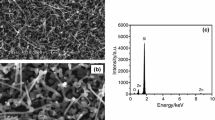
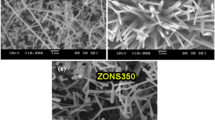
ZnO nanowires having a diameter in the range of 15–40 nm and several tens of micrometers in length were grown on steel alloy substrates by the thermal evaporation technique without the use of any catalyst or additives. A detailed structural analysis revealed that the as-grown ZnO nanowires are single crystalline with wurtzite hexagonal structures and preferentially oriented in the c-axis direction. Origination of a strong and sharp Raman-active E2 mode at 436.6 cm-1 indicated that the grown ZnO nanowires have good crystal quality with the hexagonal wurtzite phase. Photoluminescence spectra also exhibited a sharp and strong peak in UV and a suppressed and weak band in the visible region, confirming the good optical properties and less structural defects for the deposited products. Additionally, a systematic growth mechanism is also proposed in detail to acquire a better understanding for the growth of nanowires on steel alloy substrate.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagnall, D. M., Chen, Y. F., Zhu, Z., Yao, T., Shen, M. Y. and Goto, T., “High temperature excitonic stimulated emission from ZnO epitaxial layers,”Appl. Phys. Lett.,73, 1038 (1998).
Calleja, J. M. and Cardona, M., “Resonant Raman scattering in ZnO,”Phys. Rev. B,16, 3753 (1977).
Chiou, W., Wu, W. and Ting, J., “Growth of single crystal ZnO nanowires using sputter deposition,”Diamond Relat. Mater.,12, 1841 (2003).
Egehaaf, H. J. and Oelkrug, D., “Luminescence and nonradiative deactivation of excited states involving oxygen defect centers in polycrystalline ZnO,”J. Crystal Growth,161, 190 (1996).
Fang, Z., Wang, Y., Peng, X., Liu, X. and Zhen, C., “Structural and optical properties of ZnO films grown on the AAO templates,”Materials Letters,57, 4187 (2003).
Haga, K., Katahira, F. and Watanabe, H., “Preparation of ZnO films by atmospheric pressure chemical-vapor deposition using zinc acetylacetonate and ozone,”Thin Solid Films,343–344, 145 (1999).
Huang, M., Mao, S., Feick, H., Yan, H., Wu, Y., Kind, H., Weber, E., Russo, R. and Yang, P., “Room-temperature ultraviolet nanowire nanolasers,”Science,292, 1897 (2001).
Kang, H. S., Kang, J. S., Kim, J. W. and Lee, S. Y., “Annealing effect on the property of ultraviolet and green emissions of ZnO thin films,”J. Appl. Phys.,95, 1246 (2004).
Kim, S. H., Umar, A. and Hahn, Y. B., “Growth and formation mechanism of sea-urchin like ZnO nanostructures on Si,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,22, 489 (2005).
Kim, T. Y., Lee, S. H., Mo, Y. H., Nahm, K. S., Kim, J. Y., Suh, E. K. and Kim, M., “Growth mechanism of needle-shaped ZnO nano-structures overNiO-coated Si substrates,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21, 733 (2004).
Kind, H., Yan, H., Messer, B., Law, M. and Yang, P., “Nanowire ultraviolet photodetectors and optical switches,”Adv. Mater.,14, 158 (2002).
Lee, S., Im, Y. H. and Hahn, Y. B., “Two-step growth of ZnO films on silicon by atomic layer deposition,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,22, 334 (2005).
Li, S. Y., Lee, C. Y. and Tseng, T. Y., “Copper-catalyzed ZnO nanowires on silicon (100) grown by vapor-liquid-solid process,”J. Cryst. Growth,247, 357 (2003).
Li, W., Mao, D. S., Zheng, Z. H., Wang, X., Liu, X. H., Zou, S. C., Zhu, Y. K., Li, Q. and Xu, J. F., “ZnO/Zn phosphor thin films prepared by IBED,”Surf. Coat. Technol.,128/129, 346 (2000).
Li, Y., Meng, G. W. and Zhang, L. D., “Ordered semiconductor ZnO nanowire arrays and their photoluminescence properties,”Appl. Phys. Lett.,76, 2011 (2000).
Lim, J., Shin, K., Kim, H. W. and Lee, C., “Effect of annealing on the photoluminescence characteristics of ZnO thin films grown on the sapphire substrate by atomic layer epitaxy,”Mater. Sci. Eng. B,107, 301 (2004).
Liu, Y. C., Xu, X. Y., Mu, R., Henderson, D. O., Lu, Y. M., Zhang, J. Y., Shen, D. Z., Fan, X. W. and White, C. W., “Production, structure, and optical properties of ZnO nanocrystals embedded in CaF2 matrix,”Appl. Phys. Lett.,83, 1210 (2003).
