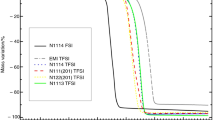
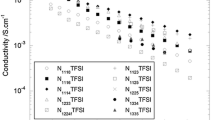
Abstract
A series of ionic liquids based on morpholinium cations were prepared. N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium bromide, N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium tetrafluoroborate, N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium hexafluorophosphate and N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide were synthesized, and then thermal and electrochemical properties of prepared ionic liquids were measured. These morpholinium salts were found to be thermally stable near 673 K and electrochemically stable up to 6 V at room temperature. In conclusion, these new series of morpholinium based ILs might be potential candidates for electrolytes in batteries and other electrolytic devices.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blanchard, L. A., Hancu, D., Beckman, E. J. and Brennecke, J. F., “Green processing using ionic liquids and Co2”,Nature,99, 28 (1999).
Bonhote, P., Dias, A.-P., Armand, M., Papageorgiou, N., Kalyanasundaram, K. and Gratzel, M.,“Hydrophobic, highly conductive ambient-temperature molten salts,”Inorg. Chem.,35, 1168(1996).
Bradley, D., Dyson, P. and Welton, T.,“An ion brew for cleaner chemistry,”Chem. Rev.,9(5), 18 (2000).
Choi, S., Kim, K.-S., Lee, H., Oh, J. S. and Lee, B.-B.,“Synthesis and ionic conductivities of lithium doped morpholinium salts,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,22, 281 (2005).
de Souza, R. F., Padilha, J. C., GonÇalves, R. S. and Dupont, J.,“Room temperature dialkylimidazolium ionic liquid-based fuel cells,”Electrochem. Commun.,5, 728 (2003).
Ding, M. S., Xu, K. and Jow, T. R.,“Liquid-solid phase diagrams of binary carbonates for lithium batteries,”J. Electrochem. Soc.,147, 1688 (2000).
Forsyth, C. M., MacFarlane, D. R., Golding, J. J., Huang, J., Sun, J. and Forsyth, M.,“Structural characterization of novel ionic materials incorporating the bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)amide anion,”Chem. Mater.,14, 2103(2002).
Hagiwara, R. and Ito, Y.,“Room temperature ionic liquids of alkylimidazolium cations and fluoroanions,”J. Fluorine Chem.,105, 221 (2000).
Hagiwara, R. and Ito, Y.,“Room temperature molten fluorometallates: 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium hexafluoroniobate (V) and hexafluorotantalate (V),”J. Fluorine Chem.,221, 133 (2002).
Huddleston, J. G., Willauer, H. D., Swatloski, R. P., Visser, A. E. and Rogers, R. D.,Chem. Commun., 1765 (1998).
Kim, K. S., Choi, S., Demberelnyamba, D., Lee, H., Oh, J., Lee, B. B. and Mun, S. J.,“Ionic liquids based on N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium salts as potential electrolytes,”Chem. Commun., 828 (2004b).
Kim, K.-S., Shin, B.-K. and Lee, H.,“Physical and electrochemical properties of 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide, 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium iodide, and 1-butyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,21, 1010 (2004a).
MacFarlane, D. R., Meakin, P., Sun, J., Amini, N. and Forsyth, M., “Pyrrolidinium imides: A new family of molten salts and conductive plastic crystal phases,”J. Phys. Chem. B,103, 4164 (1999).
Marsh, K. N., Deev, A., Wu, A. C.-T., Tran, E. and Klamt, A.,“Room temperature ionic liquids as replacements for conventional solvents — A review,”Korean J. Chem. Eng.,19, 357 (2002).
McEwen, A. B., Ngo, H. L., LeCompte, K. and Goldman, J. L.,“Electrochemical properties of imidazolium salt electrolytes for electrochemical capacitor applications,”J. Electrochem. Soc.,146, 1687 (1999).
Ngo, H. L., Lecompte, K., Hargens, L. and McEwen, A. B.,“Thermal properties of imidazolium ionic liquids,”Thermochimica Acta.,97, 357 (2000).
Ohno, H. and Yoshizawa, M.,“Ion conductive characteristics of ionic liquids prepared by neutralization of alkylimidazoles,”Solid State Ionics,154/155, 303 (2002).
Qin, W., Wei, H. and Li, S. F. Y.,“1,3-Dialkylimidazolium-based room-temperature ionic liquids as background electrolyte and coating material in aqueous capillary electrophoresis,”J. Chromatogr. A,985, 447 (2003).
Quinn, B. M., Ding, Z., Moulton, R. and Bard, A. J.,“Novel electrochemical studies of ionic liquids,”Langmuir,18, 1734 (2002).
Sato, T., Masuda, G. and Takagi, K.,“Electrochemical properties of novel ionic liquids for electric double layer capacitor applications,”Electrochim. Acta,49, 3603 (2004).
Sun, J., Forsyth, M. and MacFarlane, D. R.,“Room-temperature molten salts based on the quaternary ammonium ion,”J. Phys. Chem. B,102, 8858 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, S., Kim, KS., Cha, JH. et al. Thermal and electrochemical properties of ionic liquids based on N-methyl-N-alkyl morpholinium cations. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 23, 795–799 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705930
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02705930
Key words
- Ionic Liquids
- Electrochemical Property
- N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium Bromide ([Mor][Br])
- N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium Tetrafluoroborate ([Mor][BF4])
- N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium Hexafluorophosphate ([Mor][PF6])
- N-alkyl-N-methylmorpholinium Bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide ([Mor][TFSI])
- Lithium Doped Electrolyte