Meng, X. Q., Shen, D. Z., Zhang, J. Y., Zhao, D. X., Lu, Y. M., Dong, L., Zhang, Z. Z., Liu, Y. C. and Fan, X. W., “The structural and optical properties of ZnO nanorod arrays,”Solid State Communications,135, 179 (2005).
Ogata, K., Kawanishi, T., Maejima, K., Sakurai, K., Fujita, S. and Fujita, S., “Improvements of ZnO qualities grown by metal-organic vapor phase epitaxy using a molecular beam epitaxy grown ZnO layer as a substrate,”Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. Part-2,40, L657 (2001).
Rajalakshmi, M., Arora, A. K., Bendre, B. S. and Mahamuni, S., “Optical phonon confinement in zinc oxide nanoparticles,”J. Appl. Phys.,87, 2445 (2000).
Sekar, A., Kim, S. H., Umar, A. and Hahn, Y. B., “Catalyst-free synthesis of ZnO nanowires on Si by oxidation of Zn powders,”J. Crystal Growth,277, 471 (2005).
Studenikin, S. A., Golego, N. and Cocivera, M., “Fabrication of green and orange photoluminescence undoped ZnO films using spray pyrolysis,”J. Appl. Phys.,84, 2287 (1998).
Sun, Y., Fuge, G. M. and Ashfold, M. N. R., “Growth of aligned ZnO nanorod arrays by catalyst-free pulsed laser deposition methods,”Chem. Phys. Lett.,396, 21 (2004).
Umar, A., Kim, S. H., Lee, Y.-S., Nahm, K. S. and Hahn, Y. B., “Catalyst free large-scale synthesis of ZnO nanorods by a vapor-solid growth mechanism: Structural and optical properties,”J. Crystal Growth,282, 131 (2005).
Umar, A., Lee, S., Im, Y. H. and Hahn, Y. B., “Flower-shaped ZnO nano-structures obtained by cyclic feeding chemical vapor deposition: Structural and optical properties,”Nanotechnology,16, 2462 (2005).
Umar, A., Lee, S., Lee, Y. S., Nahm, K. S. and Hahn, Y. B., “Star-shaped ZnO nanostructures on silicon by cyclic feeding chemical vapor deposition,”J. Crystal Growth,277, 479 (2005).
Vanheusdan, K., Seager, C. H., Warren, W. L., Tallent, D. R. and Voigt, J. A., “Correlation between photoluminescence and oxygen vacancies in ZnO phosphors,”Appl. Phys. Lett.,68, 403 (1995).
Vanheusdan, K., Warren, W. L., Seager, C. H., Tallent, D. R., Voigt, J. A. and Gnade, B. E., “Mechanism behind green photoluminescence in ZnO phosphor powders,”J. Appl. Phys.,79, 7983 (1996).
Verghese, P. M. and Clarke, D. R., “Piezoelectric contributions to the electrical behavior of ZnO varistors,”J. Appl. Phys.,87, 4430 (2000).
Wang, F. Z., Ye, Z. Z., Ma, D. W., Zhu, L. P. and Zhuge, F., “Novel morphologies of ZnO nanotetrapods,”Materials Letters,59, 560 (2005).
Wang, Z. L., “Nanostructures of zinc oxide,”Materials Today,7(6), 26 (2004).
Wang, Z. L. (Ed.), “Nanowires and Nanobelts — Materials, Properties and Devices, Metal and Semiconductor Nanowires,” vol. I and vol. II Kluwer Academic Publisher, Dordrecht (2003).
Wang, Z. L., Kong, X. Y. and Zuo, J. M., “Induced growth of asymmetric nanocantilever arrays on polar surfaces,”Phys. Rev. Lett.,91, 185502 (2003).
Xu, X. Y., Zhang, H. Z., Zhao, Q., Chen, Y. F., Xu, J. and Yu, D. P., “Patterned growth of ZnO nanorod arrays on a large-area stainless steel grid,”J. Phys. Chem. B,109, 1699 (2005).
Yao, B. D., Chan, Y. F. and Wang, N., “Formation of ZnO nanostructures by a simple way of thermal evaporation,”Appl. Phys. Lett.,81, 757 (2002).
Ye, J. D., Gu, S. L., Zhu, S. M., Qin, F., Liu, S. M., Liu, W., Zhou, X., Hu, L. Q., Zhang, R., Shi, Y. and Zheng, Y. D., “Production of high-quality ZnO films by the two-step annealing method,”J. Appl. Phys.,96, 5308 (2004).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Umar, A., Jeong, JP., Suh, EK. et al. Synthesis of ZnO nanowires on steel alloy substrate by thermal evaporation: Growth mechanism and structural and optical properties. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 860–865 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705941
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705